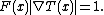Fast marching method
Encyclopedia
The fast marching method is introduced by James A. Sethian
as a numerical method for solving boundary value problems
of the Eikonal equation
:
Typically, such a problem describes the evolution of a closed curve as a function of time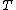 with speed
with speed 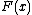 in the normal direction at a point
in the normal direction at a point  on the curve. The speed function is specified, and the time at which the contour crosses a point
on the curve. The speed function is specified, and the time at which the contour crosses a point  is obtained by solving the equation.
is obtained by solving the equation.
The algorithm is similar to Dijkstra's algorithm
and uses the fact that information only flows outward from the seeding area.
This problem is a special case of level set method
s. More general algorithms exist but are normally slower.
Extensions to non-flat (triangulated) domains solving:
James Sethian
James Albert Sethian is a professor of mathematics at the University of California, Berkeley, and the head of the Mathematics Group at the United States Department of Energy's Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory....
as a numerical method for solving boundary value problems
Boundary value problem
In mathematics, in the field of differential equations, a boundary value problem is a differential equation together with a set of additional restraints, called the boundary conditions...
of the Eikonal equation
Eikonal equation
The eikonal equation is a non-linear partial differential equation encountered in problems of wave propagation, when the wave equation is approximated using the WKB theory...
:
Typically, such a problem describes the evolution of a closed curve as a function of time
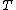 with speed
with speed 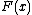 in the normal direction at a point
in the normal direction at a point  on the curve. The speed function is specified, and the time at which the contour crosses a point
on the curve. The speed function is specified, and the time at which the contour crosses a point  is obtained by solving the equation.
is obtained by solving the equation.The algorithm is similar to Dijkstra's algorithm
Dijkstra's algorithm
Dijkstra's algorithm, conceived by Dutch computer scientist Edsger Dijkstra in 1956 and published in 1959, is a graph search algorithm that solves the single-source shortest path problem for a graph with nonnegative edge path costs, producing a shortest path tree...
and uses the fact that information only flows outward from the seeding area.
This problem is a special case of level set method
Level set method
The level set method is a numerical technique for tracking interfaces and shapes. The advantage of the level set method is that one can perform numerical computations involving curves and surfaces on a fixed Cartesian grid without having to parameterize these objects...
s. More general algorithms exist but are normally slower.
Extensions to non-flat (triangulated) domains solving:
-
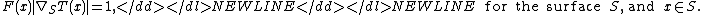
was introduced by Ron KimmelRon KimmelRon Kimmel is a professor of Computer Science atthe Technion Israel Institute of Technology.He holds a D.Sc. degree in electrical engineering from the Technion,and spent a post-doctoral position at UC Berkeley and Berkeley Labs, and a visiting...
and Sethian.
External links