.gif)
Erosion (dental)
Encyclopedia
Acid erosion, also known as dental erosion, is the irreversible loss of tooth structure due to chemical dissolution by acids not of bacteria
l origin. Dental erosion is the most common chronic disease of children ages 5–17, although it is only relatively recently that it has been recognised as a dental health problem. There is generally widespread ignorance of the damaging effects of acid erosion; this is particularly the case with erosion due to fruit juices, because they tend to be seen as healthy. Erosion is found initially in the enamel
and, if unchecked, may proceed to the underlying dentin
.
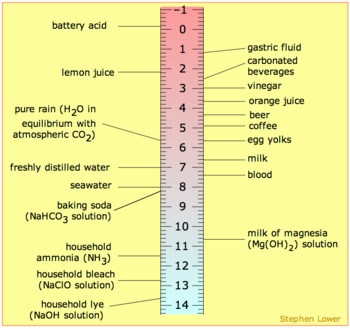 The most common cause of erosion is by acidic foods and drinks. In general, foods and drinks with a pH
The most common cause of erosion is by acidic foods and drinks. In general, foods and drinks with a pH
below 5.0–5.7 have been known to trigger dental erosion effects. Numerous clinical and laboratory reports link erosion to excessive consumption of drinks. Those thought to pose a risk are soft drinks and fruit drinks, fruit juices such as orange juice
(which contain citric acid
) and carbonated drinks
such as cola
s (in which the carbonic acid
is not the cause of erosion, but citric and phosphoric acid
). Additionally, wine
has been shown to erode teeth, with the pH of wine as low as 3.0–3.8. Other possible sources of erosive acids are from exposure to chlorinated
swimming pool
water, and regurgitation of gastric acid
s.
Saliva
acts as a buffer, regulating the pH when acidic drinks are ingested. Drinks vary in their resistance to the buffering effect of saliva. Studies show that fruit juices are the most resistant to saliva's buffering effect, followed by, in order: fruit-based carbonated drinks and flavoured mineral waters, non-fruit-based carbonated drinks, sparkling mineral waters; Mineral water
being the least resistant. Because of this, fruit juices in particular, may prolong the drop in pH levels.
A number of medications such as vitamin C, aspirin and some iron preparations are acidic and may contribute towards acid erosion.
from the stomach comes into contact with the teeth. People with diseases such as anorexia nervosa
, bulimia, and gastroesophageal reflux disease
often suffer from this. GERD is quite common and an average of 7% of adults experience reflux daily. The main cause of GERD is increased acid production by the stomach.
and attrition
. Abrasion is most often caused by brushing teeth too hard.
Throthing or swishing acidic drinks around the mouth increases the risk of acid erosion.
restorations in the mouth may be clean and non-tarnished. Fillings may also appear to be rising out of the tooth, the appearance being caused when the tooth is eroded away leaving only the filling. The teeth may form divots on the chewing surfaces when dental erosion is occurring. This mainly happens on the first, second, and third molars. One of the most severe signs of dental erosion is cracking, where teeth begin to crack off and become coarse. Other signs include pain when eating hot, cold, or sweet foods. This pain is due to the enamel having been eroded away, exposing the sensitive dentin.
Bacteria
Bacteria are a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria have a wide range of shapes, ranging from spheres to rods and spirals...
l origin. Dental erosion is the most common chronic disease of children ages 5–17, although it is only relatively recently that it has been recognised as a dental health problem. There is generally widespread ignorance of the damaging effects of acid erosion; this is particularly the case with erosion due to fruit juices, because they tend to be seen as healthy. Erosion is found initially in the enamel
Tooth enamel
Tooth enamel, along with dentin, cementum, and dental pulp is one of the four major tissues that make up the tooth in vertebrates. It is the hardest and most highly mineralized substance in the human body. Tooth enamel is also found in the dermal denticles of sharks...
and, if unchecked, may proceed to the underlying dentin
Dentin
Dentine is a calcified tissue of the body, and along with enamel, cementum, and pulp is one of the four major components of teeth. Usually, it is covered by enamel on the crown and cementum on the root and surrounds the entire pulp...
.

PH
In chemistry, pH is a measure of the acidity or basicity of an aqueous solution. Pure water is said to be neutral, with a pH close to 7.0 at . Solutions with a pH less than 7 are said to be acidic and solutions with a pH greater than 7 are basic or alkaline...
below 5.0–5.7 have been known to trigger dental erosion effects. Numerous clinical and laboratory reports link erosion to excessive consumption of drinks. Those thought to pose a risk are soft drinks and fruit drinks, fruit juices such as orange juice
Orange juice
Orange juice is a popular beverage made from oranges. It is made by extraction from the fresh fruit, by desiccation and subsequent reconstitution of dried juice, or by concentration of the juice and the subsequent addition of water to the concentrate...
