
European Union energy label
Encyclopedia
EU Directive 92/75/EC established an energy consumption
labeling scheme. The directive was implemented by several other directives thus most white goods, light bulb packaging and cars must have an EU Energy Label clearly displayed when offered for sale or rent. The energy efficiency
of the appliance is rated in terms of a set of energy efficiency classes from A to G on the label, A being the most energy efficient, G the least efficient. The labels also give other useful information to the customer as they choose between various models. The information should also be given in catalogues and included by internet retailers on their websites.
In an attempt to keep up with advances in energy efficiency, A+ and A++ grades were later introduced for refrigeration products.
Directive 92/75/EC was replaced by Directive 2010/30/EU which must be applied from 31 July 2011.
Refrigerator
Here is the table that indicates the energy use index, the index is calculated for each appliance according to its consumption and its compartments' volume taking into account the appliance type. The index is thus not calculated in kW·h
.
The label also contains:
For cold appliances (and this product alone), for models that are more economical than those of category A, categories A+ and A++ have been assigned.
The energy label also contains information on:
For tumble dryers the energy efficiency scale is calculated using the cotton drying cycle with a maximum declared load. The energy efficiency index is in kW·h per kilogramme of load. Different scales apply for condenser and vented dryers.
Condenser dryers
Vented dryers
The label also contains:
For combined washer dryers the energy efficiency scale is calculated using the cotton drying cycle with a maximum declared load. The energy efficiency index is in kW·h per kilogramme of load. Different scales apply for condenser and vented dryers.
The label also contains:
Dishwasher
The energy efficiency is calculated according to the number of place settings. For the most common size of appliance, the 12 place setting machine the following classes apply. The unit is expressed in kW·h per 12 place settings.
The label also contains:
Oven
The label also contains:
For air conditioners with heating capability, you will also find:
Note that there exists units with EER and COP > 5, so take a note of the actual number when it is A rated.
According to the lightbulb's electrical consumption relative to a standard (GLS or incandescent), the lightbulb is in one of the following classes:
efficiency rating came into effect early in September 2009.
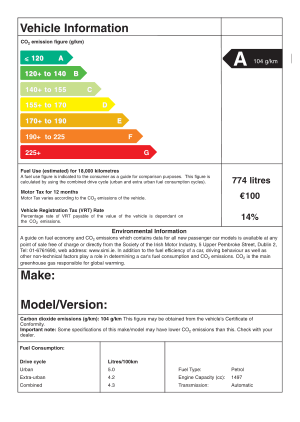 For motor-vehicle it isn't electrical efficiency that is indicated but carbon dioxide
For motor-vehicle it isn't electrical efficiency that is indicated but carbon dioxide
emissions in grammes per kilometre travelled.
Other information that is indexed for the energy label is:
Energy consumption
Energy consumption is the consumption of energy or power. It is covered in the following articles and categories:* World energy consumption* Domestic energy consumption* Fuel efficiency in transportation* Electric energy consumption* Electricity generation...
labeling scheme. The directive was implemented by several other directives thus most white goods, light bulb packaging and cars must have an EU Energy Label clearly displayed when offered for sale or rent. The energy efficiency
Efficient energy use
Efficient energy use, sometimes simply called energy efficiency, is the goal of efforts to reduce the amount of energy required to provide products and services. For example, insulating a home allows a building to use less heating and cooling energy to achieve and maintain a comfortable temperature...
of the appliance is rated in terms of a set of energy efficiency classes from A to G on the label, A being the most energy efficient, G the least efficient. The labels also give other useful information to the customer as they choose between various models. The information should also be given in catalogues and included by internet retailers on their websites.
In an attempt to keep up with advances in energy efficiency, A+ and A++ grades were later introduced for refrigeration products.
Directive 92/75/EC was replaced by Directive 2010/30/EU which must be applied from 31 July 2011.
Labelling
The energy labels are separated into at least four categories:- The appliance's details: according to each appliance, specific details, of the model and its materials
- Energy class: a colour code associated to a letter (from A to G) that gives an idea of the appliance's electrical consumption
- Consumption, efficiency, capacity, etc.: this section gives information according to appliance type
- Noise: the noise emitted by the appliance is described in decibelDecibelThe decibel is a logarithmic unit that indicates the ratio of a physical quantity relative to a specified or implied reference level. A ratio in decibels is ten times the logarithm to base 10 of the ratio of two power quantities...
s
RefrigeratorRefrigeratorA refrigerator is a common household appliance that consists of a thermally insulated compartment and a heat pump that transfers heat from the inside of the fridge to its external environment so that the inside of the fridge is cooled to a temperature below the ambient temperature of the room...
s, freezers and combined appliances
Here is the table that indicates the energy use index, the index is calculated for each appliance according to its consumption and its compartments' volume taking into account the appliance type. The index is thus not calculated in kW·hWatt-hour
The kilowatt hour, or kilowatt-hour, is a unit of energy equal to 1000 watt hours or 3.6 megajoules.For constant power, energy in watt hours is the product of power in watts and time in hours...
.
| A++ | A+ | A | B | C | D | E | F | G |
| <30 | <42 | <55 | <75 | <90 | <100 | <110 | <125 | >125 |
The label also contains:
- the annual energy consumption in kW·h per year
- the capacity of fresh foods in litres for refrigerators and combined appliances
- the capacity of frozen foods in litres for freezers and combined appliances
- the noise in dB(A)A-weightingA Weighting curve is a graph of a set of factors, that are used to 'weight' measured values of a variable according to their importance in relation to some outcome. The most commonly known example is frequency weighting in sound level measurement where a specific set of weighting curves known as A,...
For cold appliances (and this product alone), for models that are more economical than those of category A, categories A+ and A++ have been assigned.
Washing machines, tumble dryers and combined appliances
For washing machines the energy efficiency scale is calculated using a cotton cycle at 60 °C (140 °F) with a maximum declared load. This load is typically 6 kg. The energy efficiency index is in kW·h per kilogramme of washing.| A | B | C | D | E | F | G |
| <0.19 | <0.23 | <0.27 | <0.31 | <0.35 | <0.39 | >0.39 |
The energy label also contains information on:
- total consumption per cycle
- washing performance – with a class from A to G
- spin drying performance – with a class from A to G
- maximum spin speed
- the total cotton capacity in kg
- water consumption per cycle in litres
- noise in the washing and spinning cycles dB(A)
For tumble dryers the energy efficiency scale is calculated using the cotton drying cycle with a maximum declared load. The energy efficiency index is in kW·h per kilogramme of load. Different scales apply for condenser and vented dryers.
Condenser dryers
| A | B | C | D | E | F | G |
| <0.55 | <0.64 | <0.73 | <0.82 | <0.91 | <1.00 | >1.00 |
Vented dryers
| A | B | C | D | E | F | G |
| <0.51 | <0.59 | <0.67 | <0.75 | <0.83 | <0.91 | >0.91 |
The label also contains:
- the energy consumption per cycle
- the total cotton capacity
- whether the unit is vented or condensing
- noise in dB(A)
For combined washer dryers the energy efficiency scale is calculated using the cotton drying cycle with a maximum declared load. The energy efficiency index is in kW·h per kilogramme of load. Different scales apply for condenser and vented dryers.
| A | B | C | D | E | F | G |
| <0.68 | <0.81 | <0.93 | <1.05 | <1.17 | <1.29 | >1.29 |
The label also contains:
- the energy consumption per cycle (washing and drying)
- the energy consumption per cycle – washing only
- washing performance – with a class from A to G
- the maximum spin speed
- the total cotton capacity (washing and drying separately)
- water consumption for a full load washed and dried – note that condenser dryers may use significant amounts of water on the drying cycle
- noise in dB (A) (separately for washing, spinning and drying)
DishwasherDishwasherA dishwasher is a mechanical device for cleaning dishes and eating utensils. Dishwashers can be found in restaurants and private homes.Unlike manual dishwashing, which relies largely on physical scrubbing to remove soiling, the mechanical dishwasher cleans by spraying hot water, typically between ...
s
The energy efficiency is calculated according to the number of place settings. For the most common size of appliance, the 12 place setting machine the following classes apply. The unit is expressed in kW·h per 12 place settings.| A | B | C | D | E | F | G |
| <1.06 | <1.25 | <1.45 | <1.65 | <1.85 | <2.05 | >2.05 |
The label also contains:
- the energy consumption in kW·h /cycle
- the efficiency of the washing cycle with a class from A to G
- the efficiency of the drying cycle with a class from A to G
- the capacity as a number of place settings
- the water consumption in litres per cycle
- noise in dB(A)
OvenOvenAn oven is a thermally insulated chamber used for the heating, baking or drying of a substance. It is most commonly used for cooking. Kilns, and furnaces are special-purpose ovens...
