
Filter (aquarium)
Encyclopedia

Aquarium
An aquarium is a vivarium consisting of at least one transparent side in which water-dwelling plants or animals are kept. Fishkeepers use aquaria to keep fish, invertebrates, amphibians, marine mammals, turtles, and aquatic plants...
filters remove physical and soluble chemical waste products from aquaria, simplifying maintenance. Furthermore, aquarium filters are necessary to support life as aquaria are relatively small, closed volumes of water compared to the natural environment of most fish.
Overview
Animals, typically fish, kept in fish tanksAquarium
An aquarium is a vivarium consisting of at least one transparent side in which water-dwelling plants or animals are kept. Fishkeepers use aquaria to keep fish, invertebrates, amphibians, marine mammals, turtles, and aquatic plants...
produce waste from excrement and respiration. Another source of waste is uneaten food or plants and fish which have died. These waste products collect in the tanks and contaminate the water. As the degree of contamination rises, the risk to the health of the aquaria increases and removal of the contamination becomes critical. Filtration is a common method used for maintenance of healthy aquaria.
Biological filtration and the nitrogen cycle

Nitrogen cycle
The nitrogen cycle is the process by which nitrogen is converted between its various chemical forms. This transformation can be carried out by both biological and non-biological processes. Important processes in the nitrogen cycle include fixation, mineralization, nitrification, and denitrification...
is a vital element of a successful aquarium
Aquarium
An aquarium is a vivarium consisting of at least one transparent side in which water-dwelling plants or animals are kept. Fishkeepers use aquaria to keep fish, invertebrates, amphibians, marine mammals, turtles, and aquatic plants...
. Excretia and other decomposing organic matter produce ammonia
Ammonia
Ammonia is a compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . It is a colourless gas with a characteristic pungent odour. Ammonia contributes significantly to the nutritional needs of terrestrial organisms by serving as a precursor to food and fertilizers. Ammonia, either directly or...
which is highly toxic to fish. Bacterial processes oxidize this ammonia into the slightly less toxic nitrites, and these are in turn oxidized to form the much less toxic nitrates. In the natural environment these nitrates are subsequently taken up by plants as fertilizer and this does indeed happen to some extent in an aquarium planted with real plants.
An aquarium is, however, an imperfect microcosm of the natural world. Aquariums are usually much more densely stocked with fish than the natural environment. This increases the amount of ammonia produced in the relatively small volume of the aquarium. The bacteria responsible for breaking down the ammonia colonize the surface of any objects inside the aquarium. In most case, a biological filter is nothing more than a chemically inert porous sponge, which provides a greatly enlarged surface area on which these bacteria can develop. These bacterial colonies take several weeks to form, during which time the aquarium is vulnerable to a condition commonly known as "new tank syndrome" if stocked with fish too quickly. Some systems incorporate bacteria capable of converting nitrates into nitrogen gas.
Accumulation of toxic ammonia from decomposing wastes is the largest cause of fish mortality in new, poorly maintained, or overloaded aquariums. In the artificial environment of the aquarium, the nitrogen cycle effectively ends with the production of nitrates. In order that the nitrate level does not build up to a harmful level regular partial water changes are required to remove the nitrates and introduce new, uncontaminated water.
Mechanical and chemical filtration
The process of mechanical filtration removes particulate material from the water column. This particulate matter may include uneaten food, faeces or plant or algal debris. Mechanical filtration is typically achieved by passing water through materials which act as a sieve, physically trapping the particulate matter. Removal of solid waste can be as simple as physical hand netting of debris, and/or involve highly complex equipment. All removal of solid wastes involve filtering water through some form of mesh in a process known as mechanical filtration. The solid wastes are first collected, and then must be physically removed from the aquariumAquarium
An aquarium is a vivarium consisting of at least one transparent side in which water-dwelling plants or animals are kept. Fishkeepers use aquaria to keep fish, invertebrates, amphibians, marine mammals, turtles, and aquatic plants...
system. Mechanical filtration is ultimately ineffective if the solid wastes are not removed from the filter, and are allowed to decay and dissolve in the water.
Dissolved wastes are more difficult to remove from the water. Several techniques, collectively known as chemical filtration, are used for the removal of dissolved wastes, the most popular being the use of activated carbon
Activated carbon
Activated carbon, also called activated charcoal, activated coal or carbo activatus, is a form of carbon that has been processed to make it extremely porous and thus to have a very large surface area available for adsorption or chemical reactions.The word activated in the name is sometimes replaced...
and foam fractionation
Foam fractionation
Foam fractionation is a chemical process in which hydrophobic molecules are preferentially separated from a liquid solution using rising columns of foam. It is commonly used, albeit on a small scale, for the removal of organic waste from aquariums; these units are known as "protein skimmers"...
. To a certain extent, healthy plants extract dissolved chemical wastes from water when they grow, so plants can serve a role in the containment of dissolved wastes.
A final and less common situation requiring filtration involves the desire to sterilize water born pathogens. This sterilization is accomplished by passing aquarium water through filtration devices which expose the water to high intensity ultraviolet light and/or exposing the water to dissolved ozone gas.
Materials suitable for aquarium filtration