(which contain citric acid
Citric acid
Citric acid is a weak organic acid. It is a natural preservative/conservative and is also used to add an acidic, or sour, taste to foods and soft drinks...
) and carbonated drinks
Soft drink
A soft drink is a non-alcoholic beverage that typically contains water , a sweetener, and a flavoring agent...
such as cola
Cola
Cola is a carbonated beverage that was typically flavored by the kola nut as well as vanilla and other flavorings, however, some colas are now flavored artificially. It became popular worldwide after druggist John Pemberton invented Coca-Cola in 1886...
s (in which the carbonic acid
Carbonic acid
Carbonic acid is the inorganic compound with the formula H2CO3 . It is also a name sometimes given to solutions of carbon dioxide in water, because such solutions contain small amounts of H2CO3. Carbonic acid forms two kinds of salts, the carbonates and the bicarbonates...
is not the cause of erosion, but citric and phosphoric acid
Phosphoric acid
Phosphoric acid, also known as orthophosphoric acid or phosphoric acid, is a mineral acid having the chemical formula H3PO4. Orthophosphoric acid molecules can combine with themselves to form a variety of compounds which are also referred to as phosphoric acids, but in a more general way...
). Additionally, wine
Wine
Wine is an alcoholic beverage, made of fermented fruit juice, usually from grapes. The natural chemical balance of grapes lets them ferment without the addition of sugars, acids, enzymes, or other nutrients. Grape wine is produced by fermenting crushed grapes using various types of yeast. Yeast...
has been shown to erode teeth, with the pH of wine as low as 3.0–3.8. Other possible sources of erosive acids are from exposure to chlorinated
Chlorine
Chlorine is the chemical element with atomic number 17 and symbol Cl. It is the second lightest halogen, found in the periodic table in group 17. The element forms diatomic molecules under standard conditions, called dichlorine...
swimming pool
Swimming pool
A swimming pool, swimming bath, wading pool, or simply a pool, is a container filled with water intended for swimming or water-based recreation. There are many standard sizes; the largest is the Olympic-size swimming pool...
water, and regurgitation of gastric acid
Gastric acid
Gastric acid is a digestive fluid, formed in the stomach. It has a pH of 1 to 2 and is composed of hydrochloric acid , and large quantities of potassium chloride and sodium chloride...
s.
Extrinsic acidic sources
Acidic drinks and foods lower the pH level of the mouth so consuming them causes the teeth to demineralise. Drinks low in pH levels that cause dental erosion include fruit juices, sports drinks, and carbonated drinks. Orange and apple juices are common culprits among fruit juices. Carbonated drinks such as colas, lemonades are also very acidic, as are fruit-flavoured drinks and dilutables. Frequency rather than total intake of acidic juices is seen as the greater factor in dental erosion; infants using feeding bottles containing fruit juices (especially when used as a comforter) are therefore at greater risk of acid erosion.Saliva
Saliva
Saliva , referred to in various contexts as spit, spittle, drivel, drool, or slobber, is the watery substance produced in the mouths of humans and most other animals. Saliva is a component of oral fluid. In mammals, saliva is produced in and secreted from the three pairs of major salivary glands,...
acts as a buffer, regulating the pH when acidic drinks are ingested. Drinks vary in their resistance to the buffering effect of saliva. Studies show that fruit juices are the most resistant to saliva's buffering effect, followed by, in order: fruit-based carbonated drinks and flavoured mineral waters, non-fruit-based carbonated drinks, sparkling mineral waters; Mineral water
Mineral water
Mineral water is water containing minerals or other dissolved substances that alter its taste or give it therapeutic value, generally obtained from a naturally occurring mineral spring or source. Dissolved substances in the water may include various salts and sulfur compounds...
being the least resistant. Because of this, fruit juices in particular, may prolong the drop in pH levels.
A number of medications such as vitamin C, aspirin and some iron preparations are acidic and may contribute towards acid erosion.
Intrinsic acidic sources
Dental erosion can occur by non-extrinsic factors too. Intrinsic dental erosion is known as perimolysis, whereby gastric acidGastric acid
Gastric acid is a digestive fluid, formed in the stomach. It has a pH of 1 to 2 and is composed of hydrochloric acid , and large quantities of potassium chloride and sodium chloride...
from the stomach comes into contact with the teeth. People with diseases such as anorexia nervosa
Anorexia nervosa
Anorexia nervosa is an eating disorder characterized by refusal to maintain a healthy body weight and an obsessive fear of gaining weight. Although commonly called "anorexia", that term on its own denotes any symptomatic loss of appetite and is not strictly accurate...
