European Communities
Encyclopedia
The European Communities (sometimes referred to as the European Community or EC) were three international organisations that were governed by the same set of institutions
. These were the European Coal and Steel Community
(ECSC), the European Economic Community
(EEC) and the European Atomic Energy Community
(EAEC or Euratom).
They shared the same governing institutions (those of the EEC) from 1967 until those institutions became those of the European Union
(EU). The European Communities operated as the largest of the EU's three pillars
until the EEC (renamed the European Community in 1993) was absorbed when the pillar system was abolished. The ECSC expired in 2002 but Euratom remains as a distinct entity, the only one of the three communities to exist beyond 2009.
, Belgium
, France
, Germany
, Italy
, Luxembourg
and the Netherlands
came together to sign the Treaty of Paris
in 1951 which established the Community. The success of this Community led to the desire to create more, but attempts at creating a European Defence Community
and a European Political Community
failed leading to a return to economic matters. In 1957, the EAEC and EEC were created by the Treaties of Rome. They were to share some of the institutions of the ECSC but have separate executive structures.
The ECSC's aim was to combine the coal
and steel
industries of its members to create a single market in those resources. It was intended that this would increase prosperity and decrease the risk of these countries going to war through the process of European integration
. The EAEC was working on nuclear energy
co-operation between the members. The EEC was to create a customs union
and general economic co-operation. It later led to the creation of a European single market.
The EEC became the European Community pillar of the EU
, with the ECSC and EAEC continuing in a similar subordinate position, existing separately in a legal sense but governed by the institutions of the EU as if they were its own. The ECSC's treaty had a 50 year limit and thus expired in 2002, all its activities are now absorbed into the European Community. The EAEC had no such limit and thus continues to exist. Due to the sensitive nature of nuclear power
with the European electorate, the treaty has gone without amendment since its signing and was not even to be changed with the European Constitution
intended to repeal all other treaties (the Constitution's replacement, the Treaty of Lisbon
, likewise makes no attempt at amendment).
As the EAEC has a low profile, and the profile of the European Community is dwarfed by that of the EU, the term "European Communities" sees little usage. However, when the EU was established the institutions that dealt solely or mainly with the European Community (as opposed to all three pillars) retained their original names, for example the formal name of the European Court of Justice was the "Court of Justice of the European Communities".
In 1967, the Merger Treaty
combined these separate executives. The Commission and Council of the EEC were to take over the responsibilities of its counterparts in the other organisations. From then on they became known collectively as the "European Communities", for example the Commission was known as the "Commission of the European Communities", although the communities themselves remained separate in legal terms.
built upon the Single European Act
and the Solemn Declaration on European Union
in the creation of the European Union
. The treaty was signed on 7 February 1992 and came into force on 1 November 1993. The Union superseded and absorbed the European Communities as one of its three pillars
. The first Commission President
following the creation of the EU was Jacques Delors
, who briefly continued his previous EEC tenure before handing over to Jacques Santer in 1994. Only the European Communities, the Economic Community, the European Coal and Steel Community
and Euratom however had legal personalities.
Only the first pillar followed the principles of supranationalism. The pillar structure
of the EU allowed the areas of European co-operation to be increased without leaders handing a large amount of power to supranational institutions. The pillar system segregated the EU. What were formerly the competencies of the EEC fell within the European Community pillar. Justice and Home Affairs
was introduced as a new pillar while European Political Cooperation
became the second pillar (the Common Foreign and Security Policy
).
The Community institutions became the institutions of the EU but the roles of the institutions between the pillars are different. The Commission, Parliament and Court of Justice are largely cut out of activities in the second and third pillars, with the Council dominating proceedings. This is reflected in the names of the institutions, the Council is formally the "Council of the European Union" while the Commission is formally the "Commission of the European Communities". This allowed the new areas to be based on intergovernmental
ism (unanimous agreement between government
s) rather than majority voting and independent institutions according to supranational democracy.
However, after the Treaty of Maastricht, Parliament gained a much bigger role. Maastricht brought in the codecision procedure, which gave it equal legislative power with the Council on Community matters. Hence, with the greater powers of the supranational institutions and the operation of Qualified Majority Voting in the Council, the Community pillar could be described as a far more federal
method of decision making.
