
Environmental issues with energy
Encyclopedia
Energy industry
The energy industry is the totality of all of the industries involved in the production and sale of energy, including fuel extraction, manufacturing, refining and distribution...
is diverse. Energy
Energy
In physics, energy is an indirectly observed quantity. It is often understood as the ability a physical system has to do work on other physical systems...
has been harnessed by humans for millennia. Initially it was with the use of fire
Fire
Fire is the rapid oxidation of a material in the chemical process of combustion, releasing heat, light, and various reaction products. Slower oxidative processes like rusting or digestion are not included by this definition....
for light, heat, cooking and for safety, and its use can be traced back at least 1.9 million years.
In recent years there has been a trend towards the increased commercialization of various renewable energy sources
Renewable energy commercialization
Renewable energy commercialization involves the deployment of three generations of renewable energy technologies dating back more than 100 years. First-generation technologies, which are already mature and economically competitive, include biomass, hydroelectricity, geothermal power and heat...
.
In the real world of consumption of fossil fuel resources which lead to global warming
Global warming
Global warming refers to the rising average temperature of Earth's atmosphere and oceans and its projected continuation. In the last 100 years, Earth's average surface temperature increased by about with about two thirds of the increase occurring over just the last three decades...
and climate change however little change is being made in many parts of the world. Chinese oil demand for instance, is projected to grow nearly 20% in the next six years, and that country already imports over half of the 8 Moilbbl/d it uses. If the peak oil
Peak oil
Peak oil is the point in time when the maximum rate of global petroleum extraction is reached, after which the rate of production enters terminal decline. This concept is based on the observed production rates of individual oil wells, projected reserves and the combined production rate of a field...
theory proves out, more explorations of viable alternative energy sources, could be more friendly to the environment.
Rapidly advancing technologies can achieve a transition of energy generation, water and waste management, and food production towards better environmental and energy usage practices using methods of systems ecology
Systems ecology
Systems ecology is an interdisciplinary field of ecology, taking a holistic approach to the study of ecological systems, especially ecosystems. Systems ecology can be seen as an application of general systems theory to ecology. Central to the systems ecology approach is the idea that an ecosystem...
and industrial ecology
Industrial ecology
Industrial Ecology is the study of material and energy flows through industrial systems. The global industrial economy can be modeled as a network of industrial processes that extract resources from the Earth and transform those resources into commodities which can be bought and sold to meet the...
.
Climate change
Global warmingGlobal warming
Global warming refers to the rising average temperature of Earth's atmosphere and oceans and its projected continuation. In the last 100 years, Earth's average surface temperature increased by about with about two thirds of the increase occurring over just the last three decades...
and climate change
Climate change
Climate change is a significant and lasting change in the statistical distribution of weather patterns over periods ranging from decades to millions of years. It may be a change in average weather conditions or the distribution of events around that average...
due to human activity is generally accepted as being caused by anthropogenic greenhouse gas
Greenhouse gas
A greenhouse gas is a gas in an atmosphere that absorbs and emits radiation within the thermal infrared range. This process is the fundamental cause of the greenhouse effect. The primary greenhouse gases in the Earth's atmosphere are water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and ozone...
emissions. The majority of greenhouses gas emissions are due to burning fossil fuel
Fossil fuel
Fossil fuels are fuels formed by natural processes such as anaerobic decomposition of buried dead organisms. The age of the organisms and their resulting fossil fuels is typically millions of years, and sometimes exceeds 650 million years...
s with most of the rest due to deforestation
Deforestation
Deforestation is the removal of a forest or stand of trees where the land is thereafter converted to a nonforest use. Examples of deforestation include conversion of forestland to farms, ranches, or urban use....
.
