
Enterprise (1855)
Encyclopedia
The Enterprise was an early steamboat operating on the Willamette River
in Oregon and also one of the first to operate on the Fraser River
in British Columbia
. This vessel should not be confused with the many other vessels, some of similar design, also named Enterprise. In earlier times, this vessel was sometimes called Tom Wright's Enterprise after one of her captains, the famous Tom Wright.
in the fall of 1855 by Capt. Archibald Jamieson, Captain A.S. Murray, Amory Holbrook and John Torrence, in the fall of 1855, for the upper Willamette
trade. Her officers on the first trip upriver to Corvallis
(then known as Marysville) were: Jamieson, captain ; Chandler, purser; and Torrence, engineer. George A. Pease was afterward employed as pilot, and John Marshall, engineer.
 From 1855 to 1858 Enterprise was operated on the Willamette River
From 1855 to 1858 Enterprise was operated on the Willamette River
, running between Oregon City
, Canemah, and Corvallis. At that time Corvallis was considered to be the head of navigation on the Willamette. Merchants above Corvallis tried to get Captain Jamieson to bring Enterprise, which he then commanded, above Corvallis, but he would not go farther than Orleans, then a small settlement on the east side of the river across from Corvallis.
.jpg) In July 1858, Jamieson sold Enterprise to Capt. Thomas A. Wright. Jamieson used the money from the sale of Enterprise to build the steamer Onward
In July 1858, Jamieson sold Enterprise to Capt. Thomas A. Wright. Jamieson used the money from the sale of Enterprise to build the steamer Onward
. Tom Wright became one of the most famous steamboat captains in the Pacific Northwest. Like Jamieson, Wright was one of a family in the steamboat business. His father was Capt. John T. Wright, who was the owner of other steamboats, such as Sea Bird and Commodore. The other two sons, also steamboat captains, were George S. Wright and John T. Wright, Jr.
Tom Wright's plan for Enterprise was to take the vessel into British waters to serve the Fraser River Gold Rush. The first part of the journey began by moving Enterprise from the upper to the lower Willamette River by lining the vessel over Willamette Falls
. These falls could not be navigated by steamboats, and indeed Captain Jamieson was later killed when a vessel under his command was accidentally swept over them and destroyed. Lining was procedure where a heavy cable was attached to the vessel, and then to a well-anchored windlass on shore. Little by little the cable would be let out to allow the vessel to gradually pass over the falls to the lower river.
Wright then took Enterprise down the lower Willamette and Columbia
rivers to Astoria, Oregon
. Once there, Wright arranged for an ocean-going steamship to tow Enterprise to Victoria, British Columbia
. Victoria, then the largest settlement on the Pacific Coast of North America north of San Francisco. Enterprise left Astoria under tow, but the strong waves on the Columbia Bar
caused Enterprise to be so terribly racked that the vessel began leaking, and it was only by luck that they got Enterprise back into shallow water at Astoria before she sank. She was raised and repaired, and started again in August for Victoria, again under tow.
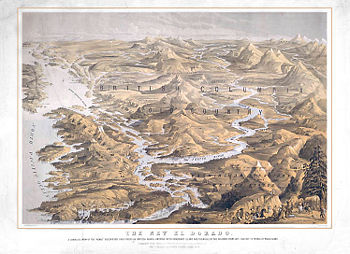 Enterprise arrived in Victoria in the middle of August 1858. 'Other steamboats that arrived at Victoria at almost the same time that summer were Wilson G. Hunt
Enterprise arrived in Victoria in the middle of August 1858. 'Other steamboats that arrived at Victoria at almost the same time that summer were Wilson G. Hunt
, Martin White, and Maria.
Enterprise with other American steamboats obtained a license from the governor of British Columbia to operate in British territory. Enterprise was the second steam-powered vessel to operate on the Fraser River, and had been brought up to Victoria in July 1858. The first vessel was another American steamer, the Umatilla ex Fashion from the Columbia River
. Enterprise was very successful on the Fraser River
, earning $25,000 in one trip up to Murderer's Bar, near Fort Hope, BC. 25,000 miners went into the Fraser diggings in the summer of 1858, but by the winter only 3,000 remained.
