Filter binding assay
Encyclopedia
In biochemistry
or chemistry
, one of the ways to learn about an interaction between two molecules is to determine the binding constant, which is a number that describes the ratio of unbound and bound molecules. This information reveals the affinity between the two molecules and allows prediction of the amount bound given any set of initial conditions.
In order to measure a binding constant, one must find a way to measure the amount of complex formed over a range of starting concentrations. This can be achieved by "labeling" one of the species with a fluorescent, or in this case, a radioactive tag. The DNA is "labeled" by the addition of radioactive Phosphate derived from Adenosine Triphosphate
.
A filter binding assay is a simple way to quickly study many samples. It measures affinities between two molecules (often protein and DNA) using a filter
. The filter is constructed of nitrocellulose
paper, which is negatively charged. Since most proteins have a net positive charge, nitrocellulose paper is ideal for immobilizing proteins. DNA is negatively charged due to the phosphate backbone and will not "stick" to the nitrocellulose on its own, however, any DNA that has been bound by protein will stick. The exact amount of DNA "stuck" to the nitrocellulose is quantified by measuring the amount of radioactivity on the filter using a scintillation counter
Protein and DNA are mixed in a series of microfuge tubes in which the amount of DNA is kept constant, but the amount of protein is incrementally increased. These samples are allowed to equilibrate. After equilibration, an equal volume from each tube is squirted onto small, round, nitrocellulose filters which are arranged on a vacuum plate (a flat surface that has a vacuum applied from below to suck fluid downward). All of the protein will stick, but only the protein that has bound DNA will register in the scintillation counter
.
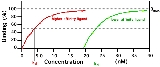
Now, you will have a number that describes the amount of DNA bound for each concentration of protein used, this information can be plotted on a binding curve to determine the binding constant.

This assay is no longer used widely, but it is rapid and simple, and can give a lot of information. It would be used for relatively detailed analysis of a particular protein-DNA interaction, for example.
Measure the equilibrium constant:
Measure the off-rate:
Another way of measuring off-rate:
Biochemistry
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes in living organisms, including, but not limited to, living matter. Biochemistry governs all living organisms and living processes...
or chemistry
Chemistry
Chemistry is the science of matter, especially its chemical reactions, but also its composition, structure and properties. Chemistry is concerned with atoms and their interactions with other atoms, and particularly with the properties of chemical bonds....
, one of the ways to learn about an interaction between two molecules is to determine the binding constant, which is a number that describes the ratio of unbound and bound molecules. This information reveals the affinity between the two molecules and allows prediction of the amount bound given any set of initial conditions.
In order to measure a binding constant, one must find a way to measure the amount of complex formed over a range of starting concentrations. This can be achieved by "labeling" one of the species with a fluorescent, or in this case, a radioactive tag. The DNA is "labeled" by the addition of radioactive Phosphate derived from Adenosine Triphosphate
Adenosine triphosphate
Adenosine-5'-triphosphate is a multifunctional nucleoside triphosphate used in cells as a coenzyme. It is often called the "molecular unit of currency" of intracellular energy transfer. ATP transports chemical energy within cells for metabolism...
.
A filter binding assay is a simple way to quickly study many samples. It measures affinities between two molecules (often protein and DNA) using a filter
Filter (chemistry)
In chemistry and common usage, a filter is a device that is designed to physically block certain objects or substances while letting others through. Filters are often used to remove solid substances suspended in fluids, for example to remove air pollution, to make water drinkable, and to prepare...
. The filter is constructed of nitrocellulose
Nitrocellulose
Nitrocellulose is a highly flammable compound formed by nitrating cellulose through exposure to nitric acid or another powerful nitrating agent. When used as a propellant or low-order explosive, it is also known as guncotton...
paper, which is negatively charged. Since most proteins have a net positive charge, nitrocellulose paper is ideal for immobilizing proteins. DNA is negatively charged due to the phosphate backbone and will not "stick" to the nitrocellulose on its own, however, any DNA that has been bound by protein will stick. The exact amount of DNA "stuck" to the nitrocellulose is quantified by measuring the amount of radioactivity on the filter using a scintillation counter
Scintillation counter
A scintillation counter measures ionizing radiation. The sensor, called a scintillator, consists of a transparent crystal, usually phosphor, plastic , or organic liquid that fluoresces when struck by ionizing radiation. A sensitive photomultiplier tube measures the light from the crystal...
Protein and DNA are mixed in a series of microfuge tubes in which the amount of DNA is kept constant, but the amount of protein is incrementally increased. These samples are allowed to equilibrate. After equilibration, an equal volume from each tube is squirted onto small, round, nitrocellulose filters which are arranged on a vacuum plate (a flat surface that has a vacuum applied from below to suck fluid downward). All of the protein will stick, but only the protein that has bound DNA will register in the scintillation counter
Scintillation counter
A scintillation counter measures ionizing radiation. The sensor, called a scintillator, consists of a transparent crystal, usually phosphor, plastic , or organic liquid that fluoresces when struck by ionizing radiation. A sensitive photomultiplier tube measures the light from the crystal...
.
Now, you will have a number that describes the amount of DNA bound for each concentration of protein used, this information can be plotted on a binding curve to determine the binding constant.

This assay is no longer used widely, but it is rapid and simple, and can give a lot of information. It would be used for relatively detailed analysis of a particular protein-DNA interaction, for example.
Measure the equilibrium constant:
- Incubate labeled DNA with protein.
- Allow enough time to allow the system to reach equilibrium.
- Filter the mixture through a filter disk made of nitrocellulose. Proteins bind to nitrocellulose, but DNA does not.
- Any DNA that is retained on the filter is there because it is interacting with the protein.
- Dry the filters and count.
Measure the off-rate:
- Take the filter with DNA-protein complex bound on it
- Wash the filter with buffer
- Quantify the amount of DNA remained on filter after it has been washed for a certain amount of time.
Another way of measuring off-rate:
- Radioactive labeled DNA and protein were pre-incubated together in high concentrations
- At time 0, the mixture was dilluted
- Aliquotes were assayed at various times using nitrocellulose filters