There is a highly publicized denial of climate change
Climate change denial
Climate change denial is a term used to describe organized attempts to downplay, deny or dismiss the scientific consensus on the extent of global warming, its significance, and its connection to human behavior, especially for commercial or ideological reasons...
but the vast majority of scientists working in climatology accept that it is due to human activity. The IPCC report Climate Change 2007: Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability predicts that climate change will cause shortages of food and water and increased risk of flooding that will affect billions of people, particularly those living in poverty.
Biofuel use
BiofuelBiofuel
Biofuel is a type of fuel whose energy is derived from biological carbon fixation. Biofuels include fuels derived from biomass conversion, as well as solid biomass, liquid fuels and various biogases...
is defined as solid, liquid or gaseous fuel obtained from relatively recently lifeless or living biological material and is different from fossil fuels, which are derived from long dead biological material. Also, various plants and plant-derived materials are used for biofuel manufacturing.
Bio fuels are a renewable energy
Renewable energy
Renewable energy is energy which comes from natural resources such as sunlight, wind, rain, tides, and geothermal heat, which are renewable . About 16% of global final energy consumption comes from renewables, with 10% coming from traditional biomass, which is mainly used for heating, and 3.4% from...
and can be sustainable (carbon neutral
Carbon neutral
Carbon neutrality, or having a net zero carbon footprint, refers to achieving net zero carbon emissions by balancing a measured amount of carbon released with an equivalent amount sequestered or offset, or buying enough carbon credits to make up the difference...
) in terms of greenhouse gas emissions since they are in the carbon cycle
Carbon cycle
The carbon cycle is the biogeochemical cycle by which carbon is exchanged among the biosphere, pedosphere, geosphere, hydrosphere, and atmosphere of the Earth...
for the short term.
Bio-diesel
High use of bio-diesel leads to land use changes including deforestationDeforestation
Deforestation is the removal of a forest or stand of trees where the land is thereafter converted to a nonforest use. Examples of deforestation include conversion of forestland to farms, ranches, or urban use....
.
Firewood
Unsustainable firewoodFirewood
Firewood is any wood-like material that is gathered and used for fuel. Generally, firewood is not highly processed and is in some sort of recognizable log or branch form....
harvesting can lead to loss of biodiversity
Biodiversity
Biodiversity is the degree of variation of life forms within a given ecosystem, biome, or an entire planet. Biodiversity is a measure of the health of ecosystems. Biodiversity is in part a function of climate. In terrestrial habitats, tropical regions are typically rich whereas polar regions...
and erosion
Erosion
Erosion is when materials are removed from the surface and changed into something else. It only works by hydraulic actions and transport of solids in the natural environment, and leads to the deposition of these materials elsewhere...
due to loss of forest cover. An example of this is a 40 year study done by the University of Leeds
University of Leeds
The University of Leeds is a British Redbrick university located in the city of Leeds, West Yorkshire, England...
of African forests, which account for a third of the world's total tropical forest which demonstrates that Africa
Africa
Africa is the world's second largest and second most populous continent, after Asia. At about 30.2 million km² including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of the Earth's total surface area and 20.4% of the total land area...
is a significant carbon sink. A climate change
Climate change
Climate change is a significant and lasting change in the statistical distribution of weather patterns over periods ranging from decades to millions of years. It may be a change in average weather conditions or the distribution of events around that average...
expert, Lee White states that "To get an idea of the value of the sink, the removal of nearly 5 billion tonnes of carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a naturally occurring chemical compound composed of two oxygen atoms covalently bonded to a single carbon atom...
from the atmosphere by intact tropical forests is at issue.
According to the U.N. the continent is losing forest twice as fast as the rest of the world. "Once upon a time, Africa boasted seven million square kilometers of forest but a third of that has been lost, most of it to charcoal
Charcoal
Charcoal is the dark grey residue consisting of carbon, and any remaining ash, obtained by removing water and other volatile constituents from animal and vegetation substances. Charcoal is usually produced by slow pyrolysis, the heating of wood or other substances in the absence of oxygen...
."
