
Four factor formula
Encyclopedia
The four-factor formula is used in nuclear engineering
to determine the multiplication of a nuclear chain reaction
in an infinite medium. The formula is
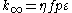
The six factor formula defines each of these terms in much more detail.
):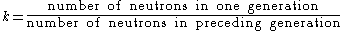
If k is greater than 1, the chain reaction is supercritical, and the neutron population will grow exponentially.
If k is less than 1, the chain reaction is subcritical, and the neutron population will exponentially decay.
If k = 1, the chain reaction is critical and the neutron population will remain constant.
In an infinite medium, neutrons cannot leak out of the system and the multiplication factor becomes the infinite multiplication factor, , which is approximated by the four-factor formula.
, which is approximated by the four-factor formula.
Nuclear engineering
Nuclear engineering is the branch of engineering concerned with the application of the breakdown as well as the fusion of atomic nuclei and/or the application of other sub-atomic physics, based on the principles of nuclear physics...
to determine the multiplication of a nuclear chain reaction
Nuclear chain reaction
A nuclear chain reaction occurs when one nuclear reaction causes an average of one or more nuclear reactions, thus leading to a self-propagating number of these reactions. The specific nuclear reaction may be the fission of heavy isotopes or the fusion of light isotopes...
in an infinite medium. The formula is
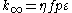
| Symbol | Name | Meaning | Formula |
|---|---|---|---|
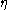 |
Reproduction Factor (Eta) | The number of fission neutron Neutron The neutron is a subatomic hadron particle which has the symbol or , no net electric charge and a mass slightly larger than that of a proton. With the exception of hydrogen, nuclei of atoms consist of protons and neutrons, which are therefore collectively referred to as nucleons. The number of... s produced per absorption in the fuel. |
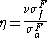 |
 |
The thermal utilization factor | Probability that a neutron that gets absorbed does so in the fuel material. | 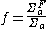 |
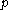 |
The resonance escape probability | Fraction of fission neutrons that manage to slow down from fission to thermal energies without being absorbed. | 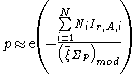 |
 |
The fast fission factor | 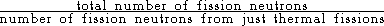 |
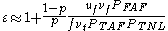 |
The six factor formula defines each of these terms in much more detail.
Multiplication
The multiplication factor, k, is defined as (see Nuclear chain reactionNuclear chain reaction
A nuclear chain reaction occurs when one nuclear reaction causes an average of one or more nuclear reactions, thus leading to a self-propagating number of these reactions. The specific nuclear reaction may be the fission of heavy isotopes or the fusion of light isotopes...
):
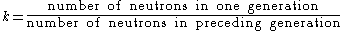
If k is greater than 1, the chain reaction is supercritical, and the neutron population will grow exponentially.
If k is less than 1, the chain reaction is subcritical, and the neutron population will exponentially decay.
If k = 1, the chain reaction is critical and the neutron population will remain constant.
In an infinite medium, neutrons cannot leak out of the system and the multiplication factor becomes the infinite multiplication factor,
 , which is approximated by the four-factor formula.
, which is approximated by the four-factor formula.See also
- Six factor formula
- Critical massCritical massA critical mass is the smallest amount of fissile material needed for a sustained nuclear chain reaction. The critical mass of a fissionable material depends upon its nuclear properties A critical mass is the smallest amount of fissile material needed for a sustained nuclear chain reaction. The...
- Nuclear chain reactionNuclear chain reactionA nuclear chain reaction occurs when one nuclear reaction causes an average of one or more nuclear reactions, thus leading to a self-propagating number of these reactions. The specific nuclear reaction may be the fission of heavy isotopes or the fusion of light isotopes...
- Nuclear reactorNuclear reactorA nuclear reactor is a device to initiate and control a sustained nuclear chain reaction. Most commonly they are used for generating electricity and for the propulsion of ships. Usually heat from nuclear fission is passed to a working fluid , which runs through turbines that power either ship's...