With the drop in the population of miners, by the fall of 1858, Enterprise was one of only two steamboats operating on the Fraser River, the other being Maria, under Capt. William A. Lubbock. For a time at least , the two boats divided the traffic between them, with Maria running upriver from Fort Langley to Fort Hope and other points, and Enterprise running between Fort Langley and Victoria, on Vancouver Island. With a monopoly on transport, the two boats were able to raise freight rates from $4 to $7 per ton in the summer to $60 a ton. Beans that cost 3 cents a pound in Victoria cost 75 cents in Lytton, British Columbia
.
On December 9, 1858, Enterprise was caught in the ice on the Fraser River between Fort Hope and Fort Langley
. The vessel was short on food and accommodations, and so 114 of the passengers decided to leave the steamer and walk the remaining distance to Fort Langley. In the cold weather, this proved a mistake, as they had inadequate clothing and insufficient clothing and camping provisions to make the journey. After three days in the ice, Captain Wright was able to hack the Enterprise free. He then cruised up and down the river, eventually rescuing all of the passengers, many of whom were suffering from frostbite.
Enterprise built for the Willamette River was not strong enough to regularly cross the often stormy Strait of Georgia
, which was the body of water that separated Vancouver Island
from the mouth of the Fraser River on the mainland. The Wrights however had no choice in the matter if they were to remain in business, because the vessel they had been running on the route, the Sea Bird was destroyed by fire in the Strait of Georgia on September 7, 1858 while enroute from Victoria to Fort Langley. By the spring of 1859, Capt. John T. Wright was able to replace Sea Bird by purchasing an interest in the sidewheeler Eliza Anderson
, and arranging to have the Anderson brought from Portland, Oregon
where she had been recently built, to Victoria, BC, where she arrived in late March, 1859. This allowed the Wrights to run the heavier more durable Anderson across the Straits to Fort Langley, while returning Enterprise to the 'Fraser River to make the run up from Fort Langley.
On March 30, 1859, with Captain Tom Wright in command, Enterprise set out upriver from Fort Langley (after meeting the Anderson). The river was rising high with the rapidly melting snowfall, and with a new boiler installed in the Enterprise Captain Wright hoped to take the vessel all the way to Fort Yale. Only one other steamboat had ever made it to Fort Yale, the Umatilla which by then was no longer on the Fraser River. This time, Captain Wright was unable to go further up than Fort Hope. Enterprise was not powerful enough to beat the strong currents forming whirlpools in the river. Another constant hazard were logs caught in the river bottom, forming "snags" which could damage or destroy a steam vessel.
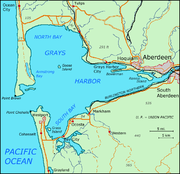 To command a steamboat at a time when there were neither roads nor railroads in the Pacific Northwest was to be in a spectacular opportunity to earn money. Tom Wright never became rich because he could never settle down to running a vessel on a particular route for a sustained period of time. As soon as he mastered one route, he would be looking for another one. In June 1859 Captain Wright was ready to make another change. Hearing of homesteading activity beginning in the valley of the Chehalis River, in the western part of what is now Washington, Wright determined to take Enterprise to the Chehalis. This would require the lightly built Enterprise to be towed, in this case by the Eliza Anderson west through the Strait of Juan de Fuca
To command a steamboat at a time when there were neither roads nor railroads in the Pacific Northwest was to be in a spectacular opportunity to earn money. Tom Wright never became rich because he could never settle down to running a vessel on a particular route for a sustained period of time. As soon as he mastered one route, he would be looking for another one. In June 1859 Captain Wright was ready to make another change. Hearing of homesteading activity beginning in the valley of the Chehalis River, in the western part of what is now Washington, Wright determined to take Enterprise to the Chehalis. This would require the lightly built Enterprise to be towed, in this case by the Eliza Anderson west through the Strait of Juan de Fuca
and then south down the coast line of the Pacific Ocean to Grays Harbor.