Fossil fuel use
The three fossil fuelFossil fuel
Fossil fuels are fuels formed by natural processes such as anaerobic decomposition of buried dead organisms. The age of the organisms and their resulting fossil fuels is typically millions of years, and sometimes exceeds 650 million years...
types are coal
Coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock usually occurring in rock strata in layers or veins called coal beds or coal seams. The harder forms, such as anthracite coal, can be regarded as metamorphic rock because of later exposure to elevated temperature and pressure...
, petroleum
Petroleum
Petroleum or crude oil is a naturally occurring, flammable liquid consisting of a complex mixture of hydrocarbons of various molecular weights and other liquid organic compounds, that are found in geologic formations beneath the Earth's surface. Petroleum is recovered mostly through oil drilling...
and natural gas
Natural gas
Natural gas is a naturally occurring gas mixture consisting primarily of methane, typically with 0–20% higher hydrocarbons . It is found associated with other hydrocarbon fuel, in coal beds, as methane clathrates, and is an important fuel source and a major feedstock for fertilizers.Most natural...
. It was estimated by the Energy Information Administration
Energy Information Administration
The U.S. Energy Information Administration is the statistical and analytical agency within the U.S. Department of Energy. EIA collects, analyzes, and disseminates independent and impartial energy information to promote sound policymaking, efficient markets, and public understanding of energy and...
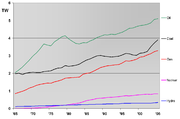
that in 2006 primary sources of energy consisted of petroleum 36.8%, coal 26.6%, natural gas 22.9%, amounting to an 86% share for fossil fuels in primary energy production in the world.
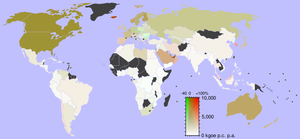
The burning of fossil fuels produces around 21.3 billion tonnes (21.3 gigatonnes) of carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a naturally occurring chemical compound composed of two oxygen atoms covalently bonded to a single carbon atom...
per year, but it is estimated that natural processes can only absorb about half of that amount, so there is a net increase of 10.65 billion tonnes of atmospheric carbon dioxide per year (one tonne of atmospheric carbon is equivalent to 44/12 or 3.7 tonnes of carbon). Carbon dioxide is one of the greenhouse gas
Greenhouse gas
A greenhouse gas is a gas in an atmosphere that absorbs and emits radiation within the thermal infrared range. This process is the fundamental cause of the greenhouse effect. The primary greenhouse gases in the Earth's atmosphere are water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and ozone...
es that enhances radiative forcing
Radiative forcing
In climate science, radiative forcing is generally defined as the change in net irradiance between different layers of the atmosphere. Typically, radiative forcing is quantified at the tropopause in units of watts per square meter. A positive forcing tends to warm the system, while a negative...
and contributes to global warming
Global warming
Global warming refers to the rising average temperature of Earth's atmosphere and oceans and its projected continuation. In the last 100 years, Earth's average surface temperature increased by about with about two thirds of the increase occurring over just the last three decades...
, causing the average surface temperature
Instrumental temperature record
The instrumental temperature record shows fluctuations of the temperature of the global land surface and oceans. This data is collected from several thousand meteorological stations, Antarctic research stations and satellite observations of sea-surface temperature. Currently, the longest-running...
of the Earth to rise in response, which climate scientists
Scientific opinion on climate change
The predominant scientific opinion on climate change is that the Earth is in an ongoing phase of global warming primarily caused by an enhanced greenhouse effect due to the anthropogenic release of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases...
agree will cause major adverse effects
Effects of global warming
This article is about the effects of global warming and climate change. The effects, or impacts, of climate change may be physical, ecological, social or economic. Evidence of observed climate change includes the instrumental temperature record, rising sea levels, and decreased snow cover in the...
.
