
Flyback diode
Encyclopedia

Diode
In electronics, a diode is a type of two-terminal electronic component with a nonlinear current–voltage characteristic. A semiconductor diode, the most common type today, is a crystalline piece of semiconductor material connected to two electrical terminals...
used to eliminate flyback, the sudden voltage spike
Voltage spike
In electrical engineering, spikes are fast, short duration electrical transients in voltage , current , or transferred energy in an electrical circuit....
seen across an inductive
Inductance
In electromagnetism and electronics, inductance is the ability of an inductor to store energy in a magnetic field. Inductors generate an opposing voltage proportional to the rate of change in current in a circuit...
load when its supply voltage is suddenly reduced or removed.
Working principle
In its most simplified form with a voltage source connected to an inductor with a switch, we have 2 states available. In the first steady-state, the switch has been closed for a long time such that the inductor has become fully energized and is behaving as though it were a short (Figure 1). Current is flowing "down" from the positive terminal of the voltage source to its negative terminal, through the inductor. When the switch is opened (Figure 2), the inductor will attempt to resist the sudden drop of current (dI/dt is large therefore V is large) by using its stored magnetic field energy to create its own voltage. An extremely large negative potential is created where there once was positive potential, and a positive potential is created where there was once negative potential. The switch, however, remains at the voltage of the power supply, but it is still in contact with the inductor pulling down a negative voltage. Since no connection is physically made to allow current to continue to flow (due to the switch being open), the large potential difference can cause electrons to "arc" across the air-gap of the open switch (or junction of a transistor). This is undesirable for the reasons mentioned above and must be prevented.A flyback diode solves this starvation-arc problem by allowing the inductor to draw current from itself (thus, "flyback") in a continuous loop until the energy is dissipated through losses in the wire and across the diode (Figure 3). When the switch is closed the diode is reverse biased against the power supply and doesn't exist in the circuit for practical purposes. However, when the switch is opened, the diode becomes forward biased relative to the inductor (instead of the power supply as before), allowing it to conduct current in a circular loop from the positive potential at the bottom of the inductor to the negative potential at the top (assuming the power supply was supplying positive voltage at the top of the inductor prior to the switch being opened). The voltage across the inductor will merely be a function of the forward voltage drop of the flyback diode, and the distance between the diode and the inductor (according to National Instruments, the flyback diode should be no greater than 18 inches from the inductor). Total time for dissipation can vary, but it will usually last for a few milliseconds.
In these images we observe classic signs of back EMF
Electromotive force
In physics, electromotive force, emf , or electromotance refers to voltage generated by a battery or by the magnetic force according to Faraday's Law, which states that a time varying magnetic field will induce an electric current.It is important to note that the electromotive "force" is not a...
and its elimination through the use of a flyback diode (1N4007). The inductor in this case is a solenoid connected to a 24V DC power supply using 20 awg wire. Each waveform was taken using a digital oscilloscope set to trigger when the voltage across the inductor dipped below zero. In Figure 1 we see the voltage as measured across the switch bounce/spike to around -300 V. In figure 2 a Flyback diode was added in parallel with the solenoid. Instead of spiking to -300 V, the flyback diode only allows approximately -1.4 V of potential to be built up. -1.4V is a combination of the forward bias of the 1N4007 diode (1.1 V) and the foot of wiring separating the diode and the solenoid. The waveform in Figure 2 is much less bouncy than the waveform in Figure 1. In both cases, the total time for the solenoid to discharge is a few milliseconds.
Design
In an ideal flyback diode selection, one would seek a diode which has very large peak forward current capacity (to handle voltage transients without burning out the diode), low forward voltage drop, and a reverse breakdown voltage suited to the inductor's power supply. Depending on the application and equipment involved, some voltage surges can be upwards of 10 times the voltage of the power source, so it is critical to not underestimate the energy contained within an energized inductor.When used with a DC coil relay
Relay
A relay is an electrically operated switch. Many relays use an electromagnet to operate a switching mechanism mechanically, but other operating principles are also used. Relays are used where it is necessary to control a circuit by a low-power signal , or where several circuits must be controlled...
