
Experiments on Plant Hybridization
Encyclopedia
Written in 1865 by Gregor Mendel
, Experiments on Plant Hybridization (German: Versuche über Pflanzen-Hybriden) was the result after years spent studying genetic
traits in pea plants. Mendel read his paper to the Natural History Society of Brünn (Brno
) on February 8 and March 8, 1865. It was published in the Proceedings of the Natural History Society of Brünn
the following year.
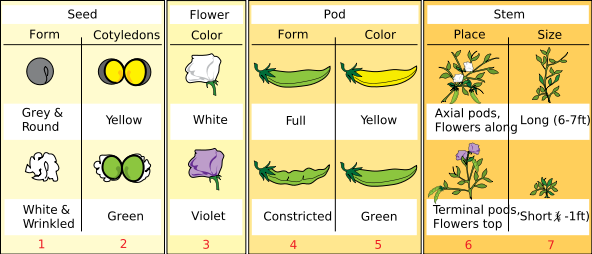
In his paper, Mendel compared seven discrete characters:
Through experimentation, Mendel discovered that one inheritable trait would invariably be dominant to its recessive alternative. This model, later known as Mendelian inheritance
or Mendelian genetics, provided an alternative to blending inheritance, which was the prevailing theory at the time. Mendel's work received little attention from the scientific community and was largely forgotten. It was not until the early 20th century that Mendel's work was rediscovered and his ideas used to help form the modern synthesis.
In 1936, the statistician R.A. Fisher
used a chi-squared test
to analyze Mendel's data and concluded that Mendel's results with the predicted ratios were far too perfect, indicating that adjustments (intentional or unconscious) had been made to the data to make the observations fit the hypothesis. Later authors have claimed Fisher's analysis was flawed, proposing various statistical and botanical explanations for Mendel's numbers. It is also possible that Mendel's results are "too good" merely because he reported the best subset of his data — Mendel mentioned in his paper that the data was from a subset of his experiments.
Gregor Mendel
Gregor Johann Mendel was an Austrian scientist and Augustinian friar who gained posthumous fame as the founder of the new science of genetics. Mendel demonstrated that the inheritance of certain traits in pea plants follows particular patterns, now referred to as the laws of Mendelian inheritance...
, Experiments on Plant Hybridization (German: Versuche über Pflanzen-Hybriden) was the result after years spent studying genetic
Genetics
Genetics , a discipline of biology, is the science of genes, heredity, and variation in living organisms....
traits in pea plants. Mendel read his paper to the Natural History Society of Brünn (Brno
Brno
Brno by population and area is the second largest city in the Czech Republic, the largest Moravian city, and the historical capital city of the Margraviate of Moravia. Brno is the administrative centre of the South Moravian Region where it forms a separate district Brno-City District...
) on February 8 and March 8, 1865. It was published in the Proceedings of the Natural History Society of Brünn
Proceedings of the Natural History Society of Brünn
The Proceedings of the Natural History Society of Brünn was the scientific journal where Gregor Mendel published his scientific discoveries on genetics which he made between 1856 to 1863...
the following year.
In his paper, Mendel compared seven discrete characters:

- Color and smoothness of the seeds (grey and round or white and wrinkled)
- Color of the cotyledons (yellow or green)
- Color of the flowers (white or violet)
- Shape of the pods (full or constricted)
- Color of unripe pods (yellow or green)
- Position of flowers and pods on the stems
- Height of the plants (short or tall)
Through experimentation, Mendel discovered that one inheritable trait would invariably be dominant to its recessive alternative. This model, later known as Mendelian inheritance
Mendelian inheritance
Mendelian inheritance is a scientific description of how hereditary characteristics are passed from parent organisms to their offspring; it underlies much of genetics...
or Mendelian genetics, provided an alternative to blending inheritance, which was the prevailing theory at the time. Mendel's work received little attention from the scientific community and was largely forgotten. It was not until the early 20th century that Mendel's work was rediscovered and his ideas used to help form the modern synthesis.
In 1936, the statistician R.A. Fisher
Ronald Fisher
Sir Ronald Aylmer Fisher FRS was an English statistician, evolutionary biologist, eugenicist and geneticist. Among other things, Fisher is well known for his contributions to statistics by creating Fisher's exact test and Fisher's equation...
used a chi-squared test
Pearson's chi-squared test
Pearson's chi-squared test is the best-known of several chi-squared tests – statistical procedures whose results are evaluated by reference to the chi-squared distribution. Its properties were first investigated by Karl Pearson in 1900...
to analyze Mendel's data and concluded that Mendel's results with the predicted ratios were far too perfect, indicating that adjustments (intentional or unconscious) had been made to the data to make the observations fit the hypothesis. Later authors have claimed Fisher's analysis was flawed, proposing various statistical and botanical explanations for Mendel's numbers. It is also possible that Mendel's results are "too good" merely because he reported the best subset of his data — Mendel mentioned in his paper that the data was from a subset of his experiments.
External links
- "Experiments on Plant Hybridization" (Translated into English)
- Librivox recording

