
Energy security
Encyclopedia
Energy security is a term for an association between national security
and the availability of natural resource
s for energy
consumption. Access to cheap energy
has become essential to the functioning of modern economies. However, the uneven distribution of energy supplies among countries has led to significant vulnerabilities. Threats to energy security include the political instability of several energy producing countries, the manipulation of energy supplies, the competition over energy sources, attacks on supply infrastructure, as well as accidents, natural disasters, rising terrorism, and dominant countries reliance to the foreign oil supply. The limited supplies, uneven distribution, and rising costs of fossil fuels, such as oil and gas, create a need to change to more sustainable energy
sources in the foreseeable future. With as much dependence that the U.S. currently has for oil and with the peaking limits of oil production; economies and societies will begin to feel the decline in the resource that we have become dependent upon. Energy security has become one of the leading issues in the world today as oil and other resources have become as vital to the world's people. However with oil production rates decreasing and oil production peak nearing the world has come to protect what resources we have left in the world. With new advancements in renewable resources, less pressure has been put on companies that produce the world's oil. These resources include geothermal, solar power, wind power and hydro-electric. Although these are not all the current and possible future options for the world to turn to as the oil depletes, the most important issue is protecting these vital resources from future threats. These new resources will become more useful as the price of exporting and importing oil increases due to the increase of demand.
One of the leading threats to energy security is the significant increase in energy price
s, either on the world markets – as has occurred in a number of energy crises
over the years – or by the imposition of price increases by an oligopoly
or monopoly
supplier, cartel
or country
. In some cases the threat might come from a single energy superpower
– those states able to significantly influence world markets by their action alone. Rather than just manipulating prices, such suppliers might go beyond this by suspending or terminating supplies. This has been done to apply pressure during economic negotiations - such as during the Russia-Belarus energy dispute
- or to apply political pressure, for example by OPEC
in response to Western support for Israel
in the Yom Kippur War
. Suspension of supplies may also come about as a result of worldwide international sanctions
against a country.
Energy plays an important role in the national security of any given country as a fuel to power the economic engine. Hence, threats to energy security can also result from physical damage to the energy infrastructure either of the supplier, or of the importer as a result of natural events, misfortune, terrorism
, or war
fare. The political and economic instability caused by war or other factors such as strike action
can also prevent the proper functioning of the energy industry in a supplier country. One example of this would be the United states, the U.S. has over 60% of its imported oil from OPEC countries and have been increasingly more dependent over the last 20 years.
New threats to energy security have emerged in the form of the increased world competition for energy resources due to the increased pace of industrialization in countries such as India
and China
. Although still a minority concern, the possibility of price rises resulting from the peaking of world oil production
is also starting to attract the attention of at least the French
government.
Increased competition over energy resources may also lead to the formation of security compacts to enable an equitable distribution of oil and gas between major powers. However, this may happen at the expense of less developed economies. The Group of Five
, precursors to the G8
, first met in 1975 to coordinate economic and energy policies in the wake of the 1973 Arab oil embargo
, a rise in inflation and a global economic slowdown.
NATO leaders meeting in Bucharest in April 2008 may discuss the possibility of using the military alliance "as an instrument of energy security." One of the possibilities include placing troops in the Caucasus region to police oil and gas pipelines.
Founded by the Germans post 1943 Energy Security has been on the minds of leading political thinkers of late
or renewable energy
resources, and reducing overall demand through energy conservation
measures. It can also involve entering into international agreements to underpin international energy trading relationships, such as the Energy Charter Treaty
in Europe. All the concern coming from security threats on oil sources long term security measures will help reduce the future cost of importing and exporting fuel into and out of countries without having to worry about harm coming to the goods being transported.
The impact of the 1973 oil crisis
and the emergence of the OPEC
cartel
was a particular milestone that prompted some countries to increase their energy security. Japan, almost totally dependent on imported oil, steadily introduced the use of natural gas
, nuclear power
, high-speed mass transit systems, and implemented energy conservation
measures, It has become one of the world leaders in the use of renewable energy
. The United Kingdom
began exploiting North Sea oil
and gas reserves, and became a net exporter of energy into the 2000s.
In other countries energy security has historically been a lower priority. The United States
, for example, has continued to increase its dependency on imported oil although, following the oil price increases since 2003, the development of biofuels has been suggested as a means of addressing this.