s
The label also contains:
- the efficiency with a class from A to G
- the energy consumption in kW·h
- the volume in litres
- the type (small/medium/large)
Air conditioners
The directive applies only to units under 12 kW. On every label, you will find:- the model,
- the energy efficiency category from A to G,
- the annual energy consumption (full load at 500 hr per year)
- the cooling output at full load in kW
- the energy efficiency ratio in cooling mode at full load
- the appliance type (cooling only, cooling/heating)
- the cooling mode (air- or water-cooled)
- the noise rating in dB (where applicable)
For air conditioners with heating capability, you will also find:
- the heat output at full load in kW
- the heating mode energy efficiency category
| A | B | C | D | E | F | G | |
| Cooling EER W/W | >3.2 | 3.0–3.2 | 2.8–3.0 | 2.6–2.8 | 2.4–2.6 | 2.2–2.4 | <2.2 |
| Heating COP W/W | >3.6 | 3.4–3.6 | 3.2–3.4 | 2.8–3.2 | 2.6–2.8 | 2.4–2.6 | <2.4 |
Note that there exists units with EER and COP > 5, so take a note of the actual number when it is A rated.
Light bulbs
On every label, you will find:- the energy efficiency category from A to G
- the luminous fluxLuminous fluxIn photometry, luminous flux or luminous power is the measure of the perceived power of light. It differs from radiant flux, the measure of the total power of light emitted, in that luminous flux is adjusted to reflect the varying sensitivity of the human eye to different wavelengths of...
of the bulb in lumenLumen (unit)The lumen is the SI derived unit of luminous flux, a measure of the total "amount" of visible light emitted by a source. Luminous flux differs from power in that luminous flux measurements reflect the varying sensitivity of the human eye to different wavelengths of light, while radiant flux...
s - the electricity consumption of the lamp in wattWattThe watt is a derived unit of power in the International System of Units , named after the Scottish engineer James Watt . The unit, defined as one joule per second, measures the rate of energy conversion.-Definition:...
s - the average life length in hours
According to the lightbulb's electrical consumption relative to a standard (GLS or incandescent), the lightbulb is in one of the following classes:
| A | B | C | D | E | F | G |
| 20–50% | 50–75% | 75–90% | 90–100% | 100–110% | 110–125% | >125% |
Television
New standards that televisions need to meet for the Energy StarEnergy Star
Energy Star is an international standard for energy efficient consumer products originated in the United States of America. It was first created as a United States government program during the early 1990s, but Australia, Canada, Japan, New Zealand, Taiwan and the European Union have also adopted...
efficiency rating came into effect early in September 2009.
Cars

Carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a naturally occurring chemical compound composed of two oxygen atoms covalently bonded to a single carbon atom...
emissions in grammes per kilometre travelled.
| A | B | C | D | E | F | G |
| <100 | <120 | <140 | <160 | <200 | <250 | >250 |
Other information that is indexed for the energy label is:
- its brand
- its model
- its version
- its fuel
- its transmission type
- its weight
- the different consumptions of fuel
- mixed consumption
- urban consumption
- extra-urban consumption
- the CO2 emissions in grammes per kilometre
See also
- EcolabelEcolabelEcolabels and Green Stickers are labelling systems for food and consumer products. Ecolabels are often voluntary, but Green Stickers are mandated by law in North America for major appliances and automobiles. They are a form of sustainability measurement directed at consumers, intended to make it...
- Home energy performance certificateEnergy Performance CertificateEnergy Performance Certificates were introduced in England and Wales on 1 August 2007 as part of Home Information Packs for domestic properties with four or more bedrooms . When the requirement for HIPs was removed in May 2010, the requirement for EPCs continued. The scheme for HIPs was extended...
- Energy policy of the European UnionEnergy policy of the European UnionAlthough the European Union has legislated in the area of energy policy for many years, and evolved out of the European Coal and Steel Community, the concept of introducing a mandatory and comprehensive European energy policy was only approved at the meeting of the European Council on 27 October...
- Fuel mix disclosureFuel mix disclosure]According to the European Union's Internal Market in Electricity Directive from July 1, 2004, electric power consumers must be informed about the sources from which the electricity they have purchased was generated...
on labelling the origins and environmental effects of electricity