Coal
The environmental impact of coal mining and burning is diverse. Legislation passed by the U.S. Congress in 1990 required the United States Environmental Protection AgencyUnited States Environmental Protection Agency
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency is an agency of the federal government of the United States charged with protecting human health and the environment, by writing and enforcing regulations based on laws passed by Congress...
(EPA) to issue a plan to alleviate toxic pollution from coal-fired power plants. After delay and litigation, the EPA now has a court-imposed deadline of March 16, 2011, to issue its report.
Petroleum

Petroleum
Petroleum or crude oil is a naturally occurring, flammable liquid consisting of a complex mixture of hydrocarbons of various molecular weights and other liquid organic compounds, that are found in geologic formations beneath the Earth's surface. Petroleum is recovered mostly through oil drilling...
is often negative because it is toxic to almost all forms of life. The possibility of climate change
Climate change
Climate change is a significant and lasting change in the statistical distribution of weather patterns over periods ranging from decades to millions of years. It may be a change in average weather conditions or the distribution of events around that average...
exists. Petroleum, commonly referred to as oil, is closely linked to virtually all aspects of present society, especially for transportation and heating for both homes and for commercial activities.
Gas
Natural gasNatural gas
Natural gas is a naturally occurring gas mixture consisting primarily of methane, typically with 0–20% higher hydrocarbons . It is found associated with other hydrocarbon fuel, in coal beds, as methane clathrates, and is an important fuel source and a major feedstock for fertilizers.Most natural...
is often described as the cleanest fossil fuel, producing less carbon dioxide per joule delivered than either coal or oil., and far fewer pollutants than other fossil fuels. However, in absolute terms it does contribute substantially to global carbon emissions, and this contribution is projected to grow. According to the IPCC Fourth Assessment Report
IPCC Fourth Assessment Report
Climate Change 2007, the Fourth Assessment Report of the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change , is the fourth in a series of reports intended to assess scientific, technical and socio-economic information concerning climate change, its potential effects, and options for...
, in 2004 natural gas produced about 5,300 Mt/yr of CO2 emissions, while coal and oil produced 10,600 and 10,200 respectively (Figure 4.4); but by 2030, according to an updated version of the SRES B2 emissions scenario, natural gas would be the source of 11,000 Mt/yr, with coal and oil now 8,400 and 17,200 respectively. (Total global emissions for 2004 were estimated at over 27,200 Mt.)
In addition, natural gas itself is a greenhouse gas far more potent than carbon dioxide when released into the atmosphere but is released in smaller amounts.
Electricity generation
The environmental impact of electricity generation is significant because modern society uses large amounts of electrical power. This power is normally generatedElectricity generation
Electricity generation is the process of generating electric energy from other forms of energy.The fundamental principles of electricity generation were discovered during the 1820s and early 1830s by the British scientist Michael Faraday...
at power plants that convert some other kind of energy into electrical power. Each such system has advantages and disadvantages, but many of them pose environmental concerns.
Reservoirs
The environmental impact of reservoirs is coming under ever increasing scrutiny as the world demand for water and energy increases and the number and size of reservoirs increases. DamDam
A dam is a barrier that impounds water or underground streams. Dams generally serve the primary purpose of retaining water, while other structures such as floodgates or levees are used to manage or prevent water flow into specific land regions. Hydropower and pumped-storage hydroelectricity are...
s and the reservoir
Reservoir
A reservoir , artificial lake or dam is used to store water.Reservoirs may be created in river valleys by the construction of a dam or may be built by excavation in the ground or by conventional construction techniques such as brickwork or cast concrete.The term reservoir may also be used to...
s can be used to supply drinking water
Drinking water
Drinking water or potable water is water pure enough to be consumed or used with low risk of immediate or long term harm. In most developed countries, the water supplied to households, commerce and industry is all of drinking water standard, even though only a very small proportion is actually...
, generate hydroelectric power, increasing the water supply for irrigation
Irrigation
Irrigation may be defined as the science of artificial application of water to the land or soil. It is used to assist in the growing of agricultural crops, maintenance of landscapes, and revegetation of disturbed soils in dry areas and during periods of inadequate rainfall...