Increasing energy security is also one of the reasons behind a block on the development of natural gas imports in Sweden. Greater investment in native renewable energy technologies and energy conservation is envisaged instead. India
is carrying out a major hunt for domestic oil to decrease its dependency on OPEC
, while Iceland
is well advanced in its plans to become energy-independent by 2050 through deploying 100% renewable energy.
as a buffer against the economic
and political impacts of an energy crisis
. All 28 members of the International Energy Agency
hold a minimum of 90 days of their oil imports, for example.
The value of such reserves was demonstrated by the relative lack of disruption caused by the 2007 Russia-Belarus energy dispute
, when Russia
indirectly cut exports to several countries in the European Union
.
Due to the theories in peak oil
and need to curb demand, the United States military and Department of Defense had made significant cuts, and have been making a number of attempts to come up with more efficient ways to use oil.
, reliance on imported natural gas
creates significant short term vulnerabilities. Many European countries saw an immediate drop in supply when Russian gas supplies were halted during the Russia-Ukraine gas dispute
in 2006.
Natural gas has been a viable source of energy in the world. Consisting of mostly methane natural gas is produced using two methods, biogenic and thermogenic. Biogenic comes from methogenic organisms located in marshes and landfills where thermogenic comes from buried material that is heated up from the earths core. Russia is the current leading country in production of natural gases. One of the biggest problems currently with natural gas is the ability to storage and transport it. With its low density it becomes harder to have pipelines in North America to transport enough natural gas as the demand increases. These pipelines are reaching near capacity and even at full capacity do not produce the amount of gas needed.
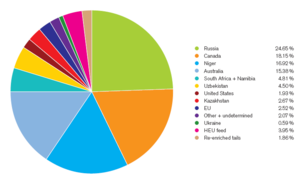 Uranium for nuclear power
Uranium for nuclear power
is mined
and enriched
in diverse and "stable" countries. These include Canada (23% of the world's total in 2007), Australia (21%), Kazakhstan (16%) and more than 10 other countries. Uranium is mined and fuel is manufactured significantly in advance of need. Nuclear fuel is considered by some to be a relatively-reliable power source, though a debate over the timing of peak uranium
does exist. Although a very viable resource nuclear power comes under fire a lot of times because of the danger that people associate to it, nuclear power is stable but if something were to happen there are very little options that have been proposed to fix that problem. Another big factor in the debate with nuclear power is that many people or companies do not want this high waste energy solution near them due to possible radiation leaks, nuclear runoff into streams and lakes and also the nuclear power plant ruins how appealing a city or state looks to other people in the country. Currently nuclear power powers a small fraction of the worlds electricity, but an even smaller fraction to the United States electricity. The incorporation of nuclear power can be seen through many different uses, for example there are currently nuclear powered ships that the navy uses to transport materials, soldiers and other resources. Three of the ships names are the USS Bainbridge, USS Longbeach and the USS Enterprise. A future use for nuclear power resides in space technology, the current way of traveling through space requires a heavy consumption of fossil fuels, however in the near future there are plans to have space shuttles incorporate nuclear power generators on the shuttle which will greatly increase the distance traveled in these units and allow us to observe more of the space around us.
Economic
Strategic
National security
National security is the requirement to maintain the survival of the state through the use of economic, diplomacy, power projection and political power. The concept developed mostly in the United States of America after World War II...
and the availability of natural resource
Natural resource
Natural resources occur naturally within environments that exist relatively undisturbed by mankind, in a natural form. A natural resource is often characterized by amounts of biodiversity and geodiversity existent in various ecosystems....
s for energy
Energy
In physics, energy is an indirectly observed quantity. It is often understood as the ability a physical system has to do work on other physical systems...
consumption. Access to cheap energy
Energy
In physics, energy is an indirectly observed quantity. It is often understood as the ability a physical system has to do work on other physical systems...
has become essential to the functioning of modern economies. However, the uneven distribution of energy supplies among countries has led to significant vulnerabilities. Threats to energy security include the political instability of several energy producing countries, the manipulation of energy supplies, the competition over energy sources, attacks on supply infrastructure, as well as accidents, natural disasters, rising terrorism, and dominant countries reliance to the foreign oil supply. The limited supplies, uneven distribution, and rising costs of fossil fuels, such as oil and gas, create a need to change to more sustainable energy
Sustainable energy
Sustainable energy is the provision of energy that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their needs. Sustainable energy sources include all renewable energy sources, such as hydroelectricity, solar energy, wind energy, wave power, geothermal...
sources in the foreseeable future. With as much dependence that the U.S. currently has for oil and with the peaking limits of oil production; economies and societies will begin to feel the decline in the resource that we have become dependent upon. Energy security has become one of the leading issues in the world today as oil and other resources have become as vital to the world's people. However with oil production rates decreasing and oil production peak nearing the world has come to protect what resources we have left in the world. With new advancements in renewable resources, less pressure has been put on companies that produce the world's oil. These resources include geothermal, solar power, wind power and hydro-electric. Although these are not all the current and possible future options for the world to turn to as the oil depletes, the most important issue is protecting these vital resources from future threats. These new resources will become more useful as the price of exporting and importing oil increases due to the increase of demand.