The Chehalis River flows into Grays Harbor on its eastern shore, near where the modern cities of Aberdeen
and Hoquiam, Washington
are now located. Wright begin this journey from Victoria on July 8, 1859 with Eliza Anderson towing Enterprise. In the Strait of Juan de Fuca Enterprise broke a shaft on her sternwheel, and the entire expedition was forced to turn back to Esquimalt, where Enterprise had to wait for a replacement shaft to be brought in from San Francisco.
. At that time the boundary between the United States and British Columbia was in dispute, with both countries claiming the San Juan Islands. British and American garrisons were established on San Juan Island. At one point a soldier shot a pig belonging to a partisan of the opposing country, and as a result the otherwise bloodless standoff became known as the Pig War
. Steamboats in the area received contracts from both countries to move troops and supplies to the islands in connection with the dispute. Once Enterprise was repaired, Tom Wright postponed his plans to move the vessel to the Chehalis to take advantage of the increase in business, making a run on August 1, 1859 from Victoria to San Juan Island carrying passengers.
By the spring of 1860, Wright was able to arrange a government contract to transport troops down the Chehalis River to Grays Harbor, and so was able to recoup some of his losses. Once the government contract work expired, there was no further business in the Grays Harbor area. Unable to move the lightly built vessel again on the open ocean, Wright dismantled Enterprise at Grays Harbor, with the machinery being shipped to China.
Willamette River
The Willamette River is a major tributary of the Columbia River, accounting for 12 to 15 percent of the Columbia's flow. The Willamette's main stem is long, lying entirely in northwestern Oregon in the United States...
in Oregon and also one of the first to operate on the Fraser River
Fraser River
The Fraser River is the longest river within British Columbia, Canada, rising at Fraser Pass near Mount Robson in the Rocky Mountains and flowing for , into the Strait of Georgia at the city of Vancouver. It is the tenth longest river in Canada...
in British Columbia
British Columbia
British Columbia is the westernmost of Canada's provinces and is known for its natural beauty, as reflected in its Latin motto, Splendor sine occasu . Its name was chosen by Queen Victoria in 1858...
. This vessel should not be confused with the many other vessels, some of similar design, also named Enterprise. In earlier times, this vessel was sometimes called Tom Wright's Enterprise after one of her captains, the famous Tom Wright.
Construction
Enterprise was built at Canemah, OregonCanemah, Oregon
Canemah was an early settlement in the U.S. state of Oregon located near Willamette Falls on the Willamette River. It is now a district within Oregon City.-Location:...
in the fall of 1855 by Capt. Archibald Jamieson, Captain A.S. Murray, Amory Holbrook and John Torrence, in the fall of 1855, for the upper Willamette
Willamette River
The Willamette River is a major tributary of the Columbia River, accounting for 12 to 15 percent of the Columbia's flow. The Willamette's main stem is long, lying entirely in northwestern Oregon in the United States...
trade. Her officers on the first trip upriver to Corvallis
Corvallis, Oregon
Corvallis is a city located in central western Oregon, United States. It is the county seat of Benton County and the principal city of the Corvallis, Oregon Metropolitan Statistical Area, which encompasses all of Benton County. As of the 2010 United States Census, the population was 54,462....
(then known as Marysville) were: Jamieson, captain ; Chandler, purser; and Torrence, engineer. George A. Pease was afterward employed as pilot, and John Marshall, engineer.
Operations on the Willamette River

Willamette River
The Willamette River is a major tributary of the Columbia River, accounting for 12 to 15 percent of the Columbia's flow. The Willamette's main stem is long, lying entirely in northwestern Oregon in the United States...
, running between Oregon City
Oregon City, Oregon
Oregon City was the first city in the United States west of the Rocky Mountains to be incorporated. It is the county seat of Clackamas County, Oregon...
, Canemah, and Corvallis. At that time Corvallis was considered to be the head of navigation on the Willamette. Merchants above Corvallis tried to get Captain Jamieson to bring Enterprise, which he then commanded, above Corvallis, but he would not go farther than Orleans, then a small settlement on the east side of the river across from Corvallis.