Aquarium
An aquarium is a vivarium consisting of at least one transparent side in which water-dwelling plants or animals are kept. Fishkeepers use aquaria to keep fish, invertebrates, amphibians, marine mammals, turtles, and aquatic plants...
filtration media. These include synthetic wools, known in the aquarium hobby as filter wool, made of polyethylene terephthalate
Polyethylene terephthalate
Polyethylene terephthalate , commonly abbreviated PET, PETE, or the obsolete PETP or PET-P, is a thermoplastic polymer resin of the polyester family and is used in synthetic fibers; beverage, food and other liquid containers; thermoforming applications; and engineering resins often in combination...
or nylon
Nylon
Nylon is a generic designation for a family of synthetic polymers known generically as polyamides, first produced on February 28, 1935, by Wallace Carothers at DuPont's research facility at the DuPont Experimental Station...
. Synthetic sponges or foams
Sponge (tool)
A sponge is a tool, implement, utensil or cleaning aid consisting of porous material. Sponges are used for cleaning impervious surfaces. They are especially good absorbers of water and water-based solutions....
, various ceramic and sintered glass and silicon products along with igneous gravel
Gravel
Gravel is composed of unconsolidated rock fragments that have a general particle size range and include size classes from granule- to boulder-sized fragments. Gravel can be sub-categorized into granule and cobble...
s are also used as mechanical filter materials. Materials with a greater surface area provide both mechanical and biological filtration. Some filter materials, such as plastic "bioballs", are best used for biological filtration.
With the notable exception of diatom filters, aquarium filters are rarely purely mechanical in action, as bacteria will colonise most filter materials effecting some degree of biological filtration. Activated carbon
Activated carbon
Activated carbon, also called activated charcoal, activated coal or carbo activatus, is a form of carbon that has been processed to make it extremely porous and thus to have a very large surface area available for adsorption or chemical reactions.The word activated in the name is sometimes replaced...
and zeolites are also frequently added to aquarium filters. These highly porous materials act as adsorbates
Adsorption
Adsorption is the adhesion of atoms, ions, biomolecules or molecules of gas, liquid, or dissolved solids to a surface. This process creates a film of the adsorbate on the surface of the adsorbent. It differs from absorption, in which a fluid permeates or is dissolved by a liquid or solid...
binding various chemicals to their large external surfaces and also as sites of bacterial colonisation.
The simplest type of aquarium filter consists only of filter wool and activated carbon. The filter wool traps large debris and particles, and the activated carbon adsorbs smaller impurities. These should be changed regularly at suitable intervals. This is particularly important in the case of activated carbon filters, which may re-release their adsorbed contents in large (and therefore harmful) doses if they are allowed to saturate. Activated carbon adsorbs toxins on the surface of the carbon. It can be reactivated by boiling in clean water, and draining away the tainted water, and can then be re-used.
Types of aquarium filters