, provide recreational opportunities and to improve certain aspects of the environment. However, adverse environmental and sociological impacts have also been identified during and after many reservoir constructions. Whether reservoir projects are ultimately beneficial or detrimental—to both the environment and surrounding human populations— has been debated since the 1960s and probably long before that. In 1960 the construction of Llyn Celyn
Llyn Celyn
Llyn Celyn is a large reservoir constructed between 1960 and 1965 in the valley of the River Tryweryn in Gwynedd, North Wales. It measures roughly 2½ miles long by a mile wide, and has a maximum depth of...
and the flooding of Capel Celyn
Capel Celyn
Capel Celyn was a rural community to the north west of Bala in Gwynedd, north Wales, in the Afon Tryweryn valley. The village and other parts of the valley were flooded to create a reservoir, Llyn Celyn, in order to supply Liverpool and The Wirral with water for industry...
provoked political uproar which continues to this day. More recently, the construction of Three Gorges Dam
Three Gorges Dam
The Three Gorges Dam is a hydroelectric dam that spans the Yangtze River by the town of Sandouping, located in the Yiling District of Yichang, in Hubei province, China...
and other similar projects throughout Asia
Asia
Asia is the world's largest and most populous continent, located primarily in the eastern and northern hemispheres. It covers 8.7% of the Earth's total surface area and with approximately 3.879 billion people, it hosts 60% of the world's current human population...
, Africa
Africa
Africa is the world's second largest and second most populous continent, after Asia. At about 30.2 million km² including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of the Earth's total surface area and 20.4% of the total land area...
and Latin America
Latin America
Latin America is a region of the Americas where Romance languages – particularly Spanish and Portuguese, and variably French – are primarily spoken. Latin America has an area of approximately 21,069,500 km² , almost 3.9% of the Earth's surface or 14.1% of its land surface area...
have generated considerable environmental and political debate.
Nuclear power

Nuclear power
Nuclear power is the use of sustained nuclear fission to generate heat and electricity. Nuclear power plants provide about 6% of the world's energy and 13–14% of the world's electricity, with the U.S., France, and Japan together accounting for about 50% of nuclear generated electricity...
results from the nuclear fuel cycle
Nuclear fuel cycle
The nuclear fuel cycle, also called nuclear fuel chain, is the progression of nuclear fuel through a series of differing stages. It consists of steps in the front end, which are the preparation of the fuel, steps in the service period in which the fuel is used during reactor operation, and steps in...
, operation, and the effects of accidents such as the Chernobyl disaster
Chernobyl disaster
The Chernobyl disaster was a nuclear accident that occurred on 26 April 1986 at the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant in Ukraine , which was under the direct jurisdiction of the central authorities in Moscow...
(1986) and Fukushima I nuclear accidents (2011).
Wind power
Compared to the environmental effects of traditional energy sources, the environmental effects of wind power are relatively minor. Wind powerWind power
Wind power is the conversion of wind energy into a useful form of energy, such as using wind turbines to make electricity, windmills for mechanical power, windpumps for water pumping or drainage, or sails to propel ships....
consumes no fuel, and emits no air pollution
Air pollution
Air pollution is the introduction of chemicals, particulate matter, or biological materials that cause harm or discomfort to humans or other living organisms, or cause damage to the natural environment or built environment, into the atmosphere....
, unlike fossil fuel power sources. The energy consumed to manufacture and transport the materials used to build a wind power plant is equal to the new energy produced by the plant within a few months. While a wind farm may cover a large area of land, many land uses such as agriculture are compatible, with only small areas of turbine foundations and infrastructure made unavailable for use.
Energy conservation
Energy conservation refers to efforts made to reduce energy consumption. Energy conservation can be achieved through increased efficient energy useEfficient energy use
Efficient energy use, sometimes simply called energy efficiency, is the goal of efforts to reduce the amount of energy required to provide products and services. For example, insulating a home allows a building to use less heating and cooling energy to achieve and maintain a comfortable temperature...
