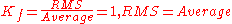Form factor (electronics)
Encyclopedia
In electronics
, the form factor of an alternating current
waveform (signal) is the ratio of the RMS (Root Mean Square
) value to the average value (mathematical mean of absolute values of all points on the waveform).
In case of a sinusoidal wave
, i.e. an analogue wave, the form factor is approximately 1.11.
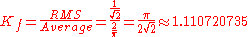
In the case of a square wave
, i.e. a digital wave, the RMS
and the average value are equal; therefore, the form factor is 1.
Electronics
Electronics is the branch of science, engineering and technology that deals with electrical circuits involving active electrical components such as vacuum tubes, transistors, diodes and integrated circuits, and associated passive interconnection technologies...
, the form factor of an alternating current
Alternating current
In alternating current the movement of electric charge periodically reverses direction. In direct current , the flow of electric charge is only in one direction....
waveform (signal) is the ratio of the RMS (Root Mean Square
Root mean square
In mathematics, the root mean square , also known as the quadratic mean, is a statistical measure of the magnitude of a varying quantity. It is especially useful when variates are positive and negative, e.g., sinusoids...
) value to the average value (mathematical mean of absolute values of all points on the waveform).
In case of a sinusoidal wave
Sine wave
The sine wave or sinusoid is a mathematical function that describes a smooth repetitive oscillation. It occurs often in pure mathematics, as well as physics, signal processing, electrical engineering and many other fields...
, i.e. an analogue wave, the form factor is approximately 1.11.
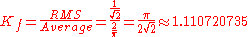
In the case of a square wave
Square wave
A square wave is a kind of non-sinusoidal waveform, most typically encountered in electronics and signal processing. An ideal square wave alternates regularly and instantaneously between two levels...
, i.e. a digital wave, the RMS
Root mean square
In mathematics, the root mean square , also known as the quadratic mean, is a statistical measure of the magnitude of a varying quantity. It is especially useful when variates are positive and negative, e.g., sinusoids...
and the average value are equal; therefore, the form factor is 1.