
Flat rate (finance)
Encyclopedia

Informal economy
The informal sector or informal economy as defined by governments, scholars, banks, etc. is the part of an economy that is not taxed, monitored by any form of government, or included in any gross national product , unlike the formal economy....
of developing countries. They are also used by many microfinance
Microfinance
Microfinance is the provision of financial services to low-income clients or solidarity lending groups including consumers and the self-employed, who traditionally lack access to banking and related services....
institutions. One reason for their popularity is their ease of use. For example, a loan of $1,200 can be structured with 12 monthly repayments of $100, plus interest, due on the same dates, of 1% ($12) a month, resulting in a total monthly payment of $112. In the example to the right, the loan contract is for 400,000 Cambodian riel
Cambodian riel
For earlier Cambodian currencies, see Cambodian tical and Cambodian franc.The riel is the currency of Cambodia. There have been two distinct riel, the first issued between 1953 and May 1975. Between 1975 and 1980, the country had no monetary system. A second currency, also named "riel", has been...
s over 4 months. Interest is set at 16,000 riels (4%) a month while principal is due in a single payment at the end.
Flat rate calculations, which are based on the amount of money the borrower receives at the beginning of the loan rather the average amount the borrow has access to during the loan, have been outlawed in developed countries (see for example the Truth in Lending Act
Truth in Lending Act
The Truth in Lending Act of 1968 is United States federal law designed to promote the informed use of consumer credit, by requiring disclosures about its terms and cost to standardize the manner in which costs associated with borrowing are calculated and disclosed...
). However, they persist in many developing countries, and have frequently been adopted by microcredit
Microcredit
Microcredit is the extension of very small loans to those in poverty designed to spur entrepreneurship. These individuals lack collateral, steady employment and a verifiable credit history and therefore cannot meet even the most minimal qualifications to gain access to traditional credit...
institutions.
For a variety of reasons (see below), flat rates can be useful in lending to poor people, and often disappear very slowly as financial systems develop.
Flat rate calculations
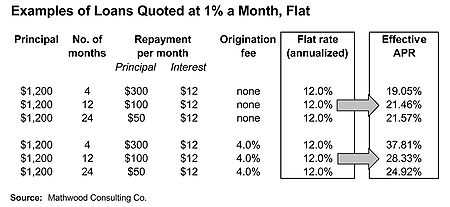
In the first 3 examples on the right the borrower will be quoted 1% a month. These are loans of $1,200 each, amortized with level payments over 4, 12 and 24 months. In the 4-month example, the borrower will make 4 equal payments of $300 in principal and 4 equal payments of $12 (1% of $1,200) in interest. This yields an annualized flat rate of 12%, and an annualized effective APR
Annual percentage rate
The term annual percentage rate , also called nominal APR, and the term effective APR, also called EAR, describe the interest rate for a whole year , rather than just a monthly fee/rate, as applied on a loan, mortgage loan, credit card, etc. It is a finance charge expressed as an annual rate...
of 19.05%.
To keep the quoted interest rate as low as possible, microcredit institutions often recover some of their lending costs by charging one-time origination or administration fees before disbursing loans. Because these fees are deemed an inherent cost of borrowing, developed countries generally require lenders to include them in APR calculations. Even an origination fee as low as 4% of the total loan can have a large impact on the borrower's total costs. This is especially true for short-term loans, as the last 3 examples in the table show. Microcredit loans are usually for 12 months or less.
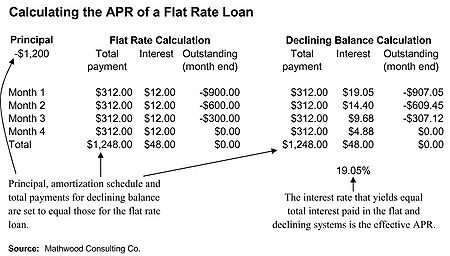
In order to recalculate a flat rate as an effective APR, it is necessary to model a comparable loan using a declining balance amortization schedule
Amortization schedule
An amortization schedule is a table detailing each periodic payment on an amortizing loan , as generated by an amortization calculator. Amortization refers to the process of paying off a debt over time through regular payments...