External filters
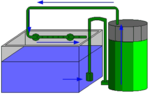
Aquarium
An aquarium is a vivarium consisting of at least one transparent side in which water-dwelling plants or animals are kept. Fishkeepers use aquaria to keep fish, invertebrates, amphibians, marine mammals, turtles, and aquatic plants...
which is then pushed (or pulled) through a series of different levels of filter media and returned to the aquarium. They are usually more effective and easier to maintain than internal filters.
Canister filters
Compared to filters that hang on the back of the aquariumAquarium
An aquarium is a vivarium consisting of at least one transparent side in which water-dwelling plants or animals are kept. Fishkeepers use aquaria to keep fish, invertebrates, amphibians, marine mammals, turtles, and aquatic plants...
, canister-style external filters offer a greater quantity of filter materials to be used along with a greater degree of flexibility with respect to filter material choice. Water enters the canister filled with the chosen filter material through an intake pipe at the bottom of the canister, passes through the material, and is pumped back to the aquarium through an electric pump on the top of the canister. Benefits of this type of filter are that they can provide a high volume of filter material without reducing the internal space in the aquarium, and that they can be disconnected from the tank for cleaning/maintenance and replaced without disturbing the aquarium interior or occupants. Disadvantages of canister filters include the increased cost and complexity relative to internal filters and difficulties in cleaning the tubes which transfer water to and from the aquarium. There is also the risk of a leak, which naturally is an issue for any filter placed outside of the aquarium.
Canister filters were initially designed to filter drinking water, under low pressure. Canister filters for aquariums use high water pressure, from a properly powered pump, to force water through the dense filter media. A pump can draw water from an under-gravel filter, and run it into a canister for double filtration.
Diatom filters
Diatom filters are used only for sporadic cleaning of tanks, they are not continuously operated on aquariumAquarium
An aquarium is a vivarium consisting of at least one transparent side in which water-dwelling plants or animals are kept. Fishkeepers use aquaria to keep fish, invertebrates, amphibians, marine mammals, turtles, and aquatic plants...
s. These filters utilise diatomaceous earth
Diatomaceous earth
Diatomaceous earth also known as diatomite or kieselgur/kieselguhr, is a naturally occurring, soft, siliceous sedimentary rock that is easily crumbled into a fine white to off-white powder. It has a particle size ranging from less than 1 micrometre to more than 1 millimetre, but typically 10 to...
to create an extremely fine filter down to 1 µm which removes particulate matter from the water column.
Trickle filters
Trickle filters, also known as wet/dry filters are another water filtration systems for marine and freshwater aquariumAquarium
An aquarium is a vivarium consisting of at least one transparent side in which water-dwelling plants or animals are kept. Fishkeepers use aquaria to keep fish, invertebrates, amphibians, marine mammals, turtles, and aquatic plants...
s. This filter comes in two configurations, one which is placed on top of the aquarium (more rarely seen) and one which is placed below the aquarium (more common).
If the wet/dry filter is placed on top of the aquarium, water is pumped over a number of perforated trays containing filter wool or some other filter material. The water trickles through the trays, keeping the filter wool wet but not completely submerged, allowing aerobic bacteria
Aerobic organism
An aerobic organism or aerobe is an organism that can survive and grow in an oxygenated environment.Faculitative anaerobes grow and survive in an oxygenated environment and so do aerotolerant anaerobes.-Glucose:...
to grow and aiding biological filtration. The water returns to the aquarium like rain.
Alternatively, the wet/dry filter may be placed below the tank. In this design, water is fed by gravity to the filter below the aquarium. Prefiltered water is delivered to a perforated plate (drip plate). Prefiltering may take place in the aquarium via a foam block or sleeve in the overflow, or weir
Weir
A weir is a small overflow dam used to alter the flow characteristics of a river or stream. In most cases weirs take the form of a barrier across the river that causes water to pool behind the structure , but allows water to flow over the top...
siphon, or it may be prefiltered by filter wool resting on the perforated plate. The waste laden water from the aquarium spreads over the drip plate, and rains down through a medium. This may be a filter wool/plastic grid rolled into a circular shape (DLS or "Double Layer Spiral") or any number of plastic media commonly known as Bio Balls. As the water cascades over the media, CO2 is given off, oxygen is picked up, and bacteria convert the waste from the tank into less harmful materials. From here the water enters the sump. The sump may contain a number of compartments, each with its own filtration material. Often, heaters and thermostats are placed in the sump.
Algae filters
Algae may be grown purposely, which removes chemicals from the water which need to be removed in order to have healthy fish, invertebrates and corals. This is a natural ("green") filtering method, which lets an aquarium operate the way oceans and lakes operate.Baffle filters

