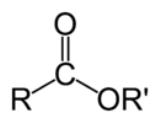
Ester
Overview
Chemical compound
A chemical compound is a pure chemical substance consisting of two or more different chemical elements that can be separated into simpler substances by chemical reactions. Chemical compounds have a unique and defined chemical structure; they consist of a fixed ratio of atoms that are held together...
s derived by reacting an oxoacid
Oxoacid
An oxoacid is an acid that contains oxygen. To be more specific, it is an acid that:#contains oxygen#contains at least one other element#has at least one hydrogen atom bound to oxygen#forms an ion by the loss of one or more protons....
with a hydroxyl
Hydroxyl
A hydroxyl is a chemical group containing an oxygen atom covalently bonded with a hydrogen atom. In inorganic chemistry, the hydroxyl group is known as the hydroxide ion, and scientists and reference works generally use these different terms though they refer to the same chemical structure in...
compound such as an alcohol
Alcohol
In chemistry, an alcohol is an organic compound in which the hydroxy functional group is bound to a carbon atom. In particular, this carbon center should be saturated, having single bonds to three other atoms....
or phenol
Phenols
In organic chemistry, phenols, sometimes called phenolics, are a class of chemical compounds consisting of a hydroxyl group bonded directly to an aromatic hydrocarbon group...
. Esters are usually derived from an inorganic acid or organic acid
Organic acid
An organic acid is an organic compound with acidic properties. The most common organic acids are the carboxylic acids, whose acidity is associated with their carboxyl group –COOH. Sulfonic acids, containing the group –SO2OH, are relatively stronger acids. The relative stability of the conjugate...
in which at least one -OH (hydroxyl) group is replaced by an -O-alkyl (alkoxy) group, and most commonly from carboxylic acid
Carboxylic acid
Carboxylic acids are organic acids characterized by the presence of at least one carboxyl group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is R-COOH, where R is some monovalent functional group...
s and alcohol
Alcohol
In chemistry, an alcohol is an organic compound in which the hydroxy functional group is bound to a carbon atom. In particular, this carbon center should be saturated, having single bonds to three other atoms....
s. That is, esters are formed by condensing
Condensation reaction
A condensation reaction is a chemical reaction in which two molecules or moieties combine to form one single molecule, together with the loss of a small molecule. When this small molecule is water, it is known as a dehydration reaction; other possible small molecules lost are hydrogen chloride,...
an acid with an alcohol.
Esters are ubiquitous. Most naturally occurring fats and oils are the fatty acid
Fatty acid
In chemistry, especially biochemistry, a fatty acid is a carboxylic acid with a long unbranched aliphatic tail , which is either saturated or unsaturated. Most naturally occurring fatty acids have a chain of an even number of carbon atoms, from 4 to 28. Fatty acids are usually derived from...
esters of glycerol
Glycerol
Glycerol is a simple polyol compound. It is a colorless, odorless, viscous liquid that is widely used in pharmaceutical formulations. Glycerol has three hydroxyl groups that are responsible for its solubility in water and its hygroscopic nature. The glycerol backbone is central to all lipids...
.
Unanswered Questions
Discussions