Security threats
The modern world relies on a vast energy supply to fuel everything from transportation to communication, to security and health delivery systems. Due to their vital roles energy sources are logical targets for attacks that seek to weaken infrastructure. That said, threats to energy sources extend beyond basic tactical aggression or terrorism.One of the leading threats to energy security is the significant increase in energy price
Energy price
The following articles relate to the price of energy:*Energy crisis*Price of petroleum*Hubbert peak theory *Energy economics*Electricity market*Cost of electricity by source- See also :**...
s, either on the world markets – as has occurred in a number of energy crises
Energy crisis
An energy crisis is any great bottleneck in the supply of energy resources to an economy. In popular literature though, it often refers to one of the energy sources used at a certain time and place, particularly those that supply national electricity grids or serve as fuel for vehicles...
over the years – or by the imposition of price increases by an oligopoly
Oligopoly
An oligopoly is a market form in which a market or industry is dominated by a small number of sellers . The word is derived, by analogy with "monopoly", from the Greek ὀλίγοι "few" + πόλειν "to sell". Because there are few sellers, each oligopolist is likely to be aware of the actions of the others...
or monopoly
Monopoly
A monopoly exists when a specific person or enterprise is the only supplier of a particular commodity...
supplier, cartel
Cartel
A cartel is a formal agreement among competing firms. It is a formal organization of producers and manufacturers that agree to fix prices, marketing, and production. Cartels usually occur in an oligopolistic industry, where there is a small number of sellers and usually involve homogeneous products...
or country
Country
A country is a region legally identified as a distinct entity in political geography. A country may be an independent sovereign state or one that is occupied by another state, as a non-sovereign or formerly sovereign political division, or a geographic region associated with a previously...
. In some cases the threat might come from a single energy superpower
Energy superpower
The term energy superpower does not have a clear definition. It has come to be used to refer to a nation that supplies large amounts of energy resources to a significant number of other states, and which therefore has the potential to influence world markets to gain a political or economic...
– those states able to significantly influence world markets by their action alone. Rather than just manipulating prices, such suppliers might go beyond this by suspending or terminating supplies. This has been done to apply pressure during economic negotiations - such as during the Russia-Belarus energy dispute
Russia-Belarus energy dispute
The Russia–Belarus energy dispute began when Russian state-owned gas supplier Gazprom demanded an increase in gas prices paid by Belarus, a country which has been closely allied with Moscow and forms a loose union state with Russia...
- or to apply political pressure, for example by OPEC
OPEC
OPEC is an intergovernmental organization of twelve developing countries made up of Algeria, Angola, Ecuador, Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Libya, Nigeria, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates, and Venezuela. OPEC has maintained its headquarters in Vienna since 1965, and hosts regular meetings...
in response to Western support for Israel
Israel
The State of Israel is a parliamentary republic located in the Middle East, along the eastern shore of the Mediterranean Sea...
in the Yom Kippur War
Yom Kippur War
The Yom Kippur War, Ramadan War or October War , also known as the 1973 Arab-Israeli War and the Fourth Arab-Israeli War, was fought from October 6 to 25, 1973, between Israel and a coalition of Arab states led by Egypt and Syria...
. Suspension of supplies may also come about as a result of worldwide international sanctions
International sanctions
International sanctions are actions taken by countries against others for political reasons, either unilaterally or multilaterally.There are several types of sanctions....
against a country.
Energy plays an important role in the national security of any given country as a fuel to power the economic engine. Hence, threats to energy security can also result from physical damage to the energy infrastructure either of the supplier, or of the importer as a result of natural events, misfortune, terrorism
Terrorism
Terrorism is the systematic use of terror, especially as a means of coercion. In the international community, however, terrorism has no universally agreed, legally binding, criminal law definition...
