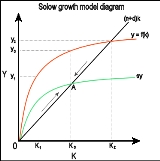
Exogenous growth model
Overview
Economic growth
In economics, economic growth is defined as the increasing capacity of the economy to satisfy the wants of goods and services of the members of society. Economic growth is enabled by increases in productivity, which lowers the inputs for a given amount of output. Lowered costs increase demand...
set within the framework of neoclassical economics
Neoclassical economics
Neoclassical economics is a term variously used for approaches to economics focusing on the determination of prices, outputs, and income distributions in markets through supply and demand, often mediated through a hypothesized maximization of utility by income-constrained individuals and of profits...
. Neoclassical growth models attempt to explain long run economic growth by looking at productivity
Productivity
Productivity is a measure of the efficiency of production. Productivity is a ratio of what is produced to what is required to produce it. Usually this ratio is in the form of an average, expressing the total output divided by the total input...
, capital accumulation
Capital accumulation
The accumulation of capital refers to the gathering or amassing of objects of value; the increase in wealth through concentration; or the creation of wealth. Capital is money or a financial asset invested for the purpose of making more money...
, population growth
Population growth
Population growth is the change in a population over time, and can be quantified as the change in the number of individuals of any species in a population using "per unit time" for measurement....
and technological progress.
The neo-classical model was an extension to the 1946 Harrod–Domar model that included a new term: productivity
Productivity
Productivity is a measure of the efficiency of production. Productivity is a ratio of what is produced to what is required to produce it. Usually this ratio is in the form of an average, expressing the total output divided by the total input...
growth.