The Treaty of Amsterdam transferred responsibility for free movement of persons (e.g. visas
, illegal immigration
, asylum
) from the Justice and Home Affairs (JHA) pillar to the European Community (JHA was renamed Police and Judicial Co-operation in Criminal Matters
(PJCC) as a result). Both Amsterdam and the Treaty of Nice
also extended codecision procedure to nearly all policy areas, giving Parliament equal power to the Council in the Community.
In 2002, the Treaty of Paris
which established the European Coal and Steel Community
(one of the three communities which comprised the European Communities) expired, having reached its 50 year limit (as the first treaty, it was the only one with a limit). No attempt was made to renew its mandate; instead, the Treaty of Nice
transferred certain of its elements to the Treaty of Rome
and hence its work continued as part of the EEC area of the Community's remit.
After the entry into force of the Treaty of Lisbon
, the pillar structure ceased to exist, abolishing the European Communities. The legal personality of the European Community was transferred to the newly consolidated EU, although Euratom remained distinct. This was originally proposed under the European Constitution
but that treaty failed ratification in 2005.
, all three Communities were governed by the same institutional framework. Prior to 1967, the Common Assembly/European Parliamentary Assembly
and the Court of Justice
, established by the ECSC, were already shared with the EEC and EAEC, but they had different executives. The 1967 treaty gave the Council and Commission of the EEC responsibility over ECSC and EAEC affairs, abolishing the Councils of the ECSC and EAEC, the Commission of the EAEC and the High Authority of the ECSC
. These governed the three Communities till the establishment of the European Union in 1993.
" (the "outer seven" were those countries who formed the European Free Trade Association
). The six founding countries were France
, West Germany
, Italy
and the three Benelux
countries: Belgium
, the Netherlands
and Luxembourg
. The first enlargement was in 1973, with the accession of Denmark
, Ireland
and the United Kingdom
. Greece
, Spain
and Portugal
joined in the 1980s. Following the creation of the EU in 1993, it has enlarged to include a further fifteen countries by 2007.
Member states are represented in some form in each institution. The Council
is also composed of one national minister who represents their national government
. Each state also has a right to one European Commissioner
each, although in the European Commission
they are not supposed to represent their national interest but that of the Community. Prior to 2004, the larger members (France, Germany, Italy and the United Kingdom) have had two Commissioners. In the European Parliament
, members are allocated a set number seats
related to their population, however these (since 1979
) have been directly elected and they sit according to political allegiance, not national origin. Most other institutions, including the European Court of Justice
, have some form of national division of its members.
Institutions of the European Union
The European Union is governed by seven institutions. Article 13 of Treaty on European Union lists them in the following order: the European Parliament, the European Council, the Council of the European Union, the European Commission, the Court of Justice of the European Union, the European...
. These were the European Coal and Steel Community
European Coal and Steel Community
The European Coal and Steel Community was a six-nation international organisation serving to unify Western Europe during the Cold War and create the foundation for the modern-day developments of the European Union...
(ECSC), the European Economic Community
European Economic Community
The European Economic Community The European Economic Community (EEC) The European Economic Community (EEC) (also known as the Common Market in the English-speaking world, renamed the European Community (EC) in 1993The information in this article primarily covers the EEC's time as an independent...
(EEC) and the European Atomic Energy Community
European Atomic Energy Community
The European Atomic Energy Community is an international organisation which is legally distinct from the European Union , but has the same membership, and is governed by the EU's institutions....
(EAEC or Euratom).
They shared the same governing institutions (those of the EEC) from 1967 until those institutions became those of the European Union
European Union
The European Union is an economic and political union of 27 independent member states which are located primarily in Europe. The EU traces its origins from the European Coal and Steel Community and the European Economic Community , formed by six countries in 1958...
(EU). The European Communities operated as the largest of the EU's three pillars
Three pillars of the European Union
Between 1993 and 2009, the European Union legally consisted of three pillars. This structure was introduced with the Treaty of Maastricht on 1 November 1993, and was eventually abandoned on 1 December 2009 with the entry into force of the Treaty of Lisbon, when the EU obtained a consolidated legal...
until the EEC (renamed the European Community in 1993) was absorbed when the pillar system was abolished. The ECSC expired in 2002 but Euratom remains as a distinct entity, the only one of the three communities to exist beyond 2009.