, or war
War
War is a state of organized, armed, and often prolonged conflict carried on between states, nations, or other parties typified by extreme aggression, social disruption, and usually high mortality. War should be understood as an actual, intentional and widespread armed conflict between political...
fare. The political and economic instability caused by war or other factors such as strike action
Strike action
Strike action, also called labour strike, on strike, greve , or simply strike, is a work stoppage caused by the mass refusal of employees to work. A strike usually takes place in response to employee grievances. Strikes became important during the industrial revolution, when mass labour became...
can also prevent the proper functioning of the energy industry in a supplier country. One example of this would be the United states, the U.S. has over 60% of its imported oil from OPEC countries and have been increasingly more dependent over the last 20 years.
New threats to energy security have emerged in the form of the increased world competition for energy resources due to the increased pace of industrialization in countries such as India
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
and China
China
Chinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture...
. Although still a minority concern, the possibility of price rises resulting from the peaking of world oil production
Hubbert peak theory
The Hubbert peak theory posits that for any given geographical area, from an individual oil-producing region to the planet as a whole, the rate of petroleum production tends to follow a bell-shaped curve...
is also starting to attract the attention of at least the French
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
government.
Increased competition over energy resources may also lead to the formation of security compacts to enable an equitable distribution of oil and gas between major powers. However, this may happen at the expense of less developed economies. The Group of Five
Group of Five
The Group of Five encompasses five nations which have joined together for an active role in the rapidly evolving international order. Individually and as a group, the G5 nations work to promote dialogue and understanding between developing and developed countries. The G5 seek to find common...
, precursors to the G8
G8
The Group of Eight is a forum, created by France in 1975, for the governments of seven major economies: Canada, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, the United Kingdom, and the United States. In 1997, the group added Russia, thus becoming the G8...
, first met in 1975 to coordinate economic and energy policies in the wake of the 1973 Arab oil embargo
1973 oil crisis
The 1973 oil crisis started in October 1973, when the members of Organization of Arab Petroleum Exporting Countries or the OAPEC proclaimed an oil embargo. This was "in response to the U.S. decision to re-supply the Israeli military" during the Yom Kippur war. It lasted until March 1974. With the...
, a rise in inflation and a global economic slowdown.
NATO leaders meeting in Bucharest in April 2008 may discuss the possibility of using the military alliance "as an instrument of energy security." One of the possibilities include placing troops in the Caucasus region to police oil and gas pipelines.
Founded by the Germans post 1943 Energy Security has been on the minds of leading political thinkers of late
Energy sector
The energy sector for not only the U.S. but for many other countries fuel the economies in the 21st century. Without these resources and the money coming in from them health and overall welfare will be risked world-wide. Oil has become what oxygen is to humans but for the economy. As the resources near peak production levels the U.S. economy will be threatened and will force other resources and big oil producing companies to start researching new sources of fuel to help revitalize the economy. The energy infrastructure is divided into three interrelated segments: electricity, petroleum and natural gas. Natural gas although very efficient is in decline and becomes very hard to harvest and very dangerous to store. Electricity when produced is very harmful to the environment due to all the greenhouse gases leaked into the atmosphere. With these concerns the U.S. and other countries including Russia and China have been researching new methods of creating electricity in a more clean way.Long term security
Long term measures to increase energy security center on reducing dependence on any one source of imported energy, increasing the number of suppliers, exploiting native fossil fuelFossil fuel
Fossil fuels are fuels formed by natural processes such as anaerobic decomposition of buried dead organisms. The age of the organisms and their resulting fossil fuels is typically millions of years, and sometimes exceeds 650 million years...
or renewable energy
Renewable energy
Renewable energy is energy which comes from natural resources such as sunlight, wind, rain, tides, and geothermal heat, which are renewable . About 16% of global final energy consumption comes from renewables, with 10% coming from traditional biomass, which is mainly used for heating, and 3.4% from...
resources, and reducing overall demand through energy conservation
Energy conservation
Energy conservation refers to efforts made to reduce energy consumption. Energy conservation can be achieved through increased efficient energy use, in conjunction with decreased energy consumption and/or reduced consumption from conventional energy sources...
measures. It can also involve entering into international agreements to underpin international energy trading relationships, such as the Energy Charter Treaty
Energy Charter Treaty
The Energy Charter Treaty is an international agreement which provides a multilateral framework for energy trade, transit and investments...
in Europe. All the concern coming from security threats on oil sources long term security measures will help reduce the future cost of importing and exporting fuel into and out of countries without having to worry about harm coming to the goods being transported.