, in conjunction with decreased energy consumption
World energy resources and consumption
]World energy consumption in 2010: over 5% growthEnergy markets have combined crisis recovery and strong industry dynamism. Energy consumption in the G20 soared by more than 5% in 2010, after the slight decrease of 2009. This strong increase is the result of two converging trends...
and/or reduced consumption from conventional energy sources.
Energy conservation can result in increased financial capital
Financial capital
Financial capital can refer to money used by entrepreneurs and businesses to buy what they need to make their products or provide their services or to that sector of the economy based on its operation, i.e. retail, corporate, investment banking, etc....
, environmental
Natural environment
The natural environment encompasses all living and non-living things occurring naturally on Earth or some region thereof. It is an environment that encompasses the interaction of all living species....
quality, national security
National security
National security is the requirement to maintain the survival of the state through the use of economic, diplomacy, power projection and political power. The concept developed mostly in the United States of America after World War II...
, personal security, and human comfort
Thermal comfort
Thermal comfort is a term used by the American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers, an international body. It is defined as the state of mind in humans that expresses satisfaction with the surrounding environment...
. Individuals and organizations that are direct consumers
Consumer
Consumer is a broad label for any individuals or households that use goods generated within the economy. The concept of a consumer occurs in different contexts, so that the usage and significance of the term may vary.-Economics and marketing:...
of energy choose to conserve energy to reduce energy costs and promote economic security
Economic security
Economic security or financial security is the condition of having stable income or other resources to support a standard of living now and in the foreseeable future...
. Industrial and commercial users can increase energy use efficiency to maximize profit
Profit (economics)
In economics, the term profit has two related but distinct meanings. Normal profit represents the total opportunity costs of a venture to an entrepreneur or investor, whilst economic profit In economics, the term profit has two related but distinct meanings. Normal profit represents the total...
.
Energy policy
Energy policy is the manner in which a given entity (often governmental) has decided to address issues of energy developmentEnergy development
Energy development is the effort to provide sufficient primary energy sources and secondary energy forms for supply, cost, impact on air pollution and water pollution, mitigation of climate change with renewable energy....
including energy production, distribution
Resource distribution
Resource distribution refers to the distribution of resources, including land, water, minerals, fuel and wealth in general among corresponding geographic entities .-Unequal resource distribution:...
and consumption
Consumption (economics)
Consumption is a common concept in economics, and gives rise to derived concepts such as consumer debt. Generally, consumption is defined in part by comparison to production. But the precise definition can vary because different schools of economists define production quite differently...
. The attributes of energy policy may include legislation
Legislation
Legislation is law which has been promulgated by a legislature or other governing body, or the process of making it...
, international treaties, incentives to investment, guidelines for energy conservation
Energy conservation
Energy conservation refers to efforts made to reduce energy consumption. Energy conservation can be achieved through increased efficient energy use, in conjunction with decreased energy consumption and/or reduced consumption from conventional energy sources...
, tax
Tax
To tax is to impose a financial charge or other levy upon a taxpayer by a state or the functional equivalent of a state such that failure to pay is punishable by law. Taxes are also imposed by many subnational entities...
ation and other public policy techniques.
Sustainable energy
Sustainable energy is the provision of energyEnergy
In physics, energy is an indirectly observed quantity. It is often understood as the ability a physical system has to do work on other physical systems...
that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their needs. Sustainable
Sustainability
Sustainability is the capacity to endure. For humans, sustainability is the long-term maintenance of well being, which has environmental, economic, and social dimensions, and encompasses the concept of union, an interdependent relationship and mutual responsible position with all living and non...
energy sources are most often regarded as including all renewable energy
Renewable energy
Renewable energy is energy which comes from natural resources such as sunlight, wind, rain, tides, and geothermal heat, which are renewable . About 16% of global final energy consumption comes from renewables, with 10% coming from traditional biomass, which is mainly used for heating, and 3.4% from...
sources, such as hydroelectricity
Hydroelectricity
Hydroelectricity is the term referring to electricity generated by hydropower; the production of electrical power through the use of the gravitational force of falling or flowing water. It is the most widely used form of renewable energy...