Three communities
The ECSC was created first. Following its proposal in 1950 in the Schuman DeclarationSchuman Declaration
The Schuman Declaration of 9 May 1950 was a governmental proposal by then-French Foreign Minister Robert Schuman to create a new form of organization of States in Europe called a supranational Community. Following the experiences of two world wars, France recognized that certain values such as...
, Belgium
Belgium
Belgium , officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a federal state in Western Europe. It is a founding member of the European Union and hosts the EU's headquarters, and those of several other major international organisations such as NATO.Belgium is also a member of, or affiliated to, many...
, France
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
, Germany
Germany
Germany , officially the Federal Republic of Germany , is a federal parliamentary republic in Europe. The country consists of 16 states while the capital and largest city is Berlin. Germany covers an area of 357,021 km2 and has a largely temperate seasonal climate...
, Italy
Italy
Italy , officially the Italian Republic languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Italy's official name is as follows:;;;;;;;;), is a unitary parliamentary republic in South-Central Europe. To the north it borders France, Switzerland, Austria and...
, Luxembourg
Luxembourg
Luxembourg , officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg , is a landlocked country in western Europe, bordered by Belgium, France, and Germany. It has two principal regions: the Oesling in the North as part of the Ardennes massif, and the Gutland in the south...
and the Netherlands
Netherlands
The Netherlands is a constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, located mainly in North-West Europe and with several islands in the Caribbean. Mainland Netherlands borders the North Sea to the north and west, Belgium to the south, and Germany to the east, and shares maritime borders...
came together to sign the Treaty of Paris
Treaty of Paris (1951)
The Treaty of Paris was signed on 18 April 1951 between France, West Germany, Italy and the three Benelux countries , establishing the European Coal and Steel Community , which subsequently became part of the European Union...
in 1951 which established the Community. The success of this Community led to the desire to create more, but attempts at creating a European Defence Community
European Defence Community
The European Defense Community was a plan proposed in 1950 by René Pleven, the French President of the Council , in response to the American call for the rearmament of West Germany...
and a European Political Community
European Political Community
The European Political Community was proposed in 1952 as a combination of the existing European Coal and Steel Community and the proposed European Defence Community...
failed leading to a return to economic matters. In 1957, the EAEC and EEC were created by the Treaties of Rome. They were to share some of the institutions of the ECSC but have separate executive structures.
The ECSC's aim was to combine the coal
Coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock usually occurring in rock strata in layers or veins called coal beds or coal seams. The harder forms, such as anthracite coal, can be regarded as metamorphic rock because of later exposure to elevated temperature and pressure...
and steel
Steel
Steel is an alloy that consists mostly of iron and has a carbon content between 0.2% and 2.1% by weight, depending on the grade. Carbon is the most common alloying material for iron, but various other alloying elements are used, such as manganese, chromium, vanadium, and tungsten...
industries of its members to create a single market in those resources. It was intended that this would increase prosperity and decrease the risk of these countries going to war through the process of European integration
European integration
European integration is the process of industrial, political, legal, economic integration of states wholly or partially in Europe...
. The EAEC was working on nuclear energy
Nuclear power
Nuclear power is the use of sustained nuclear fission to generate heat and electricity. Nuclear power plants provide about 6% of the world's energy and 13–14% of the world's electricity, with the U.S., France, and Japan together accounting for about 50% of nuclear generated electricity...
co-operation between the members. The EEC was to create a customs union
Customs union
A customs union is a type of trade bloc which is composed of a free trade area with a common external tariff. The participant countries set up common external trade policy, but in some cases they use different import quotas...
and general economic co-operation. It later led to the creation of a European single market.
The EEC became the European Community pillar of the EU
Three pillars of the European Union
Between 1993 and 2009, the European Union legally consisted of three pillars. This structure was introduced with the Treaty of Maastricht on 1 November 1993, and was eventually abandoned on 1 December 2009 with the entry into force of the Treaty of Lisbon, when the EU obtained a consolidated legal...