The impact of the 1973 oil crisis
1973 oil crisis
The 1973 oil crisis started in October 1973, when the members of Organization of Arab Petroleum Exporting Countries or the OAPEC proclaimed an oil embargo. This was "in response to the U.S. decision to re-supply the Israeli military" during the Yom Kippur war. It lasted until March 1974. With the...
and the emergence of the OPEC
OPEC
OPEC is an intergovernmental organization of twelve developing countries made up of Algeria, Angola, Ecuador, Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Libya, Nigeria, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates, and Venezuela. OPEC has maintained its headquarters in Vienna since 1965, and hosts regular meetings...
cartel
Cartel
A cartel is a formal agreement among competing firms. It is a formal organization of producers and manufacturers that agree to fix prices, marketing, and production. Cartels usually occur in an oligopolistic industry, where there is a small number of sellers and usually involve homogeneous products...
was a particular milestone that prompted some countries to increase their energy security. Japan, almost totally dependent on imported oil, steadily introduced the use of natural gas
Natural gas
Natural gas is a naturally occurring gas mixture consisting primarily of methane, typically with 0–20% higher hydrocarbons . It is found associated with other hydrocarbon fuel, in coal beds, as methane clathrates, and is an important fuel source and a major feedstock for fertilizers.Most natural...
, nuclear power
Nuclear power
Nuclear power is the use of sustained nuclear fission to generate heat and electricity. Nuclear power plants provide about 6% of the world's energy and 13–14% of the world's electricity, with the U.S., France, and Japan together accounting for about 50% of nuclear generated electricity...
, high-speed mass transit systems, and implemented energy conservation
Energy conservation
Energy conservation refers to efforts made to reduce energy consumption. Energy conservation can be achieved through increased efficient energy use, in conjunction with decreased energy consumption and/or reduced consumption from conventional energy sources...
measures, It has become one of the world leaders in the use of renewable energy
Renewable energy
Renewable energy is energy which comes from natural resources such as sunlight, wind, rain, tides, and geothermal heat, which are renewable . About 16% of global final energy consumption comes from renewables, with 10% coming from traditional biomass, which is mainly used for heating, and 3.4% from...
. The United Kingdom
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
began exploiting North Sea oil
North Sea oil
North Sea oil is a mixture of hydrocarbons, comprising liquid oil and natural gas, produced from oil reservoirs beneath the North Sea.In the oil industry, the term "North Sea" often includes areas such as the Norwegian Sea and the area known as "West of Shetland", "the Atlantic Frontier" or "the...
and gas reserves, and became a net exporter of energy into the 2000s.
In other countries energy security has historically been a lower priority. The United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
, for example, has continued to increase its dependency on imported oil although, following the oil price increases since 2003, the development of biofuels has been suggested as a means of addressing this.
Increasing energy security is also one of the reasons behind a block on the development of natural gas imports in Sweden. Greater investment in native renewable energy technologies and energy conservation is envisaged instead. India
Energy policy of India
The energy policy of India is largely defined by the country's burgeoning energy deficit and increased focus on developing alternative sources of energy, particularly nuclear, solar and wind energy....
is carrying out a major hunt for domestic oil to decrease its dependency on OPEC
OPEC
OPEC is an intergovernmental organization of twelve developing countries made up of Algeria, Angola, Ecuador, Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Libya, Nigeria, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates, and Venezuela. OPEC has maintained its headquarters in Vienna since 1965, and hosts regular meetings...
, while Iceland
Renewable energy in Iceland
About 81 percent of total primary energy supply in Iceland is derived from domestically produced renewable energy sources. In 2007, geothermal energy provided about 66 percent of primary energy, the share of hydropower was 15 percent, and fossil fuels 19 percent...
is well advanced in its plans to become energy-independent by 2050 through deploying 100% renewable energy.
Petroleum
Petroleum or otherwise known as "crude oil" has become the resource most used by countries all around the world including Russia, China and the United States of America. With all the oil wells located around the world energy security has become a main issue to ensure the safety of the petroleum that is being harvested. In the middle east oil fields become main targets for sabotage because of how heavily countries rely on oil. Many countries hold strategic petroleum reservesGlobal strategic petroleum reserves
Global strategic petroleum reserves refer to crude oil inventories held by the government of a particular country, as well as private industry, for the purpose of providing economic and national security during an energy crisis...
as a buffer against the economic
Economy
An economy consists of the economic system of a country or other area; the labor, capital and land resources; and the manufacturing, trade, distribution, and consumption of goods and services of that area...
and political impacts of an energy crisis
Energy crisis
An energy crisis is any great bottleneck in the supply of energy resources to an economy. In popular literature though, it often refers to one of the energy sources used at a certain time and place, particularly those that supply national electricity grids or serve as fuel for vehicles...
