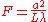Fresnel number
Encyclopedia
The Fresnel number F, named after the physicist Augustin-Jean Fresnel, is a dimensionless number occurring in optics
, in particular in diffraction theory
.
For an electromagnetic wave passing through an aperture
and hitting a screen, the Fresnel number F is defined as
where
Depending on the value of F the diffraction theory can be simplified into two special cases:
In case of , laws of geometrical optics
, laws of geometrical optics
are applied.
The agreement on this limit does not seem universal, for elaboration on this controversy see this article's discussion page. Intermediate values of the Fresnel number necessitate a more detailed analysis based on the scalar diffraction theory.
Optics
Optics is the branch of physics which involves the behavior and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behavior of visible, ultraviolet, and infrared light...
, in particular in diffraction theory
Diffraction
Diffraction refers to various phenomena which occur when a wave encounters an obstacle. Italian scientist Francesco Maria Grimaldi coined the word "diffraction" and was the first to record accurate observations of the phenomenon in 1665...
.
For an electromagnetic wave passing through an aperture
Aperture
In optics, an aperture is a hole or an opening through which light travels. More specifically, the aperture of an optical system is the opening that determines the cone angle of a bundle of rays that come to a focus in the image plane. The aperture determines how collimated the admitted rays are,...
and hitting a screen, the Fresnel number F is defined as
where
-
 is the characteristic size (e.g. radiusRadiusIn classical geometry, a radius of a circle or sphere is any line segment from its center to its perimeter. By extension, the radius of a circle or sphere is the length of any such segment, which is half the diameter. If the object does not have an obvious center, the term may refer to its...
is the characteristic size (e.g. radiusRadiusIn classical geometry, a radius of a circle or sphere is any line segment from its center to its perimeter. By extension, the radius of a circle or sphere is the length of any such segment, which is half the diameter. If the object does not have an obvious center, the term may refer to its...
) of the aperture -
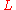 is the distance of the screen from the aperture
is the distance of the screen from the aperture -
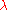 is the incident wavelengthWavelengthIn physics, the wavelength of a sinusoidal wave is the spatial period of the wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.It is usually determined by considering the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase, such as crests, troughs, or zero crossings, and is a...
is the incident wavelengthWavelengthIn physics, the wavelength of a sinusoidal wave is the spatial period of the wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.It is usually determined by considering the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase, such as crests, troughs, or zero crossings, and is a...
.
Depending on the value of F the diffraction theory can be simplified into two special cases:
- Fraunhofer diffractionFraunhofer diffractionIn optics, the Fraunhofer diffraction equation is used to model the diffraction of waves when the diffraction pattern is viewed at a long distance from the diffracting object, and also when it is viewed at the focal plane of an imaging lens....
for
- Fresnel diffractionFresnel diffractionIn optics, the Fresnel diffraction equation for near-field diffraction, is an approximation of Kirchhoff-Fresnel diffraction that can be applied to the propagation of waves in the near field....
for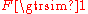
In case of
 , laws of geometrical optics
, laws of geometrical opticsGeometrical optics
Geometrical optics, or ray optics, describes light propagation in terms of "rays". The "ray" in geometric optics is an abstraction, or "instrument", which can be used to approximately model how light will propagate. Light rays are defined to propagate in a rectilinear path as far as they travel in...
are applied.
The agreement on this limit does not seem universal, for elaboration on this controversy see this article's discussion page. Intermediate values of the Fresnel number necessitate a more detailed analysis based on the scalar diffraction theory.
See also
- Fresnel integralFresnel integral250px|thumb|S and C The maximum of C is about 0.977451424. If πt²/2 were used instead of t², then the image would be scaled vertically and horizontally ....
- Fresnel zoneFresnel zoneIn optics and radio communications , a Fresnel zone , named for physicist Augustin-Jean Fresnel, is one of a number of concentric ellipsoids which define volumes in the radiation pattern of a circular aperture...
- Fraunhofer distance