Aquarium
An aquarium is a vivarium consisting of at least one transparent side in which water-dwelling plants or animals are kept. Fishkeepers use aquaria to keep fish, invertebrates, amphibians, marine mammals, turtles, and aquatic plants...
. This type of filter consists of a series of baffles that the water must pass through in order to reach the pump which is returning water to the aquarium. These baffles then act much like a series of canister filters and can be filled with different filter media for different purposes.
Internal filters

Aquarium
An aquarium is a vivarium consisting of at least one transparent side in which water-dwelling plants or animals are kept. Fishkeepers use aquaria to keep fish, invertebrates, amphibians, marine mammals, turtles, and aquatic plants...
. These include the sponge filter, variations on the corner filter (pictured top right and left), foam cartridge filter and the undergravel filter. An internal filter may have an electric pump and thus be an internal power filter, often attached to the inside of aquaria via suction cups.
Airlift filters
Sponge filters and corner filters (sometimes called box filters) work by essentially the same mechanism as an internal filter. Both generally work by airliftAirlift pump
An airlift pump is a simple pump which is powered by compressed air.-Principle:The only energy required is air.This air is usually compressed by a compressor or a blower....
, using bubbles from an air pump rising in a tube to create flow. In a sponge filter, the inlet may only be covered by a simple open-cell block of foam. A corner filter is slightly more complex. These filters are often placed in the corner on the bottom of the aquarium
Aquarium
An aquarium is a vivarium consisting of at least one transparent side in which water-dwelling plants or animals are kept. Fishkeepers use aquaria to keep fish, invertebrates, amphibians, marine mammals, turtles, and aquatic plants...
. Water enters slits in the box, passes through a layer of medium, then exits through the airlift tube to return to the aquarium. These filters tend to only be suitable for small and lightly stocked aquaria. The sponge filter is especially useful for rearing fry where the sponge prevents the small fish from entering the filter.
Undergravel filters

Aquarium
An aquarium is a vivarium consisting of at least one transparent side in which water-dwelling plants or animals are kept. Fishkeepers use aquaria to keep fish, invertebrates, amphibians, marine mammals, turtles, and aquatic plants...
and one, or more, uplift tubes. Historically, undergravel filters have been driven via air displacement. Air stones are placed at the base of uplift tubes which force water out of the uplift tube creating negative pressure beneath the undergravel filter plate. Water then percolates down through the gravel which itself is the filtration material. Greater flow rate of water through the gravel can be achieved via the use of water pump rather than air displacement.
Beneficial bacteria colonize the gravel bed and provide biological filtration, using the substrate
Substrate (aquarium)
The substrate of an aquarium refers to the material used on the tank bottom. It can affect water chemistry, filtration, and the well-being of the aquarium's inhabitants, and is also an important part of the aquarium's aesthetic appeal...
of the aquarium itself as a biological filter.
Undergravel filters can be detrimental to the health of aquatic plants. Fine substrates such as sand or peat may clog an undergravel filter. Undergravel filters are not effective if the substrate bed is uneven. In an uneven gravel bed, water will flow only through the thin portions of the bed, leaving the more heavily covered areas to become anoxic
Hypoxia (environmental)
Hypoxia, or oxygen depletion, is a phenomenon that occurs in aquatic environments as dissolved oxygen becomes reduced in concentration to a point where it becomes detrimental to aquatic organisms living in the system...
. Because of this, animals that dig, such as cichlids, are best kept in an aquarium using some other type of filtration.