, a flyback diode can cause delayed drop-out of the contacts when power is removed, due to the continued circulation of current in the relay coil and diode. When rapid opening of the contacts is important, a low value resistor can be placed in series with the diode to help dissipate the coil energy faster, at the expense of higher voltage at the switch.
Schottky diode
Schottky diode
The Schottky diode is a semiconductor diode with a low forward voltage drop and a very fast switching action...
s are preferred in flyback diode applications, because they have the lowest forward drop (~0.2 V rather than >0.7 V for low currents) and the fastest (but still "soft") reverse voltage recovery.
Low-cost applications unconcerned with efficiency often use 1N4004, 1N4005 or 1N4007 power diodes as flyback diodes.
Induction at the opening of a contact
According to Lenz's lawLenz's law
Lenz's law is a common way of understanding how electromagnetic circuits must always obey Newton's third law and The Law of Conservation of Energy...
, if the current through an inductance changes, this inductance induces a voltage so the current will go on flowing as long as there is energy in the magnetic field
Magnetic field
A magnetic field is a mathematical description of the magnetic influence of electric currents and magnetic materials. The magnetic field at any given point is specified by both a direction and a magnitude ; as such it is a vector field.Technically, a magnetic field is a pseudo vector;...
. If the current can only flow through the air, the voltage is therefore so high that the air conducts. That is why in mechanically-switched circuits, the near-instantaneous dissipation which occurs without a flyback diode is often observed as an arc across the opening mechanical contacts. Energy is dissipated in this arc primarily as intense heat which causes undesirable premature erosion of the contacts.
Similarly, for non-mechanical solid state switching (i.e., a transistor), large voltage drops across an unactivated solid state switch can destroy the component in question (either instantaneously or through accelerated wear and tear).
Some energy is also lost from the system as a whole and from the arc as a broad spectrum of electromagnetic radiation, in the form of radio waves and light. These radio waves can cause undesirable clicks and pops on nearby radio receivers.
To minimise the antenna-like radiation of this electromagnetic energy from wires connected to the inductor, the flyback diode should be connected as physically close to the inductor as practicable. This approach also minimises those parts of the circuit that are subject to an unwanted high-voltage — a good engineering practice.
Derivation
The voltage at an inductor is, by the law of electromagnetic inductionElectromagnetic induction
Electromagnetic induction is the production of an electric current across a conductor moving through a magnetic field. It underlies the operation of generators, transformers, induction motors, electric motors, synchronous motors, and solenoids....
and the definition of inductance
Inductance
In electromagnetism and electronics, inductance is the ability of an inductor to store energy in a magnetic field. Inductors generate an opposing voltage proportional to the rate of change in current in a circuit...
:
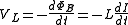
If there is no flyback diode but only something with a great resistance (such as the air between two metal contacts), say, R2, we will approximate it as:
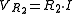
If we open the switch and ignore
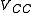 and
and  , we get:
, we get: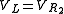
or
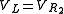
which is a differential equation
Differential equation
A differential equation is a mathematical equation for an unknown function of one or several variables that relates the values of the function itself and its derivatives of various orders...
with the solution:
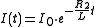
We observe that the current will decrease faster if the resistance is high, such as with air.
Now if we open the switch with the diode in place, we only need to consider L1, R1 and D1.
For
 , we can assume:
, we can assume: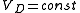
so:
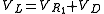
which is:

whose solution is:
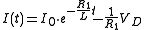
We can calculate the time it needs to switch off by determining for which
 it is
it is 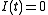 .
.Applications
Flyback diodes are used whenever inductive loads are switched off by silicon components: in relayRelay
A relay is an electrically operated switch. Many relays use an electromagnet to operate a switching mechanism mechanically, but other operating principles are also used. Relays are used where it is necessary to control a circuit by a low-power signal , or where several circuits must be controlled...
drivers, H-bridge
H-bridge
An H bridge is an electronic circuit that enables a voltage to be applied across a load in either direction. These circuits are often used in robotics and other applications to allow DC motors to run forwards and backwards...
motor drivers, and so on. A switched-mode power supply
Switched-mode power supply
A switched-mode power supply is an electronic power supply that incorporates a switching regulator in order to be highly efficient in the conversion of electrical power...
also exploits this effect, but the energy is not dissipated to heat but used to pump a packet of additional charge into a capacitor, in order to supply power to a load.

