
Flash ADC
Encyclopedia
A Flash ADC is a type of analog-to-digital converter
that uses a linear voltage ladder
with a comparator
at each "rung" of the ladder to compare the input voltage to successive reference voltages. Often these reference ladders are constructed of many resistor
s; however modern implementations show that capacitive voltage division is also possible. The output of these comparators is generally fed into a digital encoder which converts the inputs into a binary value (the collected outputs from the comparators can be thought of as a unary
value).
.
A Flash converter requires a huge number of comparator
s compared to other ADCs, especially as the precision increases. A Flash converter requires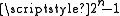 comparators for an n-bit conversion. The size and cost of all those comparators makes Flash converters generally impractical for precisions much greater than 8 bits (255 comparators). In place of these comparators, most other ADCs substitute more complex logic
comparators for an n-bit conversion. The size and cost of all those comparators makes Flash converters generally impractical for precisions much greater than 8 bits (255 comparators). In place of these comparators, most other ADCs substitute more complex logic
which can be scaled more easily for increased precision
.
(BJT) and complementary metal oxide FETs (CMOS) technologies to rarely used III-V technologies. Often this type of ADC is used as a first medium sized analog circuit verification.
The earliest implementations consisted of a reference ladder of well matched resistors connected to a reference voltage. Each tap at the resistor ladder is used for one comparator, possibly preceded by an amplification stage, and thus generates a logical '0' or '1' depending if the measured voltage is above or below the reference voltage of the resistor tap. The reason to add an amplifier is twofold: it amplifies the voltage difference and therefore suppresses the comparator offset, and the kick-back noise of the comparator towards the reference ladder is also strongly suppressed. Typically designs from 4-bit up to 6-bit, and sometimes 7-bit are produced.
Designs with power-saving capacitive reference ladders have been demonstrated. In addition to clocking the comparator(s), these systems also sample the reference value on the input stage. As the sampling is done at a very high rate, the leakage of the capacitors is negligible.
Recently, offset calibration has been introduced in the flash ADC designs. Instead of properly designing the analog circuit (which actually means increasing the components sizes to suppress variation) the offset is removed during use. A test signal is applied and each the offset of each comparator is calibrated to below the LSB size of the ADC. Due to the heavy calibration effort the design are up to now always limited to 4-bits.
Another recent improvement to many flash ADCs is the inclusion of error correction. When the ADC is used to harsh environments or constructed in very small integrated circuit processes, there is a heightened risk of a comparator randomly outputting a wrong code. Bubble error correction is a digital correction mechanism that will prevent a comparator that has tripped high from outputting a high code if it is surrounded by comparators that have not tripped high.
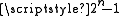 to
to 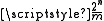 (there is always one needed to detect the range crossover). Typical folding circuits are, e.g., the Gilbert multiplier
(there is always one needed to detect the range crossover). Typical folding circuits are, e.g., the Gilbert multiplier
, or analog wired-or circuits.
loop.
Analog-to-digital converter
An analog-to-digital converter is a device that converts a continuous quantity to a discrete time digital representation. An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement...
that uses a linear voltage ladder
Voltage ladder
A voltage ladder is a simple electronic circuit consisting of several resistors connected in series with a voltage placed across the entire resistor network...
with a comparator
Comparator
In electronics, a comparator is a device that compares two voltages or currents and switches its output to indicate which is larger. They are commonly used in devices such as Analog-to-digital converters .- Input voltage range :...
at each "rung" of the ladder to compare the input voltage to successive reference voltages. Often these reference ladders are constructed of many resistor
Resistor
A linear resistor is a linear, passive two-terminal electrical component that implements electrical resistance as a circuit element.The current through a resistor is in direct proportion to the voltage across the resistor's terminals. Thus, the ratio of the voltage applied across a resistor's...
s; however modern implementations show that capacitive voltage division is also possible. The output of these comparators is generally fed into a digital encoder which converts the inputs into a binary value (the collected outputs from the comparators can be thought of as a unary
Unary numeral system
The unary numeral system is the bijective base-1 numeral system. It is the simplest numeral system to represent natural numbers: in order to represent a number N, an arbitrarily chosen symbol representing 1 is repeated N times. For example, using the symbol | , the number 6 is represented as ||||||...
value).
Benefits and drawbacks
Flash converters are extremely fast compared to many other types of ADCs which usually narrow in on the "correct" answer over a series of stages. Compared to these, a Flash converter is also quite simple and, apart from the analog comparators, only requires logic for the final conversion to binaryBinary numeral system
The binary numeral system, or base-2 number system, represents numeric values using two symbols, 0 and 1. More specifically, the usual base-2 system is a positional notation with a radix of 2...
