
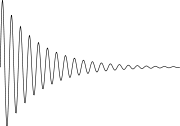
Free induction decay
Encyclopedia
Larmor precession
In physics, Larmor precession is the precession of the magnetic moments of electrons, atomic nuclei, and atoms about an external magnetic field...
about the magnetic field
Magnetic field
A magnetic field is a mathematical description of the magnetic influence of electric currents and magnetic materials. The magnetic field at any given point is specified by both a direction and a magnitude ; as such it is a vector field.Technically, a magnetic field is a pseudo vector;...
(conventionally along z).
This non-equilibrium magnetisation can be induced, generally by applying a pulse of resonant
Resonance
In physics, resonance is the tendency of a system to oscillate at a greater amplitude at some frequencies than at others. These are known as the system's resonant frequencies...
radio-frequency close to the Larmor frequency of the nuclear spins.
If the magnetisation vector has a non-zero component in the xy plane, then the precessing magnetisation will induce
Electromagnetic induction
Electromagnetic induction is the production of an electric current across a conductor moving through a magnetic field. It underlies the operation of generators, transformers, induction motors, electric motors, synchronous motors, and solenoids....
a corresponding oscillating voltage in a detection coil surrounding the sample. This time-domain signal is typically digitised and then Fourier transformed
Fourier transform
In mathematics, Fourier analysis is a subject area which grew from the study of Fourier series. The subject began with the study of the way general functions may be represented by sums of simpler trigonometric functions...
in order to obtain a frequency spectrum of the NMR signal i.e. the NMR spectrum
Spectrum
A spectrum is a condition that is not limited to a specific set of values but can vary infinitely within a continuum. The word saw its first scientific use within the field of optics to describe the rainbow of colors in visible light when separated using a prism; it has since been applied by...
.
The duration of the NMR signal is ultimately limited by T2 relaxation
Relaxation (NMR)
In nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy and magnetic resonance imaging the term relaxation describes several processes by which nuclear magnetization prepared in a non-equilibrium state return to the equilibrium distribution. In other words, relaxation describes how fast spins "forget" the...
, but mutual interference of the different NMR frequencies present also causes the signal to be damped more quickly.
When NMR frequencies are well-resolved, as is typically the case in the NMR of samples in solution, the overall decay of the FID is relaxation-limited and the FID is approximately exponential (with a time constant T2 or more accurately T2*). FID durations will then be of the order of seconds for nuclei such as 1H. If NMR lineshapes are not relaxation-limited (as is commonly the case in solid-state NMR), then the NMR signal will generally decay much more quickly e.g. microseconds for 1H NMR.
Particularly if a limited number of frequency components are present, the FID may be analysed directly for quantitative determinations of physical properties, such as hydrogen content in aviation fuel, solid and liquid ratio in dairy products (Time-Domain NMR).