, resulting in the same total cost to the borrower (see table on the left). The loan is for $1,200 repayable in level monthly payments over 4 months. The total cost of this loan includes the principal plus $48.00 in interest. The effective APR is calculated by iteration from the amortization schedule, using the compound interest
Compound interest
Compound interest arises when interest is added to the principal, so that from that moment on, the interest that has been added also itself earns interest. This addition of interest to the principal is called compounding...
formula.
Benefits of flat rate lending
Flat interest rates persist in emerging and informal financial systems due to the following advantages:- They are easy to calculate and track: Flat interest rates require no calculations to blend principal and interestInterestInterest is a fee paid by a borrower of assets to the owner as a form of compensation for the use of the assets. It is most commonly the price paid for the use of borrowed money, or money earned by deposited funds....
into a level payment, and require no compoundingCompound interestCompound interest arises when interest is added to the principal, so that from that moment on, the interest that has been added also itself earns interest. This addition of interest to the principal is called compounding...
calculations (see the example to the right). Traditional moneylenders often do not have either computers or calculators, and neither do their borrowers, who are often illiterate and/or innumerate. Flat rates keep loan commitments clear, transparent and easily tracked by both parties. Many microfinance institutions do not have computers either, and the complexity of declining balance calculations may confuse their borrowers and even their staff. Semi-formal institutions like self-help groupsSelf-help group (finance)A self-help group is a village-based financial intermediary usually composed of 10–20 local women. Most self-help groups are located in India, though SHGs can also be found in other countries, especially in South Asia and Southeast Asia....
, village banksVillage BankingVillage Banking is a microcredit methodology where-by financial services are administered locally rather than centralized in a formal bank. Village banking has its roots in ancient cultures and was most recently adopted for use by micro-finance institutions as a way to control costs...
and ASCAsRoscaRosca is a Spanish and Portuguese bread dish eaten in Mexico, South America, and other areas. It is made with flour, salt, sugar, butter, yeast, water and seasonings. It is also called ka'ake and referred to as a "Syrian-style crack ring."Roscas de reyes is an oversized version colored with candy...
also usually prefer this calculation method.
- They meet vital cash flow needs of farmers: Many borrowers in developing countries are farmers who demand loans with balloon paymentBalloon paymentWhen a debt is repaid in payments of varying amounts there are some colourful jargon terms used to describe the different loan structures. The term balloon payment arises because if you hold back most of a debt and pay it only towards the end of the agreement, both those last payments and the total...
s, repayable after they harvest their crops. Because the borrower is using the entire amount of principal borrowed throughout the entire loan term, flat rate calculations are accurate when applied to balloon loans.
- They support 'in-kind'Payment in kindPayment in kind refers to payment for goods or services with a medium other than legal tender ....
loan transactions: Flat rate loans originated before currency was invented, and are commonly used to repay loans in regular instalments of chickens, eggs, kilos of rice, and so on. For farmers accustomed to these types of transactions, flat rate cash loans are familiar and easy to understand.
Problems with flat rate lending
Flat interest rates represent a significant problem for financial sector developmentFinancial sector development
Financial sector development in developing countries and emerging markets is part of the private sector development strategy to stimulate economic growth and reduce poverty....
for the following reasons:
- They deter pre-payments by borrowers: Borrowers have an incentive to avoid pre-paying flat-rate loans, as they will lose the use of the borrowed money with no compensating discount in interest payments. Lenders are therefore ensured maximum interest income, which encourages them to continue the practice. Writing of the practices of microfinance institutions in Bangladesh, S.M. Rahman points out that "[i]f one client takes a loan today and offers to repay the entire loan the next day, the client has to repay the total loan along with the whole year's interest, reckoned on a flat rate system."