, with the ECSC and EAEC continuing in a similar subordinate position, existing separately in a legal sense but governed by the institutions of the EU as if they were its own. The ECSC's treaty had a 50 year limit and thus expired in 2002, all its activities are now absorbed into the European Community. The EAEC had no such limit and thus continues to exist. Due to the sensitive nature of nuclear power
Nuclear power
Nuclear power is the use of sustained nuclear fission to generate heat and electricity. Nuclear power plants provide about 6% of the world's energy and 13–14% of the world's electricity, with the U.S., France, and Japan together accounting for about 50% of nuclear generated electricity...
with the European electorate, the treaty has gone without amendment since its signing and was not even to be changed with the European Constitution
Treaty establishing a Constitution for Europe
The Treaty establishing a Constitution for Europe , , was an unratified international treaty intended to create a consolidated constitution for the European Union...
intended to repeal all other treaties (the Constitution's replacement, the Treaty of Lisbon
Treaty of Lisbon
The Treaty of Lisbon of 1668 was a peace treaty between Portugal and Spain, concluded at Lisbon on 13 February 1668, through the mediation of England, in which Spain recognized the sovereignty of Portugal's new ruling dynasty, the House of Braganza....
, likewise makes no attempt at amendment).
As the EAEC has a low profile, and the profile of the European Community is dwarfed by that of the EU, the term "European Communities" sees little usage. However, when the EU was established the institutions that dealt solely or mainly with the European Community (as opposed to all three pillars) retained their original names, for example the formal name of the European Court of Justice was the "Court of Justice of the European Communities".
In 1967, the Merger Treaty
Merger Treaty
The Merger Treaty was a European treaty which combined the executive bodies of the European Coal and Steel Community , European Atomic Energy Community and the European Economic Community into a single institutional structure.The treaty was signed in Brussels on 8 April 1965 and came into force...
combined these separate executives. The Commission and Council of the EEC were to take over the responsibilities of its counterparts in the other organisations. From then on they became known collectively as the "European Communities", for example the Commission was known as the "Commission of the European Communities", although the communities themselves remained separate in legal terms.
Pillar
The Maastricht TreatyMaastricht Treaty
The Maastricht Treaty was signed on 7 February 1992 by the members of the European Community in Maastricht, Netherlands. On 9–10 December 1991, the same city hosted the European Council which drafted the treaty...
built upon the Single European Act
Single European Act
The Single European Act was the first major revision of the 1957 Treaty of Rome. The Act set the European Community an objective of establishing a Single Market by 31 December 1992, and codified European Political Cooperation, the forerunner of the European Union's Common Foreign and Security Policy...
and the Solemn Declaration on European Union
Solemn Declaration on European Union
The Solemn Declaration on European Union was signed by the then 10 heads of state and government on 19 June 1983, in Stuttgart.In November 1981 the German and Italian Governments submitted to the Member States a draft European Act designed to further European integration...
in the creation of the European Union
European Union
The European Union is an economic and political union of 27 independent member states which are located primarily in Europe. The EU traces its origins from the European Coal and Steel Community and the European Economic Community , formed by six countries in 1958...
. The treaty was signed on 7 February 1992 and came into force on 1 November 1993. The Union superseded and absorbed the European Communities as one of its three pillars
Three pillars of the European Union
Between 1993 and 2009, the European Union legally consisted of three pillars. This structure was introduced with the Treaty of Maastricht on 1 November 1993, and was eventually abandoned on 1 December 2009 with the entry into force of the Treaty of Lisbon, when the EU obtained a consolidated legal...
. The first Commission President
President of the European Commission
The President of the European Commission is the head of the European Commission ― the executive branch of the :European Union ― the most powerful officeholder in the EU. The President is responsible for allocating portfolios to members of the Commission and can reshuffle or dismiss them if needed...
following the creation of the EU was Jacques Delors
Jacques Delors
Jacques Lucien Jean Delors is a French economist and politician, the eighth President of the European Commission and the first person to serve three terms in that office .-French Politics:...
, who briefly continued his previous EEC tenure before handing over to Jacques Santer in 1994. Only the European Communities, the Economic Community, the European Coal and Steel Community
European Coal and Steel Community
The European Coal and Steel Community was a six-nation international organisation serving to unify Western Europe during the Cold War and create the foundation for the modern-day developments of the European Union...
and Euratom however had legal personalities.