. All 28 members of the International Energy Agency
International Energy Agency
The International Energy Agency is a Paris-based autonomous intergovernmental organization established in the framework of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development in 1974 in the wake of the 1973 oil crisis...
hold a minimum of 90 days of their oil imports, for example.
The value of such reserves was demonstrated by the relative lack of disruption caused by the 2007 Russia-Belarus energy dispute
Russia-Belarus energy dispute
The Russia–Belarus energy dispute began when Russian state-owned gas supplier Gazprom demanded an increase in gas prices paid by Belarus, a country which has been closely allied with Moscow and forms a loose union state with Russia...
, when Russia
Russia
Russia or , officially known as both Russia and the Russian Federation , is a country in northern Eurasia. It is a federal semi-presidential republic, comprising 83 federal subjects...
indirectly cut exports to several countries in the European Union
European Union
The European Union is an economic and political union of 27 independent member states which are located primarily in Europe. The EU traces its origins from the European Coal and Steel Community and the European Economic Community , formed by six countries in 1958...
.
Due to the theories in peak oil
Peak oil
Peak oil is the point in time when the maximum rate of global petroleum extraction is reached, after which the rate of production enters terminal decline. This concept is based on the observed production rates of individual oil wells, projected reserves and the combined production rate of a field...
and need to curb demand, the United States military and Department of Defense had made significant cuts, and have been making a number of attempts to come up with more efficient ways to use oil.
Natural gas
Compared to petroleumPetroleum
Petroleum or crude oil is a naturally occurring, flammable liquid consisting of a complex mixture of hydrocarbons of various molecular weights and other liquid organic compounds, that are found in geologic formations beneath the Earth's surface. Petroleum is recovered mostly through oil drilling...
, reliance on imported natural gas
Natural gas
Natural gas is a naturally occurring gas mixture consisting primarily of methane, typically with 0–20% higher hydrocarbons . It is found associated with other hydrocarbon fuel, in coal beds, as methane clathrates, and is an important fuel source and a major feedstock for fertilizers.Most natural...
creates significant short term vulnerabilities. Many European countries saw an immediate drop in supply when Russian gas supplies were halted during the Russia-Ukraine gas dispute
Russia-Ukraine gas dispute
The Russia–Ukraine gas disputes refer to a number of disputes between Ukrainian oil and gas company Naftogaz Ukrainy and Russian gas supplier Gazprom over natural gas supplies, prices, and debts...
in 2006.
Natural gas has been a viable source of energy in the world. Consisting of mostly methane natural gas is produced using two methods, biogenic and thermogenic. Biogenic comes from methogenic organisms located in marshes and landfills where thermogenic comes from buried material that is heated up from the earths core. Russia is the current leading country in production of natural gases. One of the biggest problems currently with natural gas is the ability to storage and transport it. With its low density it becomes harder to have pipelines in North America to transport enough natural gas as the demand increases. These pipelines are reaching near capacity and even at full capacity do not produce the amount of gas needed.
Nuclear power

Nuclear power
Nuclear power is the use of sustained nuclear fission to generate heat and electricity. Nuclear power plants provide about 6% of the world's energy and 13–14% of the world's electricity, with the U.S., France, and Japan together accounting for about 50% of nuclear generated electricity...
is mined
Uranium mining
Uranium mining is the process of extraction of uranium ore from the ground. The worldwide production of uranium in 2009 amounted to 50,572 tonnes, of which 27% was mined in Kazakhstan. Kazakhstan, Canada, and Australia are the top three producers and together account for 63% of world uranium...
and enriched
Enriched uranium
Enriched uranium is a kind of uranium in which the percent composition of uranium-235 has been increased through the process of isotope separation. Natural uranium is 99.284% 238U isotope, with 235U only constituting about 0.711% of its weight...
in diverse and "stable" countries. These include Canada (23% of the world's total in 2007), Australia (21%), Kazakhstan (16%) and more than 10 other countries. Uranium is mined and fuel is manufactured significantly in advance of need. Nuclear fuel is considered by some to be a relatively-reliable power source, though a debate over the timing of peak uranium
Peak uranium
Peak uranium is the point in time that the maximum global uranium production rate is reached. After that peak, the rate of production enters a terminal decline. While uranium is used in nuclear weapons, its primary use is for energy generation via nuclear fission of uranium-235 isotope in a nuclear...
