External electric load
Encyclopedia
If an electric circuit
has a well-defined output terminal, the circuit connected to this terminal (or its input impedance
) is the load. (The term 'load' may also refer to the power
consumed by a circuit; that topic is not discussed here.)
Load affects the performance of circuits that output volt
ages or currents, such as sensor
s, voltage source
s, and amplifier
s. Mains
power outlet
s provide an easy example: they supply power at constant voltage, with electrical appliances connected to the power circuit collectively making up the load. When a high-power appliance switches on, it dramatically reduces the load impedance
.
If the load impedance is not very much higher than the power supply impedance, the voltage will drop. In a domestic environment, switching on a heating appliance may cause incandescent lights to dim noticeably.
. It uses simple resistances
, but can be readily generalized to impedance
s for AC analysis
.)
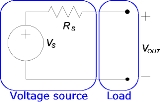
When discussing the effect of load on a circuit, it is helpful to disregard the circuit's actual design and consider only the Thévenin equivalent. (The Norton equivalent
could be used instead, with the same results.) The Thévenin equivalent of a circuit looks like this:
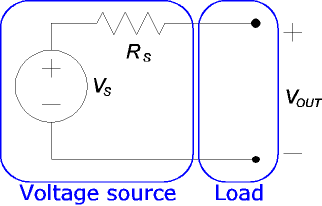 With no load (open-circuited terminals), all of
With no load (open-circuited terminals), all of  falls across the output; the output voltage is
falls across the output; the output voltage is 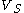 . However, the circuit will behave differently if a load is added. We would like to ignore the details of the load circuit, as we did for the power supply, and represent it as simply as possible. If we use an input resistance
. However, the circuit will behave differently if a load is added. We would like to ignore the details of the load circuit, as we did for the power supply, and represent it as simply as possible. If we use an input resistance
to represent the load, the complete circuit looks like this:
 Whereas the voltage source by itself was an open circuit
Whereas the voltage source by itself was an open circuit
, adding the load makes a closed circuit and allows current to flow. This current places a voltage drop across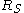 , so the voltage at the output terminal is no longer
, so the voltage at the output terminal is no longer 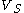 . The output voltage can be determined by the voltage division
. The output voltage can be determined by the voltage division
rule:
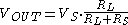
If the source resistance is not negligibly small compared to the load impedance, the output voltage will fall.
Electrical network
An electrical network is an interconnection of electrical elements such as resistors, inductors, capacitors, transmission lines, voltage sources, current sources and switches. An electrical circuit is a special type of network, one that has a closed loop giving a return path for the current...
has a well-defined output terminal, the circuit connected to this terminal (or its input impedance
Input impedance
The input impedance of an electrical network is the equivalent impedance "seen" by a power source connected to that network. If the source provides known voltage and current, such impedance can be calculated using Ohm's Law...
) is the load. (The term 'load' may also refer to the power
Electric power
Electric power is the rate at which electric energy is transferred by an electric circuit. The SI unit of power is the watt.-Circuits:Electric power, like mechanical power, is represented by the letter P in electrical equations...
consumed by a circuit; that topic is not discussed here.)
Load affects the performance of circuits that output volt
Volt
The volt is the SI derived unit for electric potential, electric potential difference, and electromotive force. The volt is named in honor of the Italian physicist Alessandro Volta , who invented the voltaic pile, possibly the first chemical battery.- Definition :A single volt is defined as the...
ages or currents, such as sensor
Sensor
A sensor is a device that measures a physical quantity and converts it into a signal which can be read by an observer or by an instrument. For example, a mercury-in-glass thermometer converts the measured temperature into expansion and contraction of a liquid which can be read on a calibrated...
s, voltage source
Voltage source
In electric circuit theory, an ideal voltage source is a circuit element where the voltage across it is independent of the current through it. A voltage source is the dual of a current source. In analysis, a voltage source supplies a constant DC or AC potential between its terminals for any current...
