
Frequency divider
Encyclopedia
A frequency divider, also called a clock divider or scaler or prescaler, is a circuit
that takes an input signal of a frequency
, , and generates an output signal of a frequency:
, and generates an output signal of a frequency:
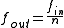
where is an integer. Phase-locked loop
is an integer. Phase-locked loop
frequency synthesizer
s make use of frequency dividers to generate a frequency that is a multiple of a reference frequency. Frequency dividers can be implemented for both analog and digital
applications.
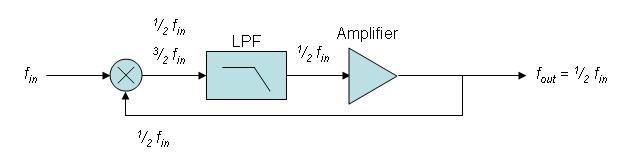 The feedback signal is
The feedback signal is 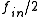 . This produces sum and difference frequencies
. This produces sum and difference frequencies 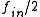 ,
, 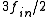 at the output of the mixer. A low pass filter removes the higher frequency and the
at the output of the mixer. A low pass filter removes the higher frequency and the 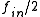 frequency is amplified and fed back into mixer.
frequency is amplified and fed back into mixer.
Steady state examination seems simple enough however startup is more complicated. In order to establish a stable 1/2 frequency feedback, the amplifier gain at the half frequency must be greater than unity. The phase shift must also be an integer multiple of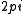 .
.
.
It operates similarly to an injection locked oscillator. In an injection locked frequency divider, the frequency of the input signal is a multiple (or fraction) of the free-running frequency of the oscillator. While these frequency dividers tend to be lower power than broadband static (or flip-flop based) frequency dividers, the drawback is their low locking range. The ILFD locking range is inversely proportional to the quality factor (Q) of the oscillator tank. In integrated circuit designs, this makes an ILFD sensitive to process variations. Care must be taken to ensure the tuning range of the driving circuit (for example, a voltage-controlled oscillator) must fall within the input locking range of the ILFD.
are a classic method for integer-n division. Such division is frequency and phase coherent to the source over environmental variations including temperature. The easiest configuration is a series where each flip-flop is a divide-by-2. For a series of three of these, such system would be a divide-by-8. By adding additional logic gates to the chain of flip flops, other division ratios can be obtained. Integrated circuit logic families can provide a single chip solution for some common division ratios.
Another popular circuit to divide a digital signal by an even integer multiple is a Johnson counter. This is a type of shift register
network that is clocked by the input signal. The last register's complemented output is fed back to the first register's input. The output signal is derived from one or more of the register outputs. For example, a divide-by-6 divider can be constructed with a 3-register Johnson counter. The three valid values for each register are 000, 100, 110, 111, 011, and 001. This pattern repeats each time the network is clocked by the input signal. The output of each register is a f/6 square wave with 60° of phase shift between registers. Additional registers can be added to provide additional integer divisors.
sequential logic
)
An arrangement of D flip-flops are a classic method for integer-n division. Such division is frequency and phase coherent to the source over environmental variations including temperature. The easiest configuration is a series where each D flip-flop is a divide-by-2. For a series of three of these, such system would be a divide-by-8. More complicated configurations have been found that generate odd factors such as a divide-by-5. Standard, classic logic chips that implement this or similar frequency division functions include the 7456, 7457, 74292, and 74294. (see List of 7400 series integrated circuits)
alternates between one locked frequency and the other. The VCO stabilizes at a frequency that is the time average of the two locked frequencies. By varying the percentage of time the frequency divider spends at the two divider values, the frequency of the locked VCO can be selected with very fine granularity.
Electronic circuit
An electronic circuit is composed of individual electronic components, such as resistors, transistors, capacitors, inductors and diodes, connected by conductive wires or traces through which electric current can flow...
that takes an input signal of a frequency
Frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit time. It is also referred to as temporal frequency.The period is the duration of one cycle in a repeating event, so the period is the reciprocal of the frequency...
,
 , and generates an output signal of a frequency:
, and generates an output signal of a frequency: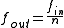
where
 is an integer. Phase-locked loop
is an integer. Phase-locked loopPhase-locked loop
A phase-locked loop or phase lock loop is a control system that generates an output signal whose phase is related to the phase of an input "reference" signal. It is an electronic circuit consisting of a variable frequency oscillator and a phase detector...
frequency synthesizer
Frequency synthesizer
A frequency synthesizer is an electronic system for generating any of a range of frequencies from a single fixed timebase or oscillator. They are found in many modern devices, including radio receivers, mobile telephones, radiotelephones, walkie-talkies, CB radios, satellite receivers, GPS systems,...
s make use of frequency dividers to generate a frequency that is a multiple of a reference frequency. Frequency dividers can be implemented for both analog and digital
Digital
A digital system is a data technology that uses discrete values. By contrast, non-digital systems use a continuous range of values to represent information...
applications.
Analog dividers
Analog frequency dividers are really something special and nowadays used only at very high frequencies. Digital dividers implemented in modern IC technologies can work up to tens of GHz.Regenerative frequency divider
A regenerative frequency divider, also known as a Miller frequency divider, mixes the input signal with the feedback signal from the mixer.
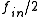 . This produces sum and difference frequencies
. This produces sum and difference frequencies 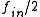 ,
, 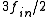 at the output of the mixer. A low pass filter removes the higher frequency and the
at the output of the mixer. A low pass filter removes the higher frequency and the 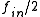 frequency is amplified and fed back into mixer.
frequency is amplified and fed back into mixer.Steady state examination seems simple enough however startup is more complicated. In order to establish a stable 1/2 frequency feedback, the amplifier gain at the half frequency must be greater than unity. The phase shift must also be an integer multiple of
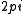 .