Transfer to British Columbia
.jpg)
Onward (sternwheeler 1858)
Onward was an early steamboat on the Willamette River built at Canemah, Oregon in 1858. This vessel should not be confused other steamboats named Onward, including in particular the Onward of 1867, a similar but somewhat smaller vessel built at Tualatin Landing , which operated on the Tualatin...
. Tom Wright became one of the most famous steamboat captains in the Pacific Northwest. Like Jamieson, Wright was one of a family in the steamboat business. His father was Capt. John T. Wright, who was the owner of other steamboats, such as Sea Bird and Commodore. The other two sons, also steamboat captains, were George S. Wright and John T. Wright, Jr.
Tom Wright's plan for Enterprise was to take the vessel into British waters to serve the Fraser River Gold Rush. The first part of the journey began by moving Enterprise from the upper to the lower Willamette River by lining the vessel over Willamette Falls
Willamette Falls
The Willamette Falls is a natural waterfall on the Willamette River between Oregon City and West Linn, Oregon, in the United States. It is the largest waterfall in the Pacific Northwest and the eighteenth largest in the world by water volume. Horseshoe in shape, it is wide and high with a flow...
. These falls could not be navigated by steamboats, and indeed Captain Jamieson was later killed when a vessel under his command was accidentally swept over them and destroyed. Lining was procedure where a heavy cable was attached to the vessel, and then to a well-anchored windlass on shore. Little by little the cable would be let out to allow the vessel to gradually pass over the falls to the lower river.
Wright then took Enterprise down the lower Willamette and Columbia
Columbia River
The Columbia River is the largest river in the Pacific Northwest region of North America. The river rises in the Rocky Mountains of British Columbia, Canada, flows northwest and then south into the U.S. state of Washington, then turns west to form most of the border between Washington and the state...
rivers to Astoria, Oregon
Astoria, Oregon
Astoria is the county seat of Clatsop County, Oregon, United States. Situated near the mouth of the Columbia River, the city was named after the American investor John Jacob Astor. His American Fur Company founded Fort Astoria at the site in 1811...
. Once there, Wright arranged for an ocean-going steamship to tow Enterprise to Victoria, British Columbia
Victoria, British Columbia
Victoria is the capital city of British Columbia, Canada and is located on the southern tip of Vancouver Island off Canada's Pacific coast. The city has a population of about 78,000 within the metropolitan area of Greater Victoria, which has a population of 360,063, the 15th most populous Canadian...
. Victoria, then the largest settlement on the Pacific Coast of North America north of San Francisco. Enterprise left Astoria under tow, but the strong waves on the Columbia Bar
Columbia Bar
The Columbia Bar is a system of bars and shoals at the mouth of the Columbia River spanning the US states of Oregon and Washington. The bar is about wide and long....
caused Enterprise to be so terribly racked that the vessel began leaking, and it was only by luck that they got Enterprise back into shallow water at Astoria before she sank. She was raised and repaired, and started again in August for Victoria, again under tow.
Operations in British Columbia

Wilson G. Hunt (sidewheeler)
Wilson G. Hunt was a steamboat that ran in the early days of steam navigation on Puget Sound and Sacramento, Fraser, and Columbia Rivers. She was generally known as the Hunt during her years of operation. She had a long career on the west coast of the United States and Canada, and played an...
, Martin White, and Maria.
Enterprise with other American steamboats obtained a license from the governor of British Columbia to operate in British territory. Enterprise was the second steam-powered vessel to operate on the Fraser River, and had been brought up to Victoria in July 1858. The first vessel was another American steamer, the Umatilla ex Fashion from the Columbia River
Columbia River
The Columbia River is the largest river in the Pacific Northwest region of North America. The river rises in the Rocky Mountains of British Columbia, Canada, flows northwest and then south into the U.S. state of Washington, then turns west to form most of the border between Washington and the state...
