
Free energy perturbation
Encyclopedia
Free energy perturbation (FEP) theory is a method based on statistical mechanics
that is used in computational chemistry
for computing free energy
differences from molecular dynamics
or Metropolis Monte Carlo simulations. The FEP method was introduced by R. W. Zwanzig in 1954. According to free-energy perturbation theory, the free energy difference for going from state A to state B is obtained from the following equation, known as the Zwanzig equation:
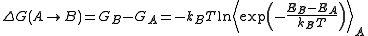
where T is the temperature
, kB is Boltzmann's constant, and the triangular brackets denote an average over a simulation run for state A. In practice, one
runs a normal simulation for state A, but each time a
new configuration is accepted, the energy for state B is also computed. The difference
between states A and B may be in the atom types involved, in which case the ΔG
obtained is for "mutating" one molecule onto another, or it may be a difference of
geometry, in which case one obtains a free energy map along one or more reaction coordinate
s.
This free energy map is also known as a potential of mean force
or PMF.
Free energy perturbation calculations only converge properly when the difference
between the two states is small enough; therefore it is usually necessary to divide a
perturbation into a series of smaller “windows”, which are computed independently.
Since there is no need for constant communication between the simulation for one
window and the next, the process can be trivially parallelized by running each window in
a different CPU, in what is known as an “embarrassingly parallel
” setup.
FEP calculations have been used for studying host-guest binding energetics,
pKa
predictions, solvent effects
on reactions, and enzymatic reactions. For the
study of reactions it is often necessary to involve a quantum-mechanical
representation of
the reaction center because the molecular mechanics
force field
s used for FEP simulations can't handle
breaking bonds. A hybrid method that has the advantages of both QM and MM
calculations is called QM/MM
.
Umbrella sampling is another free-energy calculation technique that is typically used for calculating the free-energy change associated with a change in "position" coordinates as opposed to "chemical" coordinates, although Umbrella sampling can also be used for a chemical transformation when the "chemical" coordinate is treated as a dynamic variable (as in the case of the Lambda dynamics approach of Kong and Brooks).
An alternative to free energy perturbation for computing potentials of mean force in chemical space is thermodynamic integration
. Another alternative, which is probably more efficient, is the Bennett acceptance ratio
method.
Statistical mechanics
Statistical mechanics or statistical thermodynamicsThe terms statistical mechanics and statistical thermodynamics are used interchangeably...
that is used in computational chemistry
Computational chemistry
Computational chemistry is a branch of chemistry that uses principles of computer science to assist in solving chemical problems. It uses the results of theoretical chemistry, incorporated into efficient computer programs, to calculate the structures and properties of molecules and solids...
for computing free energy
Thermodynamic free energy
The thermodynamic free energy is the amount of work that a thermodynamic system can perform. The concept is useful in the thermodynamics of chemical or thermal processes in engineering and science. The free energy is the internal energy of a system less the amount of energy that cannot be used to...
differences from molecular dynamics
Molecular dynamics
Molecular dynamics is a computer simulation of physical movements of atoms and molecules. The atoms and molecules are allowed to interact for a period of time, giving a view of the motion of the atoms...
or Metropolis Monte Carlo simulations. The FEP method was introduced by R. W. Zwanzig in 1954. According to free-energy perturbation theory, the free energy difference for going from state A to state B is obtained from the following equation, known as the Zwanzig equation:
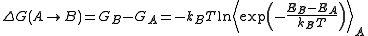
where T is the temperature
Temperature
Temperature is a physical property of matter that quantitatively expresses the common notions of hot and cold. Objects of low temperature are cold, while various degrees of higher temperatures are referred to as warm or hot...
, kB is Boltzmann's constant, and the triangular brackets denote an average over a simulation run for state A. In practice, one
runs a normal simulation for state A, but each time a
new configuration is accepted, the energy for state B is also computed. The difference
between states A and B may be in the atom types involved, in which case the ΔG
obtained is for "mutating" one molecule onto another, or it may be a difference of
geometry, in which case one obtains a free energy map along one or more reaction coordinate
Reaction coordinate
In chemistry, a reaction coordinate is an abstract one-dimensional coordinate which represents progress along a reaction pathway. It is usually a geometric parameter that changes during the conversion of one or more molecular entities....
s.
This free energy map is also known as a potential of mean force
Potential of mean force
The Potential of Mean Force of a system with N molecules is strictly the potential that gives the average force over all the configurations of all the n+1...N molecules acting on a particle at any fixed configuration keeping fixed a set of molecules 1...n...
or PMF.
Free energy perturbation calculations only converge properly when the difference
between the two states is small enough; therefore it is usually necessary to divide a
perturbation into a series of smaller “windows”, which are computed independently.
Since there is no need for constant communication between the simulation for one
window and the next, the process can be trivially parallelized by running each window in
a different CPU, in what is known as an “embarrassingly parallel
Embarrassingly parallel
In parallel computing, an embarrassingly parallel workload is one for which little or no effort is required to separate the problem into a number of parallel tasks...
” setup.
FEP calculations have been used for studying host-guest binding energetics,
pKa
PKA
PKA, pKa, or other similar variations may stand for:* pKa, the symbol for the acid dissociation constant at logarithmic scale* Protein kinase A, a class of cAMP-dependent enzymes* Pi Kappa Alpha, the North-American social fraternity...
predictions, solvent effects
Solvent effects
In chemistry, Solvent effects is the group of effects that a solvent has on chemical reactivity. Solvents can have an effect on solubility, stability and reaction rates and choosing the appropriate solvent allows for thermodynamic and kinetic control over a chemical reaction.-Effects on...
on reactions, and enzymatic reactions. For the
study of reactions it is often necessary to involve a quantum-mechanical
Quantum mechanics
Quantum mechanics, also known as quantum physics or quantum theory, is a branch of physics providing a mathematical description of much of the dual particle-like and wave-like behavior and interactions of energy and matter. It departs from classical mechanics primarily at the atomic and subatomic...
representation of
the reaction center because the molecular mechanics
Molecular mechanics
Molecular mechanics uses Newtonian mechanics to model molecular systems. The potential energy of all systems in molecular mechanics is calculated using force fields...
force field
Force field (chemistry)
In the context of molecular modeling, a force field refers to the form and parameters of mathematical functions used to describe the potential energy of a system of particles . Force field functions and parameter sets are derived from both experimental work and high-level quantum mechanical...
s used for FEP simulations can't handle
breaking bonds. A hybrid method that has the advantages of both QM and MM
calculations is called QM/MM
QM/MM
The hybrid QM/MM approach is a molecular simulation method that combines the strength of both QM and MM calculations, thus allowing for the study of chemical processes in solution and in proteins. The QM/MM approach was introduced in the 1976 paper of Warshel and Levitt .An important advantage...
.
Umbrella sampling is another free-energy calculation technique that is typically used for calculating the free-energy change associated with a change in "position" coordinates as opposed to "chemical" coordinates, although Umbrella sampling can also be used for a chemical transformation when the "chemical" coordinate is treated as a dynamic variable (as in the case of the Lambda dynamics approach of Kong and Brooks).
An alternative to free energy perturbation for computing potentials of mean force in chemical space is thermodynamic integration
Thermodynamic integration
Thermodynamic integration is a method used to compare the difference in the thermodynamic quantity of two given states in molecular dynamics simulation...
. Another alternative, which is probably more efficient, is the Bennett acceptance ratio
Bennett acceptance ratio
The Bennett acceptance ratio method is an algorithm for estimating the difference in free energy between two systems .It was suggested by Charles H. Bennett in 1976....
method.