Only the first pillar followed the principles of supranationalism. The pillar structure
Three pillars of the European Union
Between 1993 and 2009, the European Union legally consisted of three pillars. This structure was introduced with the Treaty of Maastricht on 1 November 1993, and was eventually abandoned on 1 December 2009 with the entry into force of the Treaty of Lisbon, when the EU obtained a consolidated legal...
of the EU allowed the areas of European co-operation to be increased without leaders handing a large amount of power to supranational institutions. The pillar system segregated the EU. What were formerly the competencies of the EEC fell within the European Community pillar. Justice and Home Affairs
Police and Judicial Co-operation in Criminal Matters
The third of the three pillars of the European Union was Justice and Home Affairs , which was shrunk and renamed Police and Judicial Co-operation in Criminal Matters in 2003. The pillar existed between 1993 and 2009, when it was absorbed into a consolidated EU structure.The pillar focused on...
was introduced as a new pillar while European Political Cooperation
European political cooperation
The European Political Cooperation was introduced in 1970 and was the synonym for European Union foreign policy coordination until it was superseded by the Common Foreign and Security Policy in the Maastricht Treaty ....
became the second pillar (the Common Foreign and Security Policy
Common Foreign and Security Policy
The Common Foreign and Security Policy is the organised, agreed foreign policy of the European Union for mainly security and defence diplomacy and actions. CFSP deals only with a specific part of the EU's external relations, which domains include mainly Trade and Commercial Policy and other areas...
).
The Community institutions became the institutions of the EU but the roles of the institutions between the pillars are different. The Commission, Parliament and Court of Justice are largely cut out of activities in the second and third pillars, with the Council dominating proceedings. This is reflected in the names of the institutions, the Council is formally the "Council of the European Union" while the Commission is formally the "Commission of the European Communities". This allowed the new areas to be based on intergovernmental
Intergovernmental
Intergovernmental can refer to:*Intergovernmentalism*Intergovernmental Risk Pool*Intergovernmental organization...
ism (unanimous agreement between government
Government
Government refers to the legislators, administrators, and arbitrators in the administrative bureaucracy who control a state at a given time, and to the system of government by which they are organized...
s) rather than majority voting and independent institutions according to supranational democracy.
However, after the Treaty of Maastricht, Parliament gained a much bigger role. Maastricht brought in the codecision procedure, which gave it equal legislative power with the Council on Community matters. Hence, with the greater powers of the supranational institutions and the operation of Qualified Majority Voting in the Council, the Community pillar could be described as a far more federal
Federalism
Federalism is a political concept in which a group of members are bound together by covenant with a governing representative head. The term "federalism" is also used to describe a system of the government in which sovereignty is constitutionally divided between a central governing authority and...
method of decision making.
The Treaty of Amsterdam transferred responsibility for free movement of persons (e.g. visas
Visa (document)
A visa is a document showing that a person is authorized to enter the territory for which it was issued, subject to permission of an immigration official at the time of actual entry. The authorization may be a document, but more commonly it is a stamp endorsed in the applicant's passport...
, illegal immigration
Illegal immigration
Illegal immigration is the migration into a nation in violation of the immigration laws of that jurisdiction. Illegal immigration raises many political, economical and social issues and has become a source of major controversy in developed countries and the more successful developing countries.In...
, asylum
Right of asylum
Right of asylum is an ancient juridical notion, under which a person persecuted for political opinions or religious beliefs in his or her own country may be protected by another sovereign authority, a foreign country, or church sanctuaries...
) from the Justice and Home Affairs (JHA) pillar to the European Community (JHA was renamed Police and Judicial Co-operation in Criminal Matters
Police and Judicial Co-operation in Criminal Matters
The third of the three pillars of the European Union was Justice and Home Affairs , which was shrunk and renamed Police and Judicial Co-operation in Criminal Matters in 2003. The pillar existed between 1993 and 2009, when it was absorbed into a consolidated EU structure.The pillar focused on...
(PJCC) as a result). Both Amsterdam and the Treaty of Nice
Treaty of Nice
The Treaty of Nice was signed by European leaders on 26 February 2001 and came into force on 1 February 2003. It amended the Maastricht Treaty and the Treaty of Rome...
also extended codecision procedure to nearly all policy areas, giving Parliament equal power to the Council in the Community.
In 2002, the Treaty of Paris
Treaty of Paris (1951)
The Treaty of Paris was signed on 18 April 1951 between France, West Germany, Italy and the three Benelux countries , establishing the European Coal and Steel Community , which subsequently became part of the European Union...
which established the European Coal and Steel Community
European Coal and Steel Community
The European Coal and Steel Community was a six-nation international organisation serving to unify Western Europe during the Cold War and create the foundation for the modern-day developments of the European Union...