s, and amplifier
Amplifier
Generally, an amplifier or simply amp, is a device for increasing the power of a signal.In popular use, the term usually describes an electronic amplifier, in which the input "signal" is usually a voltage or a current. In audio applications, amplifiers drive the loudspeakers used in PA systems to...
s. Mains
Mains electricity
Mains is the general-purpose alternating current electric power supply. In the US, electric power is referred to by several names including household power, household electricity, powerline, domestic power, wall power, line power, AC power, city power, street power, and grid power...
power outlet
Domestic AC power plugs and sockets
AC power plugs and sockets are devices for removably connecting electrically operated devices to the power supply. Electrical plugs and sockets differ by country in rating, shape, size and type of connectors...
s provide an easy example: they supply power at constant voltage, with electrical appliances connected to the power circuit collectively making up the load. When a high-power appliance switches on, it dramatically reduces the load impedance
Electrical impedance
Electrical impedance, or simply impedance, is the measure of the opposition that an electrical circuit presents to the passage of a current when a voltage is applied. In quantitative terms, it is the complex ratio of the voltage to the current in an alternating current circuit...
.
If the load impedance is not very much higher than the power supply impedance, the voltage will drop. In a domestic environment, switching on a heating appliance may cause incandescent lights to dim noticeably.
A more technical approach
(Two sidenotes on generality, for advanced readers: This discussion assumes circuits are linearLinear circuit
A linear circuit is an electronic circuit in which, for a sinusoidal input voltage of frequency f, any output of the circuit is also sinusoidal with frequency f...
. It uses simple resistances
Electrical resistance
The electrical resistance of an electrical element is the opposition to the passage of an electric current through that element; the inverse quantity is electrical conductance, the ease at which an electric current passes. Electrical resistance shares some conceptual parallels with the mechanical...
, but can be readily generalized to impedance
Impedance
Impedance may refer to:*Electrical impedance, the ratio of the voltage phasor to the electric current phasor, a measure of the opposition to time-varying electric current in an electric circuit**Characteristic impedance of a transmission line...
s for AC analysis
Alternating current
In alternating current the movement of electric charge periodically reverses direction. In direct current , the flow of electric charge is only in one direction....
.)
When discussing the effect of load on a circuit, it is helpful to disregard the circuit's actual design and consider only the Thévenin equivalent. (The Norton equivalent
Norton's theorem
Norton's theorem for linear electrical networks, known in Europe as the Mayer–Norton theorem, states that any collection of voltage sources, current sources, and resistors with two terminals is electrically equivalent to an ideal current source, I, in parallel with a single resistor, R...
could be used instead, with the same results.) The Thévenin equivalent of a circuit looks like this:

 falls across the output; the output voltage is
falls across the output; the output voltage is 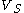 . However, the circuit will behave differently if a load is added. We would like to ignore the details of the load circuit, as we did for the power supply, and represent it as simply as possible. If we use an input resistance
. However, the circuit will behave differently if a load is added. We would like to ignore the details of the load circuit, as we did for the power supply, and represent it as simply as possible. If we use an input resistanceInput impedance
The input impedance of an electrical network is the equivalent impedance "seen" by a power source connected to that network. If the source provides known voltage and current, such impedance can be calculated using Ohm's Law...
to represent the load, the complete circuit looks like this:

Open circuit
The term Open circuit may refer to:*Open-circuit scuba, a type of SCUBA-diving equipment where the user breathes from the set and then exhales to the surroundings without recycling the exhaled air...
, adding the load makes a closed circuit and allows current to flow. This current places a voltage drop across
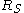 , so the voltage at the output terminal is no longer
, so the voltage at the output terminal is no longer 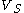 . The output voltage can be determined by the voltage division
. The output voltage can be determined by the voltage divisionVoltage divider rule
In electronics, a voltage divider is a simple linear circuit that produces an output voltage that is a fraction of its input voltage...
rule:
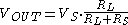
If the source resistance is not negligibly small compared to the load impedance, the output voltage will fall.

