Epsilon Scuti
Encyclopedia
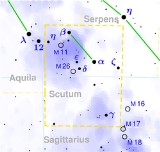
Epsilon Scuti is a star system
in the constellation
Scutum
. It is approximately 523 light years
from Earth
.
The primary component, Epsilon Scuti A, is a yellow G-type
bright giant
with an apparent magnitude
of +4.88. It has at least three faint companions, two 14th magnitude stars, B and D, separated from the primary by 13.6 and 15.4 arcseconds respectively, and the 13th magnitude C, which is 38 arcseconds away.
Star system
A star system or stellar system is a small number of stars which orbit each other, bound by gravitational attraction. A large number of stars bound by gravitation is generally called a star cluster or galaxy, although, broadly speaking, they are also star systems.-Binary star systems:A stellar...
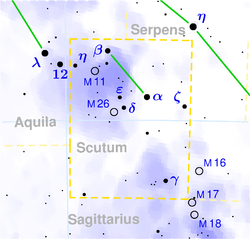
in the constellation
Constellation
In modern astronomy, a constellation is an internationally defined area of the celestial sphere. These areas are grouped around asterisms, patterns formed by prominent stars within apparent proximity to one another on Earth's night sky....
Scutum
Scutum
Scutum is a small constellation introduced in the seventeenth century. Its name is Latin for shield.-History:Scutum is the only constellation that owes its name to a non-classical historical figure...
. It is approximately 523 light years
Light Years
Light Years is the seventh studio album by Australian recording artist Kylie Minogue. It was released on 25 September 2000 by Parlophone and Mushroom Records. The album's style was indicative of her return to "mainstream pop dance tunes"....
from Earth
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun, and the densest and fifth-largest of the eight planets in the Solar System. It is also the largest of the Solar System's four terrestrial planets...
.
The primary component, Epsilon Scuti A, is a yellow G-type
Stellar classification
In astronomy, stellar classification is a classification of stars based on their spectral characteristics. The spectral class of a star is a designated class of a star describing the ionization of its chromosphere, what atomic excitations are most prominent in the light, giving an objective measure...
bright giant
Bright giant
The luminosity class II in the Yerkes spectral classification is given to bright giants. These are stars which straddle the boundary between giants and supergiants, and the classification is in general given to giant stars with exceptionally high luminosity, but which are not sufficiently bright...
with an apparent magnitude
Apparent magnitude
The apparent magnitude of a celestial body is a measure of its brightness as seen by an observer on Earth, adjusted to the value it would have in the absence of the atmosphere...
of +4.88. It has at least three faint companions, two 14th magnitude stars, B and D, separated from the primary by 13.6 and 15.4 arcseconds respectively, and the 13th magnitude C, which is 38 arcseconds away.