does exist. Although a very viable resource nuclear power comes under fire a lot of times because of the danger that people associate to it, nuclear power is stable but if something were to happen there are very little options that have been proposed to fix that problem. Another big factor in the debate with nuclear power is that many people or companies do not want this high waste energy solution near them due to possible radiation leaks, nuclear runoff into streams and lakes and also the nuclear power plant ruins how appealing a city or state looks to other people in the country. Currently nuclear power powers a small fraction of the worlds electricity, but an even smaller fraction to the United States electricity. The incorporation of nuclear power can be seen through many different uses, for example there are currently nuclear powered ships that the navy uses to transport materials, soldiers and other resources. Three of the ships names are the USS Bainbridge, USS Longbeach and the USS Enterprise. A future use for nuclear power resides in space technology, the current way of traveling through space requires a heavy consumption of fossil fuels, however in the near future there are plans to have space shuttles incorporate nuclear power generators on the shuttle which will greatly increase the distance traveled in these units and allow us to observe more of the space around us.
Renewable energy
The deployment of renewable technologies usually increases the diversity of electricity sources and, through local generation, contributes to the flexibility of the system and its resistance to central shocks. For those countries where growing dependence on imported gas is a significant energy security issue, renewable technologies can provide alternative sources of electric power as well as displacing electricity demand through direct heat production. Renewable biofuels for transport represent a key source of diversification from petroleum products. As the resources that have been so crucial to survival in the world to this day start declining in numbers, countries will begin to realize that the need for renewable fuel sources will be as vital as ever. With the production of new types of energy including, solar, geothermal, hydro-electric, biofuel and wind power. With the amount of sun that hits the world in one hour there is enough energy to power the world for one year. With the addition of solar panels all around the world a little less pressure is taken off the need to produce more oil. Geothermal can potentially lead to other sources of fuel, if companies would take the heat from the inner core of the earth to heat up water sources we could essentially use the steam creating from the heated water to power machines, this option is one of the cleanest and efficient options. Hydro-electric which has been incorporated into many of the dams around the world produces a lot of energy and is very easy to produce the energy as the dams control the water that is allowed through seams which power turbines located inside of the dam. Bio-fuels have been researched using many different sources including ethanol and algae, these options are substantially cleaner than the consumption of petroleum.See also
By area- :Category:Energy policy by country
- Energy security of the People's Republic of China
- Energy security of Afghanistan
- U.S. Energy IndependenceU.S. energy independenceU.S. energy independence relates to the goal of reducing the U.S imports of oil and other foreign sources of energy. If total energy is looked at, the U.S. is over 70% self-sufficient. Energy independence is espoused by those who want to leave America unaffected by global energy supply...
- Energy Security ActEnergy Security ActThe Energy Security Act was signed into law by U.S. President Jimmy Carter on June 30, 1980.It consisted of six major acts:* U.S. Synthetic Fuels Corporation Act* Biomass Energy and Alcohol Fuels Act* Renewable Energy Resources Act...
- Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007The Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 is an Act of Congress concerning the energy policy of the United States...
- Cebu Declaration on East Asian Energy SecurityCebu Declaration on East Asian Energy SecurityThe Cebu Declaration on East Asian Energy Security was signed by 16 nations after a three hour meeting of delegates at the East Asia Summit in Cebu on January 15, 2007. The countries have agreed to promote energy security and find energy alternatives to conventional fuels.The Declaration lists a...
Economic
- Energy priceEnergy priceThe following articles relate to the price of energy:*Energy crisis*Price of petroleum*Hubbert peak theory *Energy economics*Electricity market*Cost of electricity by source- See also :**...
- Energy supplyEnergy supplyEnergy supply is the delivery of fuels or transformed fuels to point of consumption. It potentially encompasses the extraction, transmission, generation, distribution and storage of fuels...
- Oil ShockwaveOil ShockwaveThe Oil Shockwave event was a policy wargaming scenario created by the joint effort of several energy policy think tanks, the National Commission on Energy Policy and Securing America's Future Energy. It outlined a series of hypothetical international events taking place in December 2005, all...