(one of the three communities which comprised the European Communities) expired, having reached its 50 year limit (as the first treaty, it was the only one with a limit). No attempt was made to renew its mandate; instead, the Treaty of Nice
Treaty of Nice
The Treaty of Nice was signed by European leaders on 26 February 2001 and came into force on 1 February 2003. It amended the Maastricht Treaty and the Treaty of Rome...
transferred certain of its elements to the Treaty of Rome
Treaty of Rome
The Treaty of Rome, officially the Treaty establishing the European Economic Community, was an international agreement that led to the founding of the European Economic Community on 1 January 1958. It was signed on 25 March 1957 by Belgium, France, Italy, Luxembourg, the Netherlands and West Germany...
and hence its work continued as part of the EEC area of the Community's remit.
After the entry into force of the Treaty of Lisbon
Treaty of Lisbon
The Treaty of Lisbon of 1668 was a peace treaty between Portugal and Spain, concluded at Lisbon on 13 February 1668, through the mediation of England, in which Spain recognized the sovereignty of Portugal's new ruling dynasty, the House of Braganza....
, the pillar structure ceased to exist, abolishing the European Communities. The legal personality of the European Community was transferred to the newly consolidated EU, although Euratom remained distinct. This was originally proposed under the European Constitution
Treaty establishing a Constitution for Europe
The Treaty establishing a Constitution for Europe , , was an unratified international treaty intended to create a consolidated constitution for the European Union...
but that treaty failed ratification in 2005.
Institutions
By virtue of the Merger TreatyMerger Treaty
The Merger Treaty was a European treaty which combined the executive bodies of the European Coal and Steel Community , European Atomic Energy Community and the European Economic Community into a single institutional structure.The treaty was signed in Brussels on 8 April 1965 and came into force...
, all three Communities were governed by the same institutional framework. Prior to 1967, the Common Assembly/European Parliamentary Assembly
European Parliament
The European Parliament is the directly elected parliamentary institution of the European Union . Together with the Council of the European Union and the Commission, it exercises the legislative function of the EU and it has been described as one of the most powerful legislatures in the world...
and the Court of Justice
European Court of Justice
The Court can sit in plenary session, as a Grand Chamber of 13 judges, or in chambers of three or five judges. Plenary sitting are now very rare, and the court mostly sits in chambers of three or five judges...
, established by the ECSC, were already shared with the EEC and EAEC, but they had different executives. The 1967 treaty gave the Council and Commission of the EEC responsibility over ECSC and EAEC affairs, abolishing the Councils of the ECSC and EAEC, the Commission of the EAEC and the High Authority of the ECSC
High Authority of the European Coal and Steel Community
The High Authority was the executive branch of the former European Coal and Steel Community . It was created in 1951 and disbanded in 1967 when it was merged into the European Commission.-History:...
. These governed the three Communities till the establishment of the European Union in 1993.
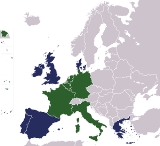
Members
The three Communities shared the same membership, the six states that signed the Treaty of Paris and subsequent treaties were known as the "inner sixInner Six
The Inner Six, or simply The Six, are the six founding member states of the European Communities. This was in contrast to the outer seven who formed the European Free Trade Association rather than be involved in supranational European integration .-History:The inner six are those who responded to...
" (the "outer seven" were those countries who formed the European Free Trade Association
European Free Trade Association
The European Free Trade Association or EFTA is a free trade organisation between four European countries that operates parallel to, and is linked to, the European Union . EFTA was established on 3 May 1960 as a trade bloc-alternative for European states who were either unable to, or chose not to,...
). The six founding countries were France
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
, West Germany
West Germany
West Germany is the common English, but not official, name for the Federal Republic of Germany or FRG in the period between its creation in May 1949 to German reunification on 3 October 1990....
, Italy
Italy
Italy , officially the Italian Republic languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Italy's official name is as follows:;;;;;;;;), is a unitary parliamentary republic in South-Central Europe. To the north it borders France, Switzerland, Austria and...
and the three Benelux
Benelux
The Benelux is an economic union in Western Europe comprising three neighbouring countries, Belgium, the Netherlands, and Luxembourg. These countries are located in northwestern Europe between France and Germany...
countries: Belgium
Belgium
Belgium , officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a federal state in Western Europe. It is a founding member of the European Union and hosts the EU's headquarters, and those of several other major international organisations such as NATO.Belgium is also a member of, or affiliated to, many...