. Enterprise was very successful on the Fraser River
Fraser River
The Fraser River is the longest river within British Columbia, Canada, rising at Fraser Pass near Mount Robson in the Rocky Mountains and flowing for , into the Strait of Georgia at the city of Vancouver. It is the tenth longest river in Canada...
, earning $25,000 in one trip up to Murderer's Bar, near Fort Hope, BC. 25,000 miners went into the Fraser diggings in the summer of 1858, but by the winter only 3,000 remained.
With the drop in the population of miners, by the fall of 1858, Enterprise was one of only two steamboats operating on the Fraser River, the other being Maria, under Capt. William A. Lubbock. For a time at least , the two boats divided the traffic between them, with Maria running upriver from Fort Langley to Fort Hope and other points, and Enterprise running between Fort Langley and Victoria, on Vancouver Island. With a monopoly on transport, the two boats were able to raise freight rates from $4 to $7 per ton in the summer to $60 a ton. Beans that cost 3 cents a pound in Victoria cost 75 cents in Lytton, British Columbia
Lytton, British Columbia
Lytton in British Columbia, Canada, sits at the confluence of the Thompson River and Fraser River on the east side of the Fraser. The location has been inhabited by the Nlaka'pamux people for over 10,000 years, and is one of the earliest locations settled by non-natives in the Southern Interior of...
.
On December 9, 1858, Enterprise was caught in the ice on the Fraser River between Fort Hope and Fort Langley
Fort Langley, British Columbia
Fort Langley is a village with a population of 2,700 and forms part of the Township of Langley. It is the home of Fort Langley National Historic Site, a former fur trade post of the Hudson's Bay Company.-History:...
. The vessel was short on food and accommodations, and so 114 of the passengers decided to leave the steamer and walk the remaining distance to Fort Langley. In the cold weather, this proved a mistake, as they had inadequate clothing and insufficient clothing and camping provisions to make the journey. After three days in the ice, Captain Wright was able to hack the Enterprise free. He then cruised up and down the river, eventually rescuing all of the passengers, many of whom were suffering from frostbite.
Enterprise built for the Willamette River was not strong enough to regularly cross the often stormy Strait of Georgia
Strait of Georgia
The Strait of Georgia or the Georgia Strait is a strait between Vancouver Island and the mainland coast of British Columbia, Canada. It is approximately long and varies in width from...
, which was the body of water that separated Vancouver Island
Vancouver Island
Vancouver Island is a large island in British Columbia, Canada. It is one of several North American locations named after George Vancouver, the British Royal Navy officer who explored the Pacific Northwest coast of North America between 1791 and 1794...
from the mouth of the Fraser River on the mainland. The Wrights however had no choice in the matter if they were to remain in business, because the vessel they had been running on the route, the Sea Bird was destroyed by fire in the Strait of Georgia on September 7, 1858 while enroute from Victoria to Fort Langley. By the spring of 1859, Capt. John T. Wright was able to replace Sea Bird by purchasing an interest in the sidewheeler Eliza Anderson
Eliza Anderson (sidewheeler)
The PS Eliza Anderson operated from 1858 to 1898 mainly on Puget Sound, the Strait of Georgia, and the Fraser River but also for short periods in Alaska. She was generally known as the Old Anderson and was considered slow and underpowered even for the time...
, and arranging to have the Anderson brought from Portland, Oregon
Portland, Oregon
Portland is a city located in the Pacific Northwest, near the confluence of the Willamette and Columbia rivers in the U.S. state of Oregon. As of the 2010 Census, it had a population of 583,776, making it the 29th most populous city in the United States...
where she had been recently built, to Victoria, BC, where she arrived in late March, 1859. This allowed the Wrights to run the heavier more durable Anderson across the Straits to Fort Langley, while returning Enterprise to the 'Fraser River to make the run up from Fort Langley.
On March 30, 1859, with Captain Tom Wright in command, Enterprise set out upriver from Fort Langley (after meeting the Anderson). The river was rising high with the rapidly melting snowfall, and with a new boiler installed in the Enterprise Captain Wright hoped to take the vessel all the way to Fort Yale. Only one other steamboat had ever made it to Fort Yale, the Umatilla which by then was no longer on the Fraser River. This time, Captain Wright was unable to go further up than Fort Hope. Enterprise was not powerful enough to beat the strong currents forming whirlpools in the river. Another constant hazard were logs caught in the river bottom, forming "snags" which could damage or destroy a steam vessel.
