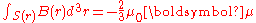Fermi contact interaction
Encyclopedia
The Fermi contact interaction is the magnetic
interaction between an electron
and an atomic nucleus
when the electron is inside that nucleus. It is of magnitude
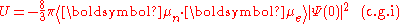
and
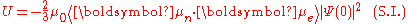
where U is the energy of the interaction, μn is the nuclear magnetic moment
, μe is the electron magnetic dipole moment
, and Ψ(0) is the electron wavefunction
at the nucleus.
Within an atom
, only s-orbitals
have non-zero electron density at the nucleus, so the contact interaction can only occur for s-electrons. Its major manifestation is in electron paramagnetic resonance
and nuclear magnetic resonance
spectroscopies, where it is responsible for the appearance of isotropic hyperfine coupling.
The interaction was first derived by Enrico Fermi
in 1930.. A classical derivation of this term is contained in J.D. Jackson. In short the classical energy U may be written in terms of the energy of one magnetic dipole
moment in the magnetic field B (r) of another. This field acquires a simple expression when the distance r between the two moments goes to zero, since:
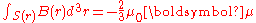
Magnetism
Magnetism is a property of materials that respond at an atomic or subatomic level to an applied magnetic field. Ferromagnetism is the strongest and most familiar type of magnetism. It is responsible for the behavior of permanent magnets, which produce their own persistent magnetic fields, as well...
interaction between an electron
Electron
The electron is a subatomic particle with a negative elementary electric charge. It has no known components or substructure; in other words, it is generally thought to be an elementary particle. An electron has a mass that is approximately 1/1836 that of the proton...
and an atomic nucleus
Atomic nucleus
The nucleus is the very dense region consisting of protons and neutrons at the center of an atom. It was discovered in 1911, as a result of Ernest Rutherford's interpretation of the famous 1909 Rutherford experiment performed by Hans Geiger and Ernest Marsden, under the direction of Rutherford. The...
when the electron is inside that nucleus. It is of magnitude
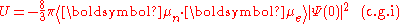
and
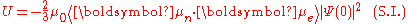
where U is the energy of the interaction, μn is the nuclear magnetic moment
Nuclear magnetic moment
The nuclear magnetic moment is the magnetic moment of an atomic nucleus and arises from the spin of the protons and neutrons. It is mainly a magnetic dipole moment; the quadrupole moment does cause some small shifts in the hyperfine structure as well....
, μe is the electron magnetic dipole moment
Electron magnetic dipole moment
In atomic physics, the electron magnetic dipole moment is the magnetic moment of an electron caused by its intrinsic property of spin.-Magnetic moment of an electron:...
, and Ψ(0) is the electron wavefunction
Wavefunction
Not to be confused with the related concept of the Wave equationA wave function or wavefunction is a probability amplitude in quantum mechanics describing the quantum state of a particle and how it behaves. Typically, its values are complex numbers and, for a single particle, it is a function of...
at the nucleus.
Within an atom
Atom
The atom is a basic unit of matter that consists of a dense central nucleus surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged electrons. The atomic nucleus contains a mix of positively charged protons and electrically neutral neutrons...
, only s-orbitals
Atomic orbital
An atomic orbital is a mathematical function that describes the wave-like behavior of either one electron or a pair of electrons in an atom. This function can be used to calculate the probability of finding any electron of an atom in any specific region around the atom's nucleus...
have non-zero electron density at the nucleus, so the contact interaction can only occur for s-electrons. Its major manifestation is in electron paramagnetic resonance
Electron paramagnetic resonance
Electron paramagnetic resonance or electron spin resonance spectroscopyis a technique for studying chemical species that have one or more unpaired electrons, such as organic and inorganic free radicals or inorganic complexes possessing a transition metal ion...
and nuclear magnetic resonance
Nuclear magnetic resonance
Nuclear magnetic resonance is a physical phenomenon in which magnetic nuclei in a magnetic field absorb and re-emit electromagnetic radiation...
spectroscopies, where it is responsible for the appearance of isotropic hyperfine coupling.
The interaction was first derived by Enrico Fermi
Enrico Fermi
Enrico Fermi was an Italian-born, naturalized American physicist particularly known for his work on the development of the first nuclear reactor, Chicago Pile-1, and for his contributions to the development of quantum theory, nuclear and particle physics, and statistical mechanics...
in 1930.. A classical derivation of this term is contained in J.D. Jackson. In short the classical energy U may be written in terms of the energy of one magnetic dipole
Magnetic dipole
A magnetic dipole is the limit of either a closed loop of electric current or a pair of poles as the dimensions of the source are reduced to zero while keeping the magnetic moment constant. It is a magnetic analogue of the electric dipole, but the analogy is not complete. In particular, a magnetic...
moment in the magnetic field B (r) of another. This field acquires a simple expression when the distance r between the two moments goes to zero, since: