
Fried parameter
Encyclopedia
The Fried parameter or Fried's coherence length (commonly written as 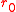 ) measures the optical quality of the atmosphere
) measures the optical quality of the atmosphere
. This parameter is usually expressed in centimeters and corresponds to an area over which the rms
wavefront
aberration is less than 1 radian
. As such,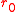 indicates the size of a telescope which can just operate at the diffraction limit. Any larger and resolution will be seeing
indicates the size of a telescope which can just operate at the diffraction limit. Any larger and resolution will be seeing
-limited, any smaller and it will be limited by the telescope itself.
Although not explicitly written in his article, Fried's parameter is usually written as
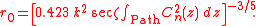
where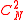 is the strength of turbulence versus altitude,
is the strength of turbulence versus altitude, 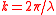 is the angular Wavenumber
is the angular Wavenumber
, and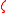 is the angle of the telescope, measured from zenith.
is the angle of the telescope, measured from zenith.
Typical values for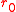 are 10 cm for average seeing and 20 cm for good to excellent seeing on the best sites. The seeing-limited angular resolution is
are 10 cm for average seeing and 20 cm for good to excellent seeing on the best sites. The seeing-limited angular resolution is 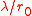 . Since almost all professional telescopes have diameter
. Since almost all professional telescopes have diameter 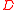 larger than
larger than 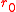 , they employ adaptive optics
, they employ adaptive optics
to correct the aberrations and get diffraction limited images, with resolution of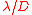 .
.
Because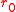 varies with wavelength as
varies with wavelength as 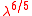 , it is usually specified at
, it is usually specified at 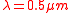
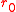 ) measures the optical quality of the atmosphere
) measures the optical quality of the atmosphereAtmosphere
An atmosphere is a layer of gases that may surround a material body of sufficient mass, and that is held in place by the gravity of the body. An atmosphere may be retained for a longer duration, if the gravity is high and the atmosphere's temperature is low...
. This parameter is usually expressed in centimeters and corresponds to an area over which the rms
RMS
-Science and technology:* Root mean square, a concept encapsulating the "average", in some sense, of a quantity. Frequently encountered in statistics, the physical sciences and electronics...
wavefront
Wavefront
In physics, a wavefront is the locus of points having the same phase. Since infrared, optical, x-ray and gamma-ray frequencies are so high, the temporal component of electromagnetic waves is usually ignored at these wavelengths, and it is only the phase of the spatial oscillation that is described...
aberration is less than 1 radian
Radian
Radian is the ratio between the length of an arc and its radius. The radian is the standard unit of angular measure, used in many areas of mathematics. The unit was formerly a SI supplementary unit, but this category was abolished in 1995 and the radian is now considered a SI derived unit...
. As such,
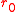 indicates the size of a telescope which can just operate at the diffraction limit. Any larger and resolution will be seeing
indicates the size of a telescope which can just operate at the diffraction limit. Any larger and resolution will be seeingSeeing
The word seeing can mean more than one thing:* In common usage, the word means visual perception* Astronomical seeing, the blurring effects of air turbulence in the atmosphere...
-limited, any smaller and it will be limited by the telescope itself.
Although not explicitly written in his article, Fried's parameter is usually written as
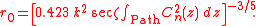
where
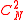 is the strength of turbulence versus altitude,
is the strength of turbulence versus altitude, 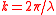 is the angular Wavenumber
is the angular WavenumberWavenumber
In the physical sciences, the wavenumber is a property of a wave, its spatial frequency, that is proportional to the reciprocal of the wavelength. It is also the magnitude of the wave vector...
, and
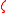 is the angle of the telescope, measured from zenith.
is the angle of the telescope, measured from zenith.Typical values for
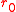 are 10 cm for average seeing and 20 cm for good to excellent seeing on the best sites. The seeing-limited angular resolution is
are 10 cm for average seeing and 20 cm for good to excellent seeing on the best sites. The seeing-limited angular resolution is 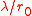 . Since almost all professional telescopes have diameter
. Since almost all professional telescopes have diameter  larger than
larger than 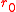 , they employ adaptive optics
, they employ adaptive opticsAdaptive optics
Adaptive optics is a technology used to improve the performance of optical systems by reducing the effect of wavefront distortions. It is used in astronomical telescopes and laser communication systems to remove the effects of atmospheric distortion, and in retinal imaging systems to reduce the...
to correct the aberrations and get diffraction limited images, with resolution of
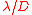 .
.Because
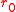 varies with wavelength as
varies with wavelength as 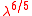 , it is usually specified at
, it is usually specified at 

