.gif)
Fort Ward (Virginia)
Encyclopedia
Fort Ward is a former Union Army
installation
now located in the city of Alexandria
in the U.S. state
of Virginia
. It was the fifth largest fort built to defend Washington, D.C.
in the American Civil War
. It is currently well-preserved with 90-95% of its earthen walls intact.
, at the far southeastern corner of the county. In 1861, the rest of the county largely consisted of scattered farms, the occasional house, fields for grazing livestock, and Arlington House
, owned by Mary Custis
, wife of Robert E. Lee
.
Following the surrender of Fort Sumter
in Charleston
, South Carolina
, on April 14, 1861, new American president Abraham Lincoln declared that "an insurrection existed," and called for 75,000 troops to be called up to quash the rebellion. The move sparked resentment in many other southern states, which promptly moved to convene discussions of secession. The Virginia State Convention passed "an ordinance of secession" and ordered a May 23 referendum to decide whether or not the state should secede from the Union. The U.S. Army responded by creating the Department of Washington, which united all Union troops in the District of Columbia and Maryland under one command.
Brigadier General
J.F.K. Mansfield
, commander of the Department of Washington, argued that Northern Virginia should be occupied as soon as possible in order to prevent the possibility of the Confederate Army mounting artillery on the hills of Arlington and shelling government buildings in Washington. He also urged the erection of fortifications on the Virginia side of the Potomac River
to protect the southern terminuses of the Chain Bridge, Long Bridge, and Aqueduct Bridge
. His superiors approved these recommendations, but decided to wait until after Virginia voted for or against secession.
On May 23, 1861, Virginia voted by a margin of 3 to 1 in favor of leaving the Union. That night, U.S. Army troops began crossing the bridges linking Washington, D.C. to Virginia. The march, which began at 10 p.m. on the night of the 23rd, was described in colorful terms by the New York Herald
two days later:

The occupation of Northern Virginia was peaceful, with the sole exception of the town of Alexandria. There, as Colonel
Elmer E. Ellsworth
, commander of the New York Fire Zouaves (11th New York Volunteer Infantry Regiment
), entered a local hotel to remove the Confederate flag flying above it, he was shot and killed by James Jackson, the proprietor. Ellsworth was one of the first men killed in the American Civil War. Throughout the remainder of the war, Alexandria would lean strongly towards the Confederate government, necessitating continued occupation by a Union garrison
.
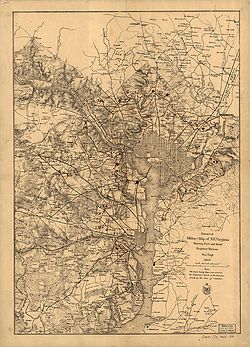 Over the seven weeks that followed the occupation of northern Virginia, forts were constructed along the banks of the Potomac River and at the approaches to each of the three major bridges (Chain Bridge, Long Bridge, and Aqueduct Bridge
Over the seven weeks that followed the occupation of northern Virginia, forts were constructed along the banks of the Potomac River and at the approaches to each of the three major bridges (Chain Bridge, Long Bridge, and Aqueduct Bridge
) connecting Virginia to Washington and Georgetown
.
While the Potomac River forts were being built, planning and surveying was ordered for an enormous new ring of forts to protect the city. Unlike the fortifications under construction, the new forts would defend the city in all directions, not just the most direct route through Arlington. In mid-July, this work was interrupted by the First Battle of Bull Run
. As the Army of Northeastern Virginia
marched south to Manassas
, the soldiers previously assigned to construction duties marched instead to battle. In the days that followed the Union defeat at Bull Run, panicked efforts were made to defend Washington from what was perceived as an imminent Confederate attack. The makeshift trenches and earthworks that resulted were largely confined to Arlington and the direct approaches to Washington.