, solar energy, wind energy
Wind energy
Wind energy is the kinetic energy of air in motion; see also wind power.Total wind energy flowing through an imaginary area A during the time t is:E = ½ m v2 = ½ v 2...
, wave power
Wave power
Wave power is the transport of energy by ocean surface waves, and the capture of that energy to do useful work — for example, electricity generation, water desalination, or the pumping of water...
, geothermal energy, bioenergy
Bioenergy
Bioenergy is renewable energy made available from materials derived from biological sources. Biomass is any organic material which has stored sunlight in the form of chemical energy. As a fuel it may include wood, wood waste, straw, manure, sugarcane, and many other byproducts from a variety of...
, and tidal power
Tidal power
Tidal power, also called tidal energy, is a form of hydropower that converts the energy of tides into useful forms of power - mainly electricity....
. It usually also includes technologies that improve energy efficiency
Efficient energy use
Efficient energy use, sometimes simply called energy efficiency, is the goal of efforts to reduce the amount of energy required to provide products and services. For example, insulating a home allows a building to use less heating and cooling energy to achieve and maintain a comfortable temperature...
.
Economic instruments
Various economic instruments can be used to steer society toward sustainable energy. Some of these methods include ecotaxes and emissions tradingEmissions trading
Emissions trading is a market-based approach used to control pollution by providing economic incentives for achieving reductions in the emissions of pollutants....
.
Ecological economics
Ecological economics
Image:Sustainable development.svg|right|The three pillars of sustainability. Clickable.|275px|thumbpoly 138 194 148 219 164 240 182 257 219 277 263 291 261 311 264 331 272 351 283 366 300 383 316 394 287 408 261 417 224 424 182 426 154 423 119 415 87 403 58 385 40 368 24 347 17 328 13 309 16 286 26...
aims to address some of the interdependence and coevolution of human economies
Economy
An economy consists of the economic system of a country or other area; the labor, capital and land resources; and the manufacturing, trade, distribution, and consumption of goods and services of that area...
and natural ecosystem
Ecosystem
An ecosystem is a biological environment consisting of all the organisms living in a particular area, as well as all the nonliving , physical components of the environment with which the organisms interact, such as air, soil, water and sunlight....
s over time and space. Environmental economics
Environmental economics
Environmental economics is a subfield of economics concerned with environmental issues. Quoting from the National Bureau of Economic Research Environmental Economics program:...
, is the mainstream economic
Mainstream economics
Mainstream economics is a loose term used to refer to widely-accepted economics as taught in prominent universities and in contrast to heterodox economics...
analysis of the environment, which views the economy
Economy
An economy consists of the economic system of a country or other area; the labor, capital and land resources; and the manufacturing, trade, distribution, and consumption of goods and services of that area...
as a subsystem of the ecosystem, while ecological economics emphasis is upon preserving natural capital
Natural capital
Natural capital is the extension of the economic notion of capital to goods and services relating to the natural environment. Natural capital is thus the stock of natural ecosystems that yields a flow of valuable ecosystem goods or services into the future...
.
Biophysical economics sometimes referred to as thermoeconomics is discussed in the field of ecological economics
Ecological economics
Image:Sustainable development.svg|right|The three pillars of sustainability. Clickable.|275px|thumbpoly 138 194 148 219 164 240 182 257 219 277 263 291 261 311 264 331 272 351 283 366 300 383 316 394 287 408 261 417 224 424 182 426 154 423 119 415 87 403 58 385 40 368 24 347 17 328 13 309 16 286 26...
and relates directly to energy conversion
Energy conversion
Transforming energy is when the energy changes into another form.In physics, the term energy describes the capacity to produce changes within a system, without regard to limitations in transformation imposed by entropy...