, bulimia, and gastroesophageal reflux disease
Gastroesophageal reflux disease
Gastroesophageal reflux disease , gastro-oesophageal reflux disease , gastric reflux disease, or acid reflux disease is chronic symptoms or mucosal damage caused by stomach acid coming up from the stomach into the esophagus...
often suffer from this. GERD is quite common and an average of 7% of adults experience reflux daily. The main cause of GERD is increased acid production by the stomach.
Behaviour
Acid erosion often coexists with abrasionAbrasion (dental)
Abrasion is the loss of tooth structure by mechanical forces from a foreign element. If this force begins at the cementoenamel junction, then progression of tooth loss can be rapid since enamel is very thin in this region of the tooth...
and attrition
Attrition (dental)
Attrition is the loss of teeth structure by mechanical forces from opposing teeth. Attrition initially affects the enamel and, if unchecked, may proceed to the underlying dentin. Once past the enamel, attrition quickly destroys the softer dentin. Erosion is a very important contributing factor to...
. Abrasion is most often caused by brushing teeth too hard.
Throthing or swishing acidic drinks around the mouth increases the risk of acid erosion.
Signs
There are many signs of dental erosion, including changes in appearance and sensitivity. One of the physical changes can be the color of teeth. There are two different colors teeth may turn if dental erosion is occurring, the first being a change of color that usually happens on the cutting edge of the central incisors. This causes the cutting edge of the tooth to become transparent. A second sign is if the tooth has a yellowish tint. This occurs because the white enamel has eroded away to reveal the yellowish dentin. A change in shape of the teeth is also a sign of dental erosion. Teeth will begin to appear with a broad rounded concavity, and the gaps between teeth will become larger. There can be evidence of wear on surfaces of teeth not expected to be in contact with one another. If dental erosion occurs in children, a loss of enamel surface characteristics can occur. AmalgamAmalgam (dentistry)
Amalgam is an alloy containing mercury. The term is commonly used for the amalgam employed as material for dental fillings, which consists of mercury , silver , tin , copper , and other trace metals...
restorations in the mouth may be clean and non-tarnished. Fillings may also appear to be rising out of the tooth, the appearance being caused when the tooth is eroded away leaving only the filling. The teeth may form divots on the chewing surfaces when dental erosion is occurring. This mainly happens on the first, second, and third molars. One of the most severe signs of dental erosion is cracking, where teeth begin to crack off and become coarse. Other signs include pain when eating hot, cold, or sweet foods. This pain is due to the enamel having been eroded away, exposing the sensitive dentin.
Prevention and management
Preventive and management strategies include the following:- Treating the underlying medical disorder or disease.
- Modifying the pH of the food or beverage contributing to the problem, or changing lifestyle to avoid the food or beverage.
- Decrease abrasive forces. Use a soft bristled toothbrush and brush gently. No brushing immediately after consuming acidic food and drink as teeth will be softened. Leave at least half an hour of time space. Rinsing with water is better than brushing after consuming acidic foods and drinks.
- Drinking through a straw
- Using a remineralizingRemineralisation of teethRemineralisation of teeth is a process in which minerals are returned to the molecular structure of the tooth itself. Teeth are porous allowing fluids and demineralisation beneath the surface of the tooth. When demineralised, these pores become larger...
agent, such as sodium fluorideSodium fluorideSodium fluoride is an inorganic chemical compound with the formula NaF. A colorless solid, it is a source of the fluoride ion in diverse applications. Sodium fluoride is less expensive and less hygroscopic than the related salt potassium fluoride....
solution in the form of a fluoride mouthrinse, tablet, or lozenge, immediately before brushing teeth. - Applying fluoride gels or varnishes to the teeth.
- Drinking milk or using other dairy products.
- Using a neutralizing agent such as antacid tablets.
- Dentine bonding agents applied to areas of exposed dentin
See also
- AbrasionAbrasion (dental)Abrasion is the loss of tooth structure by mechanical forces from a foreign element. If this force begins at the cementoenamel junction, then progression of tooth loss can be rapid since enamel is very thin in this region of the tooth...
- AbfractionAbfractionAbfraction is the loss of tooth structure from flexural forces. It is hypothesized that enamel, especially at the cementoenamel junction , undergo this pattern of destruction by separating the enamel rods....
- AttritionAttrition (dental)Attrition is the loss of teeth structure by mechanical forces from opposing teeth. Attrition initially affects the enamel and, if unchecked, may proceed to the underlying dentin. Once past the enamel, attrition quickly destroys the softer dentin. Erosion is a very important contributing factor to...
- BruxismBruxismBruxism is characterized by the grinding of the teeth and typically includes the clenching of the jaw. It is an oral parafunctional activity that occurs in most humans at some time in their lives. In most people, bruxism is mild enough not to be a health problem...
External links
Further reading
- Adrian Lussi. Dental Erosion: From Diagnosis to Therapy. Karger Publishers, 2006. (ISBN 9783805580977)

