
GDP gap
Encyclopedia
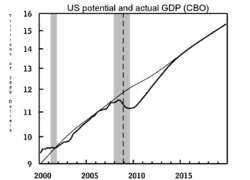
Aggregate demand
In macroeconomics, aggregate demand is the total demand for final goods and services in the economy at a given time and price level. It is the amount of goods and services in the economy that will be purchased at all possible price levels. This is the demand for the gross domestic product of a...
is outpacing the growth of aggregate supply
Aggregate supply
In economics, aggregate supply is the total supply of goods and services that firms in a national economy plan on selling during a specific time period...
—possibly creating inflation
Inflation
In economics, inflation is a rise in the general level of prices of goods and services in an economy over a period of time.When the general price level rises, each unit of currency buys fewer goods and services. Consequently, inflation also reflects an erosion in the purchasing power of money – a...
; if the calculation yields a negative number it is called a recessionary gap—possibly signifying deflation.
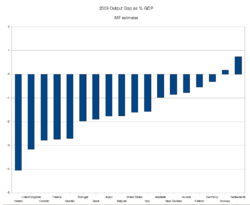
The percentage GDP gap is the actual GDP minus the potential GDP divided by the potential GDP.
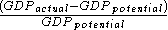 .
.Okun's Law: The relationship between output and unemployment
Okun's LawOkun's law
In economics, Okun's law is an empirically observed relationship relating unemployment to losses in a country's production first quantified by Arthur M. Okun. The "gap version" states that for every 1% increase in the unemployment rate, a country's GDP will be at an additional roughly 2% lower...
is based on regression analysis of US data that shows a correlation between unemployment and GDP. Okun's law can be stated as: For every 1% increase in cyclical unemployment (actual unemployment - natural rate of unemployment
Natural rate of unemployment
The natural rate of unemployment is a concept of economic activity developed in particular by Milton Friedman and Edmund Phelps in the 1960s, both recipients of the Nobel prize in economics...
), GDP will decrease by β%.
%Output gap = -β x %Cyclical unemployment
This can also be expressed as:
(Y-Y*) / Y* = -β(u-ū)
where:
- Y is actual output
- Y* is potential output
- u is actual unemployment
- ū is the natural rate of unemployment
- β is a constant derived from regression show the link between deviations from natural output & natural unemployment.
External links


Aggregate demand
In macroeconomics, aggregate demand is the total demand for final goods and services in the economy at a given time and price level. It is the amount of goods and services in the economy that will be purchased at all possible price levels. This is the demand for the gross domestic product of a...
is outpacing the growth of aggregate supply
Aggregate supply
In economics, aggregate supply is the total supply of goods and services that firms in a national economy plan on selling during a specific time period...
—possibly creating inflation
Inflation
In economics, inflation is a rise in the general level of prices of goods and services in an economy over a period of time.When the general price level rises, each unit of currency buys fewer goods and services. Consequently, inflation also reflects an erosion in the purchasing power of money – a...
; if the calculation yields a negative number it is called a recessionary gap—possibly signifying deflation.
The percentage GDP gap is the actual GDP minus the potential GDP divided by the potential GDP.
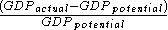 .
.Okun's Law: The relationship between output and unemployment
Okun's LawOkun's law
In economics, Okun's law is an empirically observed relationship relating unemployment to losses in a country's production first quantified by Arthur M. Okun. The "gap version" states that for every 1% increase in the unemployment rate, a country's GDP will be at an additional roughly 2% lower...
is based on regression analysis of US data that shows a correlation between unemployment and GDP. Okun's law can be stated as: For every 1% increase in cyclical unemployment (actual unemployment - natural rate of unemployment
Natural rate of unemployment
The natural rate of unemployment is a concept of economic activity developed in particular by Milton Friedman and Edmund Phelps in the 1960s, both recipients of the Nobel prize in economics...
), GDP will decrease by β%.
%Output gap = -β x %Cyclical unemployment
This can also be expressed as:
(Y-Y*) / Y* = -β(u-ū)
where:
- Y is actual output
- Y* is potential output
- u is actual unemployment
- ū is the natural rate of unemployment
- β is a constant derived from regression show the link between deviations from natural output & natural unemployment.
External links


Aggregate demand
In macroeconomics, aggregate demand is the total demand for final goods and services in the economy at a given time and price level. It is the amount of goods and services in the economy that will be purchased at all possible price levels. This is the demand for the gross domestic product of a...
is outpacing the growth of aggregate supply
Aggregate supply
In economics, aggregate supply is the total supply of goods and services that firms in a national economy plan on selling during a specific time period...
—possibly creating inflation
Inflation
In economics, inflation is a rise in the general level of prices of goods and services in an economy over a period of time.When the general price level rises, each unit of currency buys fewer goods and services. Consequently, inflation also reflects an erosion in the purchasing power of money – a...
; if the calculation yields a negative number it is called a recessionary gap—possibly signifying deflation.
The percentage GDP gap is the actual GDP minus the potential GDP divided by the potential GDP.
 .
.Okun's Law: The relationship between output and unemployment
Okun's LawOkun's law
In economics, Okun's law is an empirically observed relationship relating unemployment to losses in a country's production first quantified by Arthur M. Okun. The "gap version" states that for every 1% increase in the unemployment rate, a country's GDP will be at an additional roughly 2% lower...
is based on regression analysis of US data that shows a correlation between unemployment and GDP. Okun's law can be stated as: For every 1% increase in cyclical unemployment (actual unemployment - natural rate of unemployment
Natural rate of unemployment
The natural rate of unemployment is a concept of economic activity developed in particular by Milton Friedman and Edmund Phelps in the 1960s, both recipients of the Nobel prize in economics...
), GDP will decrease by β%.
%Output gap = -β x %Cyclical unemployment
This can also be expressed as:
(Y-Y*) / Y* = -β(u-ū)
where:
- Y is actual output
- Y* is potential output
- u is actual unemployment
- ū is the natural rate of unemployment
- β is a constant derived from regression show the link between deviations from natural output & natural unemployment.
External links