- They offer convenient level of disclosure for the lender (but not for the borrower): Flat interest rates generally prevail only where declining balance calculations are not familiar to most borrowers, or are not required by law. In such places loans quoted using declining balance rates may be rejected by borrowers, who mistakenly believe that flat rates are cheaper. "Not only the clients but even educated people sometimes have trouble understanding this system. The problem is that the flat rate gives an impression of a lower rate than it actually is."
In addition, microfinance institutions (MFIs) that use flat rates calculations are slightly understating the size of their outstanding loan portfolios, which results in the appearance of a higher portfolio
Portfolio (finance)
Portfolio is a financial term denoting a collection of investments held by an investment company, hedge fund, financial institution or individual.-Definition:The term portfolio refers to any collection of financial assets such as stocks, bonds and cash...
yield
Yield (finance)
In finance, the term yield describes the amount in cash that returns to the owners of a security. Normally it does not include the price variations, at the difference of the total return...
and lower average loan sizes. Both of these characteristics appeal to donors and external financiers.
Towards consumer protection in borrowing
Flat interest rates are controversial in microfinance. Chuck Waterfield, designer of Microfin, a widely used financial modeling tool for MFIs, asks "Why did such a system appear in microfinance lending? The answer is obvious and cannot be debated: it allows the institution to charge nearly twice as much interest for the quoted interest rate as with the declining balance method."As early as 1889, F.W. Raiffeisen
Friedrich Wilhelm Raiffeisen
Friedrich Wilhelm Raiffeisen was a German mayor and cooperative pioneer. Several credit union systems and cooperative banks have been named after Raiffeisen, who pioneered rural credit unions.- Life :...
used both ethical and practical grounds to dissuade the credit union
Credit union
A credit union is a cooperative financial institution that is owned and controlled by its members and operated for the purpose of promoting thrift, providing credit at competitive rates, and providing other financial services to its members...
s then emerging in Germany from adopting flat rate loan pricing. “It is immoral to charge interest in advance, and also objectionable as a business method. Every member shall have the right at any time to pay back his loan. If interest has been charged for a full year in advance, the members who have made repayments ahead of time, pay too much interest, unless the Credit Union makes a refund. The first arrangement is unjust, the latter involves complicated bookkeeping.”
The less developed an economy, the more active informal moneylenders usually are, and the less capacity the government may have to regulate them effectively. As a result, Brigit Helms argues for an evolutionary approach to interest rates, in which they can be expected to gradually drop as competition increases and the government gains greater capacity to effectively enforce comparable interest rate disclosures on financial sector actors. At the same time, interest rate ceilings, and popular conflation of flat rates with declining balance ones, has led many microfinance institutions to replace interest rate points with transaction fees and other charges, circumventing disclosure norms consistent with APR.
See also
- Annual percentage rateAnnual percentage rateThe term annual percentage rate , also called nominal APR, and the term effective APR, also called EAR, describe the interest rate for a whole year , rather than just a monthly fee/rate, as applied on a loan, mortgage loan, credit card, etc. It is a finance charge expressed as an annual rate...
- Flat rateFlat rateA flat fee, also referred to as a flat rate or a linear rate, refers to a pricing structure that charges a single fixed fee for a service, regardless of usage. Rarely, it may refer to a rate that does not vary with usage or time of use...
- InterestInterestInterest is a fee paid by a borrower of assets to the owner as a form of compensation for the use of the assets. It is most commonly the price paid for the use of borrowed money, or money earned by deposited funds....
- MicrofinanceMicrofinanceMicrofinance is the provision of financial services to low-income clients or solidarity lending groups including consumers and the self-employed, who traditionally lack access to banking and related services....
- Truth in Lending ActTruth in Lending ActThe Truth in Lending Act of 1968 is United States federal law designed to promote the informed use of consumer credit, by requiring disclosures about its terms and cost to standardize the manner in which costs associated with borrowing are calculated and disclosed...