On July 26, 1861, five days after the battle, Maj. Gen. George B. McClellan
was named commander of the military district of Washington and the subsequently renamed Army of the Potomac
. Upon arriving in Washington, McClellan was appalled by the condition of the city's defenses.
To remedy the situation, one of McClellan's first orders upon taking command was to greatly expand the defenses of Washington. At all points of the compass, forts and entrenchments would be constructed in sufficient strength to defeat any attack. Alexandria, which contained the southern terminus of the Chesapeake and Ohio Canal
and one of the largest ports in the Chesapeake Bay, was an object of "anxious study."
Liberated slaves, also known as “contrabands”, helped build the defenses to protect Washington from invasion by Confederate forces during the Civil War. The Fort was named for the first Union naval officer to die in the war. Fort Ward never saw any attacks, and was dismantled in November 1865, though many African- Americans continued to live there into the 1900s.
, and the museum offers rotating exhibits on American Civil War subjects and a Civil War library. It is listed on the National Register of Historic Places
and hosts Civil War and Revolutionary War
reenactments
. The historic area now includes a museum, an Officer’s Hut, Ceremonial Gate, and reconstructed northwest bastion. The site can be found at 4301 West Braddock Road in Alexandria, Virginia.
Union Army
The Union Army was the land force that fought for the Union during the American Civil War. It was also known as the Federal Army, the U.S. Army, the Northern Army and the National Army...
installation
Military base
A military base is a facility directly owned and operated by or for the military or one of its branches that shelters military equipment and personnel, and facilitates training and operations. In general, a military base provides accommodations for one or more units, but it may also be used as a...
now located in the city of Alexandria
Alexandria, Virginia
Alexandria is an independent city in the Commonwealth of Virginia. As of 2009, the city had a total population of 139,966. Located along the Western bank of the Potomac River, Alexandria is approximately six miles south of downtown Washington, D.C.Like the rest of northern Virginia, as well as...
in the U.S. state
U.S. state
A U.S. state is any one of the 50 federated states of the United States of America that share sovereignty with the federal government. Because of this shared sovereignty, an American is a citizen both of the federal entity and of his or her state of domicile. Four states use the official title of...
of Virginia
Virginia
The Commonwealth of Virginia , is a U.S. state on the Atlantic Coast of the Southern United States. Virginia is nicknamed the "Old Dominion" and sometimes the "Mother of Presidents" after the eight U.S. presidents born there...
. It was the fifth largest fort built to defend Washington, D.C.
Washington, D.C.
Washington, D.C., formally the District of Columbia and commonly referred to as Washington, "the District", or simply D.C., is the capital of the United States. On July 16, 1790, the United States Congress approved the creation of a permanent national capital as permitted by the U.S. Constitution....
in the American Civil War
American Civil War
The American Civil War was a civil war fought in the United States of America. In response to the election of Abraham Lincoln as President of the United States, 11 southern slave states declared their secession from the United States and formed the Confederate States of America ; the other 25...
. It is currently well-preserved with 90-95% of its earthen walls intact.
Occupation of Arlington
Before the outbreak of the Civil War, Alexandria County (renamed Arlington County in 1920), the northernmost county in Virginia and the closest to Washington, D.C., was a predominantly rural area. Originally part of the District of Columbia, the land now comprising the county was retroceded to Virginia in a July 9, 1846 act of Congress that took effect in 1847. Most of the county is hilly, and at the time, most of the county's population was concentrated in the city of AlexandriaAlexandria, Virginia
Alexandria is an independent city in the Commonwealth of Virginia. As of 2009, the city had a total population of 139,966. Located along the Western bank of the Potomac River, Alexandria is approximately six miles south of downtown Washington, D.C.Like the rest of northern Virginia, as well as...
, at the far southeastern corner of the county. In 1861, the rest of the county largely consisted of scattered farms, the occasional house, fields for grazing livestock, and Arlington House
Arlington House, The Robert E. Lee Memorial
Arlington House, The Robert E. Lee Memorial, formerly named the Custis-Lee Mansion, is a Greek revival style mansion located in Arlington, Virginia, USA that was once the home of Confederate General Robert E. Lee. It overlooks the Potomac River, directly across from the National Mall in Washington,...