.Injection-locked frequency divider
A free-running oscillator which has a small amount of a higher-frequency signal fed to it will tend to oscillate in step with the input signal. Such frequency dividers were essential in the development of televisionTelevision
Television is a telecommunication medium for transmitting and receiving moving images that can be monochrome or colored, with accompanying sound...
.
It operates similarly to an injection locked oscillator. In an injection locked frequency divider, the frequency of the input signal is a multiple (or fraction) of the free-running frequency of the oscillator. While these frequency dividers tend to be lower power than broadband static (or flip-flop based) frequency dividers, the drawback is their low locking range. The ILFD locking range is inversely proportional to the quality factor (Q) of the oscillator tank. In integrated circuit designs, this makes an ILFD sensitive to process variations. Care must be taken to ensure the tuning range of the driving circuit (for example, a voltage-controlled oscillator) must fall within the input locking range of the ILFD.
Digital dividers
For power-of-2 integer division, a simple binary counter can be used, clocked by the input signal. The least-significant output bit alternates at 1/2 the rate of the input clock, the next bit at 1/4 the rate, the third bit at 1/8 the rate, etc. An arrangement of flipflopsFlip-flop (electronics)
In electronics, a flip-flop or latch is a circuit that has two stable states and can be used to store state information. The circuit can be made to change state by signals applied to one or more control inputs and will have one or two outputs. It is the basic storage element in sequential logic...
are a classic method for integer-n division. Such division is frequency and phase coherent to the source over environmental variations including temperature. The easiest configuration is a series where each flip-flop is a divide-by-2. For a series of three of these, such system would be a divide-by-8. By adding additional logic gates to the chain of flip flops, other division ratios can be obtained. Integrated circuit logic families can provide a single chip solution for some common division ratios.
Another popular circuit to divide a digital signal by an even integer multiple is a Johnson counter. This is a type of shift register
Shift register
In digital circuits, a shift register is a cascade of flip flops, sharing the same clock, which has the output of any one but the last flip-flop connected to the "data" input of the next one in the chain, resulting in a circuit that shifts by one position the one-dimensional "bit array" stored in...
network that is clocked by the input signal. The last register's complemented output is fed back to the first register's input. The output signal is derived from one or more of the register outputs. For example, a divide-by-6 divider can be constructed with a 3-register Johnson counter. The three valid values for each register are 000, 100, 110, 111, 011, and 001. This pattern repeats each time the network is clocked by the input signal. The output of each register is a f/6 square wave with 60° of phase shift between registers. Additional registers can be added to provide additional integer divisors.
Mixed signal division
(Classification: asynchronousAsynchronous circuit
An asynchronous circuit is a circuit in which the parts are largely autonomous. They are not governed by a clock circuit or global clock signal, but instead need only wait for the signals that indicate completion of instructions and operations. These signals are specified by simple data transfer...
sequential logic
Sequential logic
In digital circuit theory, sequential logic is a type of logic circuit whose output depends not only on the present input but also on the history of the input. This is in contrast to combinational logic, whose output is a function of, and only of, the present input...
)
An arrangement of D flip-flops are a classic method for integer-n division. Such division is frequency and phase coherent to the source over environmental variations including temperature. The easiest configuration is a series where each D flip-flop is a divide-by-2. For a series of three of these, such system would be a divide-by-8. More complicated configurations have been found that generate odd factors such as a divide-by-5. Standard, classic logic chips that implement this or similar frequency division functions include the 7456, 7457, 74292, and 74294. (see List of 7400 series integrated circuits)
Fractional-n dividers
A fractional-n frequency synthesizer can be constructed using two integer dividers, a divide-by-n and a divide-by-(n + 1) frequency divider. With a modulus controller, n is toggled between the two values so that the VCOVoltage-controlled oscillator
A voltage-controlled oscillator or VCO is an electronic oscillator designed to be controlled in oscillation frequency by a voltage input. The frequency of oscillation is varied by the applied DC voltage, while modulating signals may also be fed into the VCO to cause frequency modulation or phase...
alternates between one locked frequency and the other. The VCO stabilizes at a frequency that is the time average of the two locked frequencies. By varying the percentage of time the frequency divider spends at the two divider values, the frequency of the locked VCO can be selected with very fine granularity.
Delta-sigma fractional-n synthesizers
If the sequence of divide by n and divide by (n + 1) is periodic, spurious signals appear at the VCO output in addition to the desired frequency. Delta-sigma fractional-n dividers overcome this problem by randomizing the selection of n and (n + 1), while maintaining the time-averaged ratios.See also
- Phase-locked loopPhase-locked loopA phase-locked loop or phase lock loop is a control system that generates an output signal whose phase is related to the phase of an input "reference" signal. It is an electronic circuit consisting of a variable frequency oscillator and a phase detector...
- PrescalerPrescalerA prescaler is an electronic counting circuit used to reduce a high frequency electrical signal to a lower frequency by integer division.-Example of use:...
- pulse swallowing counterPulse swallowing counterA pulse-swallowing counter is a component in an all-digital feedback system. The overall pulse-swallowing system is used as part of a fractional-N frequency divider. The overall pulse-swallowing system cancels beatnotes created when switching between N, N+1, or N−1 in a fractional-N...
, pulse swallowing divider

