
Epipubic bones
Encyclopedia
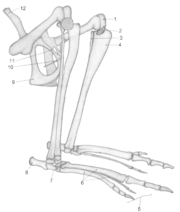
Pelvis
In human anatomy, the pelvis is the lower part of the trunk, between the abdomen and the lower limbs .The pelvis includes several structures:...
of modern marsupials and of some fossil mammals: multituberculates, monotreme
Monotreme
Monotremes are mammals that lay eggs instead of giving birth to live young like marsupials and placental mammals...
s, and even basal
Basal (phylogenetics)
In phylogenetics, a basal clade is the earliest clade to branch in a larger clade; it appears at the base of a cladogram.A basal group forms an outgroup to the rest of the clade, such as in the following example:...
eutheria
Eutheria
Eutheria is a group of mammals consisting of placental mammals plus all extinct mammals that are more closely related to living placentals than to living marsupials . They are distinguished from noneutherians by various features of the feet, ankles, jaws and teeth...
ns (the ancestors of placental
Eutheria
Eutheria is a group of mammals consisting of placental mammals plus all extinct mammals that are more closely related to living placentals than to living marsupials . They are distinguished from noneutherians by various features of the feet, ankles, jaws and teeth...
mammals).
In modern marsupials the epipubic bones are often called "marsupial bones" because they support the mother's pouch ("marsupium" is Latin for "pouch"), but their presence on other groups of mammals indicates that this was not their original function, which some researchers think was to assist locomotion by supporting some of the muscles that flex
Flexion
In anatomy, flexion is a position that is made possible by the joint angle decreasing. The skeletal and muscular systems work together to move the joint into a "flexed" position. For example the elbow is flexed when the hand is brought closer to the shoulder...
the thigh.
The epipubic bones were first described in 1698 but their functions have remained unresolved. It has been suggested that they form part of a kinetic linkage stretching from the femur on one side to the ribs on the opposite side. This linkage is formed by a series of muscles: each epipubic bone is connected to the femur by the pectineus muscle
Pectineus muscle
The pectineus muscle is a flat, quadrangular muscle, situated at the anterior part of the upper and medial aspect of the thigh....
, and to the ribs and vertebrae by the pyramidalis
Pyramidalis muscle
The pyramidalis is a small and triangular muscle, anterior to the Rectus abdominis, and contained in the rectus sheath.-Attachments and actions:...
, rectus abdominis
Rectus abdominis muscle
The rectus abdominis muscle, also known as the "six pack", is a paired muscle running vertically on each side of the anterior wall of the human abdomen . There are two parallel muscles, separated by a midline band of connective tissue called the linea alba...
, and external
Abdominal external oblique muscle
The external oblique muscle is the largest and the most superficial of the three flat muscles of the lateral anterior abdomen.-Structure:...
and internal obliques
Abdominal internal oblique muscle
The internal oblique muscle is the intermediate muscle of the abdomen, lying just underneath the external oblique and just above the transverse abdominal muscle.-Structure:...
. The epipubic bones act as levers to stiffen the trunk.
See also
- Evolution of mammalsEvolution of mammals__FORCETOC__The evolution of mammals within the synapsid lineage was a gradual process that took approximately 70 million years, beginning in the mid-Permian. By the mid-Triassic, there were many species that looked like mammals, and the first true mammals appeared in the early Jurassic...
- Obturator processObturator processThe obturator process is an anatomical feature on the pelvis of archosaurs. It is a raised area of the ischium bone of the pelvis. It is the origin of muscles that attach to the femur and aid in running. These muscles are called M. pubo-ischio-femoralis externus 1 and 2 in crocodylians. In birds...
- Proximodorsal processProximodorsal processThe proximodorsal process is a feature of the skeleton of archosaurs. It may be a pair of tabs or blade - shaped flanges on the pelvis, and serves as an anchor point for the attachment of leg muscles. This process is of particular importance in the anatomy and comparative morphology of Mesozoic...