, owned by Mary Custis
Mary Anna Custis Lee
Mary Anna Randolph Custis Lee was the wife of Confederate General Robert E. Lee.-Biography:Mary Anna Custis Lee was the only surviving child of George Washington Parke Custis, George Washington's step-grandson and adopted son and founder of Arlington House, and Mary Lee Fitzhugh Custis, daughter...
, wife of Robert E. Lee
Robert E. Lee
Robert Edward Lee was a career military officer who is best known for having commanded the Confederate Army of Northern Virginia in the American Civil War....
.
Following the surrender of Fort Sumter
Fort Sumter
Fort Sumter is a Third System masonry coastal fortification located in Charleston Harbor, South Carolina. The fort is best known as the site upon which the shots initiating the American Civil War were fired, at the Battle of Fort Sumter.- Construction :...
in Charleston
Charleston, South Carolina
Charleston is the second largest city in the U.S. state of South Carolina. It was made the county seat of Charleston County in 1901 when Charleston County was founded. The city's original name was Charles Towne in 1670, and it moved to its present location from a location on the west bank of the...
, South Carolina
South Carolina
South Carolina is a state in the Deep South of the United States that borders Georgia to the south, North Carolina to the north, and the Atlantic Ocean to the east. Originally part of the Province of Carolina, the Province of South Carolina was one of the 13 colonies that declared independence...
, on April 14, 1861, new American president Abraham Lincoln declared that "an insurrection existed," and called for 75,000 troops to be called up to quash the rebellion. The move sparked resentment in many other southern states, which promptly moved to convene discussions of secession. The Virginia State Convention passed "an ordinance of secession" and ordered a May 23 referendum to decide whether or not the state should secede from the Union. The U.S. Army responded by creating the Department of Washington, which united all Union troops in the District of Columbia and Maryland under one command.
Brigadier General
Brigadier General
Brigadier general is a senior rank in the armed forces. It is the lowest ranking general officer in some countries, usually sitting between the ranks of colonel and major general. When appointed to a field command, a brigadier general is typically in command of a brigade consisting of around 4,000...
J.F.K. Mansfield
Joseph K. Mansfield
Joseph King Fenno Mansfield was a career United States Army officer, civil engineer, and a Union general in the American Civil War, mortally wounded at the Battle of Antietam.-Early life:...
, commander of the Department of Washington, argued that Northern Virginia should be occupied as soon as possible in order to prevent the possibility of the Confederate Army mounting artillery on the hills of Arlington and shelling government buildings in Washington. He also urged the erection of fortifications on the Virginia side of the Potomac River
Potomac River
The Potomac River flows into the Chesapeake Bay, located along the mid-Atlantic coast of the United States. The river is approximately long, with a drainage area of about 14,700 square miles...
to protect the southern terminuses of the Chain Bridge, Long Bridge, and Aqueduct Bridge
Aqueduct Bridge
Aqueduct Bridge may refer to:*Potomac Aqueduct Bridge*Aqueduct Bridge , see List of bridges on the National Register of Historic Places in Indiana...
. His superiors approved these recommendations, but decided to wait until after Virginia voted for or against secession.
On May 23, 1861, Virginia voted by a margin of 3 to 1 in favor of leaving the Union. That night, U.S. Army troops began crossing the bridges linking Washington, D.C. to Virginia. The march, which began at 10 p.m. on the night of the 23rd, was described in colorful terms by the New York Herald
New York Herald
The New York Herald was a large distribution newspaper based in New York City that existed between May 6, 1835, and 1924.-History:The first issue of the paper was published by James Gordon Bennett, Sr., on May 6, 1835. By 1845 it was the most popular and profitable daily newspaper in the UnitedStates...
two days later:

There can be no more complaints of inactivity of the government. The forward march movement into Virginia, indicated in my despatches last night, took place at the precise time this morning that I named, but in much more imposing and powerful numbers.
