
Fresnel lantern
Encyclopedia


Stage lighting instrument
Stage lighting instruments are used in stage lighting to illuminate theatrical productions, concerts, and other performances taking place in live performance venues. They are also used to light television studios and sound stages.Many stagecraft terms vary between the United States and the United...
used in theatre
Theatre
Theatre is a collaborative form of fine art that uses live performers to present the experience of a real or imagined event before a live audience in a specific place. The performers may communicate this experience to the audience through combinations of gesture, speech, song, music or dance...
, which employs a Fresnel lens
Fresnel lens
A Fresnel lens is a type of lens originally developed by French physicist Augustin-Jean Fresnel for lighthouses.The design allows the construction of lenses of large aperture and short focal length without the mass and volume of material that would be required by a lens of conventional design...
to wash light over an area of the stage
Stage (theatre)
In theatre or performance arts, the stage is a designated space for the performance productions. The stage serves as a space for actors or performers and a focal point for the members of the audience...
. The lens produces a wider, soft-edged beam of light, which is commonly used for back light and top light.
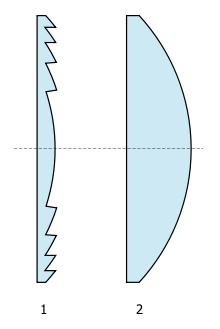
The distinctive lens
Lens (optics)
A lens is an optical device with perfect or approximate axial symmetry which transmits and refracts light, converging or diverging the beam. A simple lens consists of a single optical element...
, named after Augustin-Jean Fresnel
Augustin-Jean Fresnel
Augustin-Jean Fresnel , was a French engineer who contributed significantly to the establishment of the theory of wave optics. Fresnel studied the behaviour of light both theoretically and experimentally....
, has a 'stepped' appearance instead of the 'full' or 'smooth' appearance of other lenses. This allows the lens to have a much greater curvature than would otherwise be practical. The lens focuses the light by tilting each ring of glass slightly more towards the center as the distance is increased from the center of the lens. If the glass were completely flat, this would cause a corresponding pattern of circles of light, so Fresnel lenses are usually stippled on the flat side. This pattern of small bumps helps to break up the light passing through the lens and gives Fresnels their characteristic soft beam. This means that the intensity of the light is consistent across the spread of the beam of light, as opposed to being less intense around the edges as in an ERS. The stepped lens design causes less heat buildup than a plano-convex lens of the same angle.
Construction
Theatrical Fresnels are typically made in 8, 6 or 3 inch varieties, referring to the diameter of the lens, with lamps ranging in power from 150 W (typically with a 3-inch fresnel) to 2000 W (with an 8-inch fresnel). The 3-inch variety is referred to as an inkie. Fresnel lenses can operate close to the light source and are very cheap to produce, so the lanterns tend to be small and cheap.In film lighting, a much greater range of lens and lamp sizes are produced and used. For commonly available fixtures, lenses range in size from 2 to 24 inches, and lamp power range between 200 W and 20,000 W.
Fresnels use a spherical reflector
Mirror
A mirror is an object that reflects light or sound in a way that preserves much of its original quality prior to its contact with the mirror. Some mirrors also filter out some wavelengths, while preserving other wavelengths in the reflection...
, with the filament of the lamp
Lamp (electrical component)
A lamp is a replaceable component such as an incandescent light bulb, which is designed to produce light from electricity. These components usually have a base of ceramic, metal, glass or plastic, which makes an electrical connection in the socket of a light fixture. This connection may be made...
at the focus point of the reflector. The reflector effectively doubles the light output of the fixture, as all light that is emitted backwards into the reflector is reflected back through the filament of the lamp and out the front. As with most lighting fixtures, the lamp and reflector cannot move independently, and remain a fixed unit inside the housing. It is this unit that is moved back and forth inside the lamp to focus the light. This is done by a slider on the bottom of the lantern, or by a worm track with a crank in the back of the unit. The lamps are almost always mounted 'base down', i.e. with the bulb standing upwards. Burning these lamps upside down will shorten lamp life significantly.
Fresnels are not very efficient. The reflector cannot be larger than the lens aperture, and thus all the radiated light that is neither redirected forward by the spherical reflector behind the bulb nor emitted directly through the lens is absorbed by the casing as waste heat.
The degree to which the lamp may be focused
Focus (optics)
In geometrical optics, a focus, also called an image point, is the point where light rays originating from a point on the object converge. Although the focus is conceptually a point, physically the focus has a spatial extent, called the blur circle. This non-ideal focusing may be caused by...
is limited by the length of the housing. To reduce the width of the beam, the lamp and reflector are moved further back from the lens (spot focus). However, the farther back in the housing the lamp is placed, the more light is wasted in the housing.
Use

Special (lighting)
In stage lighting, a special refers to a lighting instrument that is used for a very specific purpose, rather than being a part of a system of light such as an area light or color wash. It is typically, although not always, used alone, or at a higher level than the other instruments...
in certain situations.
While the focus can alter the size of the beam, the distinctive scatter of light that the Fresnel lens emits also requires a way of controlling its shape. Since Fresnels cannot use internal shutters, such as those found in an ellipsoidal spotlight, they are often fitted with distinctive barn doors to control the spill and shape the beam of light. These are large metal flaps that may be mounted just beyond the color slot at the front of the lantern.