, which itself is related to the fields of sustainability
Sustainability
Sustainability is the capacity to endure. For humans, sustainability is the long-term maintenance of well being, which has environmental, economic, and social dimensions, and encompasses the concept of union, an interdependent relationship and mutual responsible position with all living and non...
and sustainable development
Sustainable development
Sustainable development is a pattern of resource use, that aims to meet human needs while preserving the environment so that these needs can be met not only in the present, but also for generations to come...
especially in the area of carbon
Carbon
Carbon is the chemical element with symbol C and atomic number 6. As a member of group 14 on the periodic table, it is nonmetallic and tetravalent—making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds...
burning.
See also
- List of environmental issues
- EnergyEnergyIn physics, energy is an indirectly observed quantity. It is often understood as the ability a physical system has to do work on other physical systems...
- Energy economicsEnergy economicsEnergy economics is a broad scientific subject area which includes topics related to supply and use of energy in societies. Due to diversity of issues and methods applied and shared with a number of academic disciplines, energy economics does not present itself as a self contained academic...
- Energy accountingEnergy accountingEnergy accounting is a system used within industry, where measuring and analyzing the energy consumption of different activities is done to improve energy efficiency.-Energy management:...
- Energy transformation
- EnergeticsEnergeticsEnergetics is the study of energy under transformation. Because energy flows at all scales, from the quantum level to the biosphere and cosmos, energetics is a very broad discipline, encompassing for example thermodynamics, chemistry, biological energetics, biochemistry and ecological energetics...
- Energy qualityEnergy qualityEnergy quality is the contrast between different forms of energy, the different trophic levels in ecological systems and the propensity of energy to convert from one form to another. The concept refers to the empirical experience of the characteristics, or qualia, of different energy forms as they...
- Ecological energeticsEcological energeticsEcological energetics is the quantitative study of the flow of energy through ecological systems. It aims to uncover the principles which describe the propensity of such energy flows through the trophic, or 'energy availing' levels of ecological networks. In systems ecology the principles of...
- Systems ecologySystems ecologySystems ecology is an interdisciplinary field of ecology, taking a holistic approach to the study of ecological systems, especially ecosystems. Systems ecology can be seen as an application of general systems theory to ecology. Central to the systems ecology approach is the idea that an ecosystem...
- ThermoeconomicsThermoeconomicsThermoeconomics, also referred to as biophysical economics, is a school of heterodox economics that applies the laws of thermodynamics to economic theory. The term "thermoeconomics" was coined in 1962 by American engineer Myron Tribus, and developed by the statistician and economist Nicholas...
- Industrial ecologyIndustrial ecologyIndustrial Ecology is the study of material and energy flows through industrial systems. The global industrial economy can be modeled as a network of industrial processes that extract resources from the Earth and transform those resources into commodities which can be bought and sold to meet the...
- Index of energy articlesIndex of energy articlesThis is a index of energy articles.-A:Alternative energy- Alternative energy indexes- American Museum of Science and Energy - Anisotropy energy-E:Ecological energetics- Electric potential energy- Energy- Energy accounting...
- Energy and EnvironmentEnergy and EnvironmentEnergy & Environment is a peer-reviewed academic journal aimed at natural scientists, technologists, and the international social science and policy communities covering the direct and indirect environmental impacts of energy acquisition, transport, production and use. Its editor-in-chief since...
- Environmental impact of aviation
- The Venus ProjectThe Venus ProjectThe Venus Project is an organization that advocates the futurist visions of the American Jacque Fresco, with the aim of improving society with a global sustainable social design that it calls a "resource-based economy"...
External links
- United Nations Development Programme - Environment and Energy for Sustainable Development