About ten o'clock last night four companies of picked men moved over the Long Bridge, as an advance guard. They were sent to reconnoitre, and if assailed were ordered to signal, when they would have been reinforced by a corps of regular infantry and a battery....
At twelve o'clock the infantry regiment, artillery and cavalry corps began to muster and assume marching order. As fast as the several regiments were ready they proceeded to the Long Bridge, those in Washington being directed to take that route.
The troops quartered at Georgetown, the Sixty-ninth, Fifth, Eighth and Twenty-eighth New York regiments, proceeded across what is known as the chain bridge, above the mouth of the Potomac Aqueduct, under the command of General McDowell. They took possession of the heights in that direction.
The imposing scene was at the Long Bridge, where the main body of the troops crossed. Eight thousand infantry, two regular cavalry companies and two sections of Sherman's artillery battalion, consisting of two batteries, were in line this side of the Long Bridge at two o'clock.
The occupation of Northern Virginia was peaceful, with the sole exception of the town of Alexandria. There, as Colonel
Colonel
Colonel , abbreviated Col or COL, is a military rank of a senior commissioned officer. It or a corresponding rank exists in most armies and in many air forces; the naval equivalent rank is generally "Captain". It is also used in some police forces and other paramilitary rank structures...
Elmer E. Ellsworth
Elmer E. Ellsworth
-External links:* * * * * *...
, commander of the New York Fire Zouaves (11th New York Volunteer Infantry Regiment
11th New York Volunteer Infantry Regiment
The 11th New York Volunteer Infantry Regiment was an infantry regiment of Union Army in the early years of the American Civil War. The regiment was organized in New York City in May 1861 as a Zouave regiment, known for its unusual dress and drill style, by Colonel Elmer E. Ellsworth, a personal...
), entered a local hotel to remove the Confederate flag flying above it, he was shot and killed by James Jackson, the proprietor. Ellsworth was one of the first men killed in the American Civil War. Throughout the remainder of the war, Alexandria would lean strongly towards the Confederate government, necessitating continued occupation by a Union garrison
Garrison
Garrison is the collective term for a body of troops stationed in a particular location, originally to guard it, but now often simply using it as a home base....
.
Battle of Bull Run

Potomac Aqueduct Bridge
The Aqueduct Bridge was a bridge between Georgetown, Washington, D.C., and Rosslyn, Virginia, in Arlington County. It was built to transport cargo-carrying boats on the Chesapeake and Ohio Canal in Georgetown across the Potomac River to the Alexandria Canal...
) connecting Virginia to Washington and Georgetown
Georgetown, Maryland
Georgetown is an unincorporated community in Kent County, Maryland, United States. The former Georgetown located in Montgomery County, Maryland, was incorporated into the District of Columbia when it was created in 1790.-References:...
.
While the Potomac River forts were being built, planning and surveying was ordered for an enormous new ring of forts to protect the city. Unlike the fortifications under construction, the new forts would defend the city in all directions, not just the most direct route through Arlington. In mid-July, this work was interrupted by the First Battle of Bull Run
First Battle of Bull Run
First Battle of Bull Run, also known as First Manassas , was fought on July 21, 1861, in Prince William County, Virginia, near the City of Manassas...
. As the Army of Northeastern Virginia
Army of the Potomac
The Army of the Potomac was the major Union Army in the Eastern Theater of the American Civil War.-History:The Army of the Potomac was created in 1861, but was then only the size of a corps . Its nucleus was called the Army of Northeastern Virginia, under Brig. Gen...
marched south to Manassas
Manassas, Virginia
The City of Manassas is an independent city surrounded by Prince William County and the independent city of Manassas Park in the Commonwealth of Virginia in the United States. Its population was 37,821 as of 2010. Manassas also surrounds the county seat for Prince William County but that county...
