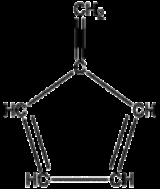
Fulvene
Encyclopedia
Fulvene is one of several hydrocarbon
s with the same formula as benzene
, C6H6. Fulvenes include the derivatives of this simple hydrocarbon, which itself is rarely encountered. Thiele
is credited with discovering the scope of the reaction between cyclopentadiene
and aldehyde
s and ketone
s that yields the brightly coloured fulvene derivatives. Most fulvenes are prepared by the reactions starting from cyclopentadiene or sodium cyclopentadienyl.
2,3,4,5-Tetramethylfulvene, abbreviated Me4Fv, is a relatively common ligand in organometallic chemistry
. It typically results from the deprotonation of cationic pentamethylcyclopentadienyl complexes.
Hydrocarbon
In organic chemistry, a hydrocarbon is an organic compound consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon. Hydrocarbons from which one hydrogen atom has been removed are functional groups, called hydrocarbyls....
s with the same formula as benzene
Benzene
Benzene is an organic chemical compound. It is composed of 6 carbon atoms in a ring, with 1 hydrogen atom attached to each carbon atom, with the molecular formula C6H6....
, C6H6. Fulvenes include the derivatives of this simple hydrocarbon, which itself is rarely encountered. Thiele
Johannes Thiele (chemist)
Friedrich Karl Johannes Thiele was a German chemist and a prominent professor at several universities, including those in Munich and Strasbourg. He developed many laboratory techniques related to isolation of organic compounds...
is credited with discovering the scope of the reaction between cyclopentadiene
Cyclopentadiene
Cyclopentadiene is an organic compound with the formula C5H6. This colorless liquid has a strong and unpleasant odor. At room temperature, this cyclic diene dimerizes over the course of hours to give dicyclopentadiene via a Diels–Alder reaction...
and aldehyde
Aldehyde
An aldehyde is an organic compound containing a formyl group. This functional group, with the structure R-CHO, consists of a carbonyl center bonded to hydrogen and an R group....
s and ketone
Ketone
In organic chemistry, a ketone is an organic compound with the structure RCR', where R and R' can be a variety of atoms and groups of atoms. It features a carbonyl group bonded to two other carbon atoms. Many ketones are known and many are of great importance in industry and in biology...
s that yields the brightly coloured fulvene derivatives. Most fulvenes are prepared by the reactions starting from cyclopentadiene or sodium cyclopentadienyl.
2,3,4,5-Tetramethylfulvene, abbreviated Me4Fv, is a relatively common ligand in organometallic chemistry
Organometallic chemistry
Organometallic chemistry is the study of chemical compounds containing bonds between carbon and a metal. Since many compounds without such bonds are chemically similar, an alternative may be compounds containing metal-element bonds of a largely covalent character...
. It typically results from the deprotonation of cationic pentamethylcyclopentadienyl complexes.