Failed transfer to Chehalis River

Strait of Juan de Fuca
The Strait of Juan de Fuca is a large body of water about long that is the Salish Sea outlet to the Pacific Ocean...
and then south down the coast line of the Pacific Ocean to Grays Harbor.
The Chehalis River flows into Grays Harbor on its eastern shore, near where the modern cities of Aberdeen
Aberdeen, Washington
Aberdeen is a city in Grays Harbor County, Washington, United States, founded by Samuel Benn in 1884. Aberdeen was incorporated on May 12, 1890. The city is the economic center of Grays Harbor County, bordering the cities of Hoquiam and Cosmopolis...
and Hoquiam, Washington
Hoquiam, Washington
Hoquiam is a city in Grays Harbor County, Washington state, United States. The town borders the city of Aberdeen at Myrtle Street with Hoquiam to the west. The two cities share a common economic history in lumbering and exporting but Hoquiam has maintained its independent identity...
are now located. Wright begin this journey from Victoria on July 8, 1859 with Eliza Anderson towing Enterprise. In the Strait of Juan de Fuca Enterprise broke a shaft on her sternwheel, and the entire expedition was forced to turn back to Esquimalt, where Enterprise had to wait for a replacement shaft to be brought in from San Francisco.
Run to San Juan Islands
Enterprise was repaired by the end of July 1859, and by that time there was a demand for steamers to carry troops to the San Juan IslandsSan Juan Islands
The San Juan Islands are an archipelago in the northwest corner of the contiguous United States between the US mainland and Vancouver Island, British Columbia, Canada. The San Juan Islands are part of the U.S...
. At that time the boundary between the United States and British Columbia was in dispute, with both countries claiming the San Juan Islands. British and American garrisons were established on San Juan Island. At one point a soldier shot a pig belonging to a partisan of the opposing country, and as a result the otherwise bloodless standoff became known as the Pig War
Pig War
The Pig War was a confrontation in 1859 between the United States and the British Empire over the boundary between the US and British North America. The territory in dispute was the San Juan Islands, which lie between Vancouver Island and the North American mainland...
. Steamboats in the area received contracts from both countries to move troops and supplies to the islands in connection with the dispute. Once Enterprise was repaired, Tom Wright postponed his plans to move the vessel to the Chehalis to take advantage of the increase in business, making a run on August 1, 1859 from Victoria to San Juan Island carrying passengers.
Completed transfer to Chehalis River
Following the San Juan Island trip, Tom Wright was finally able to get Enterprise around Cape Flattery and south to Grays Harbor and the Chehalis River. Wright's plan had been to earn huge freight rates and passenger fares from what he had thought would be the booming population in the Chehalis valley , Wright worked Enterprise to the head of navigation on the Chehalis, sinking three times on the way. When he finally arrived at the headwaters, Wright found not a booming population ready to pay lots of money for steamboat service, but only five farmers who offered to sell Wright a few eggs, butter and vegetables for fifty dollars. Disgusted with the situation, Wright tied up the Enterprise and returned to Puget Sound.By the spring of 1860, Wright was able to arrange a government contract to transport troops down the Chehalis River to Grays Harbor, and so was able to recoup some of his losses. Once the government contract work expired, there was no further business in the Grays Harbor area. Unable to move the lightly built vessel again on the open ocean, Wright dismantled Enterprise at Grays Harbor, with the machinery being shipped to China.
Further reading
- Faber, Jim, Steamer's Wake -- Voyaging down the old marine highways of Puget Sound, British Columbia, and the Columbia River, Enetai Press, Seattle, WA 1985 ISBN 0-9615811-0-7
- Newell, Gordon R., and Williamson, Joe, Pacific Steamboats, Bonanza Books, New York, NY (1958)