, the soldiers previously assigned to construction duties marched instead to battle. In the days that followed the Union defeat at Bull Run, panicked efforts were made to defend Washington from what was perceived as an imminent Confederate attack. The makeshift trenches and earthworks that resulted were largely confined to Arlington and the direct approaches to Washington.
On July 26, 1861, five days after the battle, Maj. Gen. George B. McClellan
George B. McClellan
George Brinton McClellan was a major general during the American Civil War. He organized the famous Army of the Potomac and served briefly as the general-in-chief of the Union Army. Early in the war, McClellan played an important role in raising a well-trained and organized army for the Union...
was named commander of the military district of Washington and the subsequently renamed Army of the Potomac
Army of the Potomac
The Army of the Potomac was the major Union Army in the Eastern Theater of the American Civil War.-History:The Army of the Potomac was created in 1861, but was then only the size of a corps . Its nucleus was called the Army of Northeastern Virginia, under Brig. Gen...
. Upon arriving in Washington, McClellan was appalled by the condition of the city's defenses.
"In no quarter were the dispositions for defense such as to offer a vigorous resistance to a respectable body of the enemy, either in the position and numbers of the troops or the number and character of the defensive works... not a single defensive work had been commenced on the Maryland side. There was nothing to prevent the enemy shelling the city from heights within easy range, which could be occupied by a hostile column almost without resistance."
To remedy the situation, one of McClellan's first orders upon taking command was to greatly expand the defenses of Washington. At all points of the compass, forts and entrenchments would be constructed in sufficient strength to defeat any attack. Alexandria, which contained the southern terminus of the Chesapeake and Ohio Canal
Chesapeake and Ohio Canal
The Chesapeake and Ohio Canal, abbreviated as the C&O Canal, and occasionally referred to as the "Grand Old Ditch," operated from 1831 until 1924 parallel to the Potomac River in Maryland from Cumberland, Maryland to Washington, D.C. The total length of the canal is about . The elevation change of...
and one of the largest ports in the Chesapeake Bay, was an object of "anxious study."
Planning and construction
Gen. John Newton, who was in charge of the forts south of Four Mile Run, supervised the construction and managed the flow of men and material.Liberated slaves, also known as “contrabands”, helped build the defenses to protect Washington from invasion by Confederate forces during the Civil War. The Fort was named for the first Union naval officer to die in the war. Fort Ward never saw any attacks, and was dismantled in November 1865, though many African- Americans continued to live there into the 1900s.
Fort Ward Museum
The fort is now a part of the City of Alexandria's 45 acres (18.2 ha) Fort Ward Museum and Historic Site adjacent to Braddock RoadBraddock Road (Alexandria, Virginia)
Braddock Road in the City of Alexandria runs northwestward from West Street near the Braddock Road Metro station to the Alexandria campus of the Northern Virginia Community College, just beyond Beauregard Street...
, and the museum offers rotating exhibits on American Civil War subjects and a Civil War library. It is listed on the National Register of Historic Places
National Register of Historic Places
The National Register of Historic Places is the United States government's official list of districts, sites, buildings, structures, and objects deemed worthy of preservation...
and hosts Civil War and Revolutionary War
American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War , the American War of Independence, or simply the Revolutionary War, began as a war between the Kingdom of Great Britain and thirteen British colonies in North America, and ended in a global war between several European great powers.The war was the result of the...
reenactments
Historical reenactment
Historical reenactment is an educational activity in which participants attempt torecreate some aspects of a historical event or period. This may be as narrow as a specific moment from a battle, such as the reenactment of Pickett's Charge at the Great Reunion of 1913, or as broad as an entire...
. The historic area now includes a museum, an Officer’s Hut, Ceremonial Gate, and reconstructed northwest bastion. The site can be found at 4301 West Braddock Road in Alexandria, Virginia.