- Peak oilPeak oilPeak oil is the point in time when the maximum rate of global petroleum extraction is reached, after which the rate of production enters terminal decline. This concept is based on the observed production rates of individual oil wells, projected reserves and the combined production rate of a field...
Strategic
- Eco-nationalismEco-nationalismThe term eco-nationalism is a neologism used to describe an emerging form on nationalism both on economic and ecological issues.Economic nationalism, typified in the US by individuals such as Lou Dobbs seeks to protect the working class of a country from loss of jobs due to trends such as...
- Energy independenceEnergy independenceThe following articles relate to the topic of energy independence:* Energy resilience* Energy security* North American energy independence* Swedish Commission on Oil Independence* United States energy independence...
- National securityNational securityNational security is the requirement to maintain the survival of the state through the use of economic, diplomacy, power projection and political power. The concept developed mostly in the United States of America after World War II...
- Strategic reserveStrategic reserveFor the military term see: Military reserveA strategic reserve is a term used to describe a reserve of a commodity or items, held back from normal use by governments, organisations or business in pursuance of a particular strategy or to cope with unexpected events.A strategic reserve can be:*...
- Global strategic petroleum reservesGlobal strategic petroleum reservesGlobal strategic petroleum reserves refer to crude oil inventories held by the government of a particular country, as well as private industry, for the purpose of providing economic and national security during an energy crisis...
- Energy superpowerEnergy superpowerThe term energy superpower does not have a clear definition. It has come to be used to refer to a nation that supplies large amounts of energy resources to a significant number of other states, and which therefore has the potential to influence world markets to gain a political or economic...
- Energy and Environmental Security Initiative
- Energy security and renewable technologyEnergy security and renewable technologyThe environmental benefits of renewable energy technologies are widely recognised, but the contribution thatthey can make to energy security is less well known. Renewable technologies can enhance energy security in electricity generation, heat supply, and transportation.-Energy security:Access to...
- High Speed Rail
- International Risk Governance CouncilInternational Risk Governance CouncilFounded in June 2003 at the initiative of the Swiss government, the International Risk Governance Council is an independent and neutral organisation whose purpose is to help improve the understanding and management of potentially global risks that have impacts on human health and safety, the...
- Nationalization of oil suppliesNationalization of oil suppliesThe nationalization of oil supplies refers to the process of deprivatization of oil production operations, generally in the purpose of obtaining more revenue from oil for oil producing countries. This process, which should not be confused with restrictions on crude oil exports, represents a...
- International Energy ForumInternational Energy ForumThe International Energy Forum, also known as IEF, is the world's largest recurring gathering of energy ministers. It is unique in that participants not only include IEA and OPEC countries, but also key international actors such as Brazil, China, India, Mexico, Russia, and South Africa. The IEF...
External links
- Journal of Energy Security
- Institute for the Analysis of Global Security: Energy Security Research
- United States Energy Security Council
- Energy and Environmental Security Initiative (EESI)
- NATO and Energy Security
- Closing the Gap Between Energy & National Security Policy
- Energy Security as National Security: Defining Problems Ahead of Solutions
- High Speed Rail and Energy Security
- Energy Security Implications of the US-India Nuclear Deal
- Collective Energy Security: A New Approach for Europe
- Canadian Arctic Energy Security
- Can The United States Drill Its Way to Energy Security?
- Tax Oil Organization
- Energy Export Databrowser - A visual review of production and consumption trends for individual nations; data from the British Petroleum Statistical Review
Additional sources
- http://pzl1.ed.ornl.gov/energysecurity.html
- http://www.iea.org/subjectqueries/keyresult.asp?KEYWORD_ID=4103 3. *http://www.energysecuritycouncil.org/default.aspx?AspxAutoDetectCookieSupport=1
- http://www.springerlink.com/content/f23j03184744317x/
- http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=ArticleURL&_udi=B6V2W-4CPD725-1&_user=650596&_coverDate=11/01/2005&_rdoc=1&_fmt=high&_orig=search&_origin=search&_sort=d&_docanchor=&view=c&_searchStrId=1537299852&_rerunOrigin=scholar.google&_acct=C000035098&_version=1&_urlVersion=0&_userid=650596&md5=51b30652a51ac482c89feba38bae1fe3&searchtype=a
- http://books.google.com/books?hl=en&lr=&id=2iVbs4Myu_AC&oi=fnd&pg=PR7&dq=energy+security+&ots=Fph0UBErDp&sig=uIt6LTYN1S9AfqElryWXpzQ9zTo#v=onepage&q&f=false

