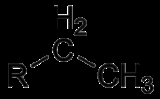
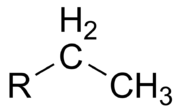
Ethyl group
Encyclopedia
Chemistry
Chemistry is the science of matter, especially its chemical reactions, but also its composition, structure and properties. Chemistry is concerned with atoms and their interactions with other atoms, and particularly with the properties of chemical bonds....
, an ethyl group is an alkyl substituent
Substituent
In organic chemistry and biochemistry, a substituent is an atom or group of atoms substituted in place of a hydrogen atom on the parent chain of a hydrocarbon...
derived from ethane
Ethane
Ethane is a chemical compound with chemical formula C2H6. It is the only two-carbon alkane that is an aliphatic hydrocarbon. At standard temperature and pressure, ethane is a colorless, odorless gas....
(C
Carbon
Carbon is the chemical element with symbol C and atomic number 6. As a member of group 14 on the periodic table, it is nonmetallic and tetravalent—making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds...
2H
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly...
6). It has the formula
Chemical formula
A chemical formula or molecular formula is a way of expressing information about the atoms that constitute a particular chemical compound....
-C
Carbon
Carbon is the chemical element with symbol C and atomic number 6. As a member of group 14 on the periodic table, it is nonmetallic and tetravalent—making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds...
2H
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly...
5 and is very often abbreviated -Et.
Ethylation is the formation of a compound by introduction of the ethyl functional group, C
Carbon
Carbon is the chemical element with symbol C and atomic number 6. As a member of group 14 on the periodic table, it is nonmetallic and tetravalent—making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds...
2H
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly...
5.
Etymology
The name of the group is derived from the AetherAether (mythology)
Aether , in Greek mythology, is one of the Protogenoi, the first-born elementals. He is the personification of the upper sky, space, and heaven, and is the elemental god of the "Bright, Glowing, Upper Air." He is the pure upper air that the gods breathe, as opposed to the normal air that mortals...
, the first-born Greek elemental god of air, and "hyle
Hyle
In philosophy, hyle refers to matter or stuff. It can also be the material cause underlying a change in Aristotelian philosophy. The Greeks originally had no word for matter in general, as opposed to raw material suitable for some specific purpose or other, so Aristotle adapted the word for...
", referring to "stuff".
Ethyl is the IUPAC nomenclature of organic chemistry
IUPAC nomenclature of organic chemistry
The IUPAC nomenclature of organic chemistry is a systematic method of naming organic chemical compounds as recommended by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry . Ideally, every possible organic compound should have a name from which an unambiguous structural formula can be drawn. ...
term for an alkane
Alkane
Alkanes are chemical compounds that consist only of hydrogen and carbon atoms and are bonded exclusively by single bonds without any cycles...
(or alkyl) molecule, using the prefix "eth-" to indicate the presence of two carbon atoms in the molecule.

