
Force of infection
Encyclopedia
In epidemiology
, force of infection (denoted λ) is the rate at which susceptible individuals become infected by an infectious disease
. Because it takes account of susceptibility it can be used to compare the rate of transmission
between different groups of the population
for the same infectious disease, or even between different infectious diseases. That is to say, λ is directly proportional to β; the effective transmission rate.
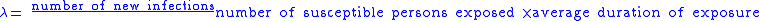
Clearly, there are all kinds of practical difficulties with such a calculation, since not all new infections are reported
, and it is often difficult to know how many susceptibles were exposed.
However, λ can be calculated for an infectious disease in an endemic
state if homogeneous mixing of the population and a rectangular population distribution
(such as that generally found in developed countries) is assumed. In this case, λ is given by:
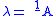
where is the average age of infection.
is the average age of infection.
To understand this relation, think of A as the average time spent in the susceptible group (remembering that for most infectious diseases, before infection an individual is susceptible to the disease but afterwards they have acquired immunity
). The rate at which susceptibles are infected, therefore, is simply 1/A (since rate is 1/time). Recall that λ is also the rate at which susceptibles are infected. This gives us the relation above.
The advantage of this method of calculating λ is that data on the average age of infection is very easily obtainable from doctors' reports, even if they are not reporting all cases of the disease.
Epidemiology
Epidemiology is the study of health-event, health-characteristic, or health-determinant patterns in a population. It is the cornerstone method of public health research, and helps inform policy decisions and evidence-based medicine by identifying risk factors for disease and targets for preventive...
, force of infection (denoted λ) is the rate at which susceptible individuals become infected by an infectious disease
Infectious disease
Infectious diseases, also known as communicable diseases, contagious diseases or transmissible diseases comprise clinically evident illness resulting from the infection, presence and growth of pathogenic biological agents in an individual host organism...
. Because it takes account of susceptibility it can be used to compare the rate of transmission
Transmission risks and rates
Transmission of an infection requires three conditions:*an infectious individual*a susceptible individual*an effective contact between themAn effective contact is defined as any kind of contact between two individuals such that, if one individual is infectious and the other susceptible, then the...
between different groups of the population
Population
A population is all the organisms that both belong to the same group or species and live in the same geographical area. The area that is used to define a sexual population is such that inter-breeding is possible between any pair within the area and more probable than cross-breeding with individuals...
for the same infectious disease, or even between different infectious diseases. That is to say, λ is directly proportional to β; the effective transmission rate.
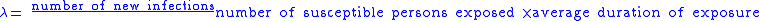
Clearly, there are all kinds of practical difficulties with such a calculation, since not all new infections are reported
UK statutory notification system
The UK statutory notification system for infectious diseases is a system whereby doctors are required to notify a "Proper Officer" of the local authority if they are presented with a case of a serious infectious disease such as diphtheria or measles...
, and it is often difficult to know how many susceptibles were exposed.
However, λ can be calculated for an infectious disease in an endemic
Endemic (epidemiology)
In epidemiology, an infection is said to be endemic in a population when that infection is maintained in the population without the need for external inputs. For example, chickenpox is endemic in the UK, but malaria is not...
state if homogeneous mixing of the population and a rectangular population distribution
Population pyramid
A population pyramid, also called an age structure diagram, is a graphical illustration that shows the distribution of various age groups in a population , which forms the shape of a pyramid when the population is growing...
(such as that generally found in developed countries) is assumed. In this case, λ is given by:
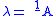
where
 is the average age of infection.
is the average age of infection.To understand this relation, think of A as the average time spent in the susceptible group (remembering that for most infectious diseases, before infection an individual is susceptible to the disease but afterwards they have acquired immunity
Immune system
An immune system is a system of biological structures and processes within an organism that protects against disease by identifying and killing pathogens and tumor cells. It detects a wide variety of agents, from viruses to parasitic worms, and needs to distinguish them from the organism's own...
). The rate at which susceptibles are infected, therefore, is simply 1/A (since rate is 1/time). Recall that λ is also the rate at which susceptibles are infected. This gives us the relation above.
The advantage of this method of calculating λ is that data on the average age of infection is very easily obtainable from doctors' reports, even if they are not reporting all cases of the disease.
See also
- Mathematical modelling in epidemiologyMathematical modelling in epidemiologyIt is possible to mathematically model the progress of most infectious diseases to discover the likely outcome of an epidemic or to help manage them by vaccination...
- Bugchasing and giftgiving