, the Netherlands
Netherlands
The Netherlands is a constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, located mainly in North-West Europe and with several islands in the Caribbean. Mainland Netherlands borders the North Sea to the north and west, Belgium to the south, and Germany to the east, and shares maritime borders...
and Luxembourg
Luxembourg
Luxembourg , officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg , is a landlocked country in western Europe, bordered by Belgium, France, and Germany. It has two principal regions: the Oesling in the North as part of the Ardennes massif, and the Gutland in the south...
. The first enlargement was in 1973, with the accession of Denmark
Denmark
Denmark is a Scandinavian country in Northern Europe. The countries of Denmark and Greenland, as well as the Faroe Islands, constitute the Kingdom of Denmark . It is the southernmost of the Nordic countries, southwest of Sweden and south of Norway, and bordered to the south by Germany. Denmark...
, Ireland
Ireland
Ireland is an island to the northwest of continental Europe. It is the third-largest island in Europe and the twentieth-largest island on Earth...
and the United Kingdom
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
. Greece
Greece
Greece , officially the Hellenic Republic , and historically Hellas or the Republic of Greece in English, is a country in southeastern Europe....
, Spain
Spain
Spain , officially the Kingdom of Spain languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Spain's official name is as follows:;;;;;;), is a country and member state of the European Union located in southwestern Europe on the Iberian Peninsula...
and Portugal
Portugal
Portugal , officially the Portuguese Republic is a country situated in southwestern Europe on the Iberian Peninsula. Portugal is the westernmost country of Europe, and is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the West and South and by Spain to the North and East. The Atlantic archipelagos of the...
joined in the 1980s. Following the creation of the EU in 1993, it has enlarged to include a further fifteen countries by 2007.

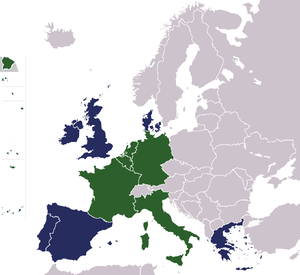
| State Member State of the European Union A member state of the European Union is a state that is party to treaties of the European Union and has thereby undertaken the privileges and obligations that EU membership entails. Unlike membership of an international organisation, being an EU member state places a country under binding laws in... |
Accession |
|---|---|
 Belgium Belgium |
25 March 1957 |
 Italy Italy |
25 March 1957 |
 Luxembourg Luxembourg |
25 March 1957 |
 Early Modern France Early Modern France |
25 March 1957 |
 Netherlands Netherlands |
25 March 1957 |
 West Germany West Germany |
25 March 1957 |
 Denmark Denmark |
1 January 1973 |
 Republic of Ireland Republic of Ireland |
1 January 1973 |
 United Kingdom United Kingdom |
1 January 1973 |
 Greece Greece |
1 January 1981 |
 Portugal Portugal |
1 January 1986 |
 Spain Spain |
1 January 1986 |
Member states are represented in some form in each institution. The Council
Council of the European Union
The Council of the European Union is the institution in the legislature of the European Union representing the executives of member states, the other legislative body being the European Parliament. The Council is composed of twenty-seven national ministers...
is also composed of one national minister who represents their national government
Government
Government refers to the legislators, administrators, and arbitrators in the administrative bureaucracy who control a state at a given time, and to the system of government by which they are organized...
. Each state also has a right to one European Commissioner
European Commissioner
A European Commissioner is a member of the 27-member European Commission. Each Member within the college holds a specific portfolio and are led by the President of the European Commission...
each, although in the European Commission
European Commission
The European Commission is the executive body of the European Union. The body is responsible for proposing legislation, implementing decisions, upholding the Union's treaties and the general day-to-day running of the Union....
they are not supposed to represent their national interest but that of the Community. Prior to 2004, the larger members (France, Germany, Italy and the United Kingdom) have had two Commissioners. In the European Parliament
European Parliament
The European Parliament is the directly elected parliamentary institution of the European Union . Together with the Council of the European Union and the Commission, it exercises the legislative function of the EU and it has been described as one of the most powerful legislatures in the world...