.
A Flash converter requires a huge number of comparator
Comparator
In electronics, a comparator is a device that compares two voltages or currents and switches its output to indicate which is larger. They are commonly used in devices such as Analog-to-digital converters .- Input voltage range :...
s compared to other ADCs, especially as the precision increases. A Flash converter requires
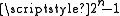 comparators for an n-bit conversion. The size and cost of all those comparators makes Flash converters generally impractical for precisions much greater than 8 bits (255 comparators). In place of these comparators, most other ADCs substitute more complex logic
comparators for an n-bit conversion. The size and cost of all those comparators makes Flash converters generally impractical for precisions much greater than 8 bits (255 comparators). In place of these comparators, most other ADCs substitute more complex logicDigital circuit
Digital electronics represent signals by discrete bands of analog levels, rather than by a continuous range. All levels within a band represent the same signal state...
which can be scaled more easily for increased precision
Accuracy and precision
In the fields of science, engineering, industry and statistics, the accuracy of a measurement system is the degree of closeness of measurements of a quantity to that quantity's actual value. The precision of a measurement system, also called reproducibility or repeatability, is the degree to which...
.
Implementation
Flash ADCs have been implemented in many technologies, varying from silicon based bipolarBipolar junction transistor
|- align = "center"| || PNP|- align = "center"| || NPNA bipolar transistor is a three-terminal electronic device constructed of doped semiconductor material and may be used in amplifying or switching applications. Bipolar transistors are so named because their operation involves both electrons...
(BJT) and complementary metal oxide FETs (CMOS) technologies to rarely used III-V technologies. Often this type of ADC is used as a first medium sized analog circuit verification.
The earliest implementations consisted of a reference ladder of well matched resistors connected to a reference voltage. Each tap at the resistor ladder is used for one comparator, possibly preceded by an amplification stage, and thus generates a logical '0' or '1' depending if the measured voltage is above or below the reference voltage of the resistor tap. The reason to add an amplifier is twofold: it amplifies the voltage difference and therefore suppresses the comparator offset, and the kick-back noise of the comparator towards the reference ladder is also strongly suppressed. Typically designs from 4-bit up to 6-bit, and sometimes 7-bit are produced.
Designs with power-saving capacitive reference ladders have been demonstrated. In addition to clocking the comparator(s), these systems also sample the reference value on the input stage. As the sampling is done at a very high rate, the leakage of the capacitors is negligible.
Recently, offset calibration has been introduced in the flash ADC designs. Instead of properly designing the analog circuit (which actually means increasing the components sizes to suppress variation) the offset is removed during use. A test signal is applied and each the offset of each comparator is calibrated to below the LSB size of the ADC. Due to the heavy calibration effort the design are up to now always limited to 4-bits.
Another recent improvement to many flash ADCs is the inclusion of error correction. When the ADC is used to harsh environments or constructed in very small integrated circuit processes, there is a heightened risk of a comparator randomly outputting a wrong code. Bubble error correction is a digital correction mechanism that will prevent a comparator that has tripped high from outputting a high code if it is surrounded by comparators that have not tripped high.
Folding ADC
The number of comparators can be reduced somewhat by adding a folding circuit in front, making a so called folding ADC. Instead of using the comparators in a Flash ADC only once, during a ramp input signal, the folding ADC re-uses the comparators multiple times. If a m-times folding circuit is used in an n-bit ADC, the actual number of comparator can be reduced from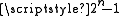 to
to 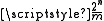 (there is always one needed to detect the range crossover). Typical folding circuits are, e.g., the Gilbert multiplier
(there is always one needed to detect the range crossover). Typical folding circuits are, e.g., the Gilbert multiplierGilbert cell
In electronics, the Gilbert cell is a transistor circuit used as an analog multiplier and frequency mixer, first described by Barrie Gilbert in 1968. The advantage of this circuit is the output current is an accurate multiplication of the base currents of both inputs...
, or analog wired-or circuits.
Application
The very high sample rate of this type of ADC enable Gigahertz applications like radar detection, wide band radio receivers and optical communication links. More often the flash ADC is embedded in a large IC containing many digital decoding functions. Also a small flash ADC circuit may be present inside a Delta-sigma modulationDelta-sigma modulation
Delta-sigma modulation is a method for encoding high-resolution or analog signals into lower-resolution digital signals. The conversion is done using error feedback, where the difference between the two signals is measured and used to improve the conversion...
loop.