, members are allocated a set number seats
Apportionment in the European Parliament
Apportionment in the European Parliament relates to the distribution of legislative seats in the European Parliament among the states of the European Union...
related to their population, however these (since 1979
European Parliament election, 1979
The 1979 European elections were parliamentary elections held across all 9 European Community member states. They were the first European elections to be held, allowing citizens to elect 410 MEPs to the European Parliament, and also the first international election in history.Seats in the...
) have been directly elected and they sit according to political allegiance, not national origin. Most other institutions, including the European Court of Justice
European Court of Justice
The Court can sit in plenary session, as a Grand Chamber of 13 judges, or in chambers of three or five judges. Plenary sitting are now very rare, and the court mostly sits in chambers of three or five judges...
, have some form of national division of its members.
Policy areas
At the time of its abolition, the Community pillar covered the following areas;
|
Economic and monetary union An economic and monetary union is a type of trade bloc which is composed of an economic union with a monetary union. It is to be distinguished from a mere monetary union , which does not involve a common market. This is the fifth stage of economic integration... Education Education in its broadest, general sense is the means through which the aims and habits of a group of people lives on from one generation to the next. Generally, it occurs through any experience that has a formative effect on the way one thinks, feels, or acts... and Culture Culture Culture is a term that has many different inter-related meanings. For example, in 1952, Alfred Kroeber and Clyde Kluckhohn compiled a list of 164 definitions of "culture" in Culture: A Critical Review of Concepts and Definitions... Environmental law Environmental law is a complex and interlocking body of treaties, conventions, statutes, regulations, and common law that operates to regulate the interaction of humanity and the natural environment, toward the purpose of reducing the impacts of human activity... Employment Employment is a contract between two parties, one being the employer and the other being the employee. An employee may be defined as:- Employee :... Trans-European Networks The Trans-European Networks were created by the European Union by Articles 154-156 of the Treaty of Rome , with the stated goals of the creation of an internal market and the reinforcement of economic and social cohesion... |
International trade International trade is the exchange of capital, goods, and services across international borders or territories. In most countries, such trade represents a significant share of gross domestic product... Research Research can be defined as the scientific search for knowledge, or as any systematic investigation, to establish novel facts, solve new or existing problems, prove new ideas, or develop new theories, usually using a scientific method... Social policy Social policy primarily refers to guidelines, principles, legislation and activities that affect the living conditions conducive to human welfare. Thus, social policy is that part of public policy that has to do with social issues... Right of asylum Right of asylum is an ancient juridical notion, under which a person persecuted for political opinions or religious beliefs in his or her own country may be protected by another sovereign authority, a foreign country, or church sanctuaries... Immigration policy An immigration policy is any policy of a state that deals with the transit of persons across its borders into the country, but especially those that intend to work and to remain in the country. Immigration policies can range from allowing no migration at all to allowing most types of migration,... |
See also
- European CommissionEuropean CommissionThe European Commission is the executive body of the European Union. The body is responsible for proposing legislation, implementing decisions, upholding the Union's treaties and the general day-to-day running of the Union....
- Delors CommissionDelors CommissionThe Delors Commission was the administration of Jacques Delors, the 8th President of the European Commission. Delors presided over the European Commission for three terms The Delors Commission was the administration of Jacques Delors, the 8th President of the European Commission. Delors presided...
- Location of European Union institutionsLocation of European Union institutionsThe governing institutions of the European Union are not concentrated in a single capital city; they are instead spread across three cities with other EU agencies and bodies based further away...
- Brussels and the European UnionBrussels and the European UnionBrussels is considered to be the de facto capital of the European Union, having a long history of hosting the institutions of the European Union within its European Quarter...
- European Institutions in StrasbourgEuropean Institutions in StrasbourgThere are a range of European Institutions in Strasbourg , the oldest of which dates back to 1815. In all, there are more than twenty different institutions based in the Alsatian city...
- European Energy Community
- European Defense Community
- European Political CommunityEuropean Political CommunityThe European Political Community was proposed in 1952 as a combination of the existing European Coal and Steel Community and the proposed European Defence Community...
External links
- European Union website
- Treaty establishing the European Economic Community European NAvigator
- History of the Rome Treaties European NAvigator

