
GPRS Roaming Exchange
Encyclopedia
A GPRS Roaming Exchange (GRX) acts as a hub for GPRS connections from roaming
users, removing the need for a dedicated link between each GPRS service provider. It was developed to facilitate a more efficient way for operators to interconnect networks, and played a large part in the transition to third-generation systems.
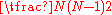 , whereby
, whereby  is the number of global operators that would require a dedicated link. This meant that mobile subscribers who wanted to use GPRS whilst roaming could only do so if their operator had a direct agreement with the operator in the country or area in which they were roaming.
is the number of global operators that would require a dedicated link. This meant that mobile subscribers who wanted to use GPRS whilst roaming could only do so if their operator had a direct agreement with the operator in the country or area in which they were roaming.
In 2000 the GSMA (GSM Association) developed the idea of GRX to handle all roaming between public land mobile networks (PLMNs).
backbone and uses GPRS Tunnelling Protocol
on the session layer
(OSI
Layer Five) between the visited PLMN(Public Land Mobile Network) and the home PLMN. Each GRX operator will have a network consisting of a set of routers and links connecting to the GPRS networks, moreover the GRX network will have links connecting to other GRX nodes in peer model.
The GRX operator can therefore act as a hub, allowing a GPRS subscriber to interconnect with many roaming partners without the need for dedicated links. For operators this is advantageous in that it allows quicker implementation of roaming partners, faster time to market for new operators and lower capital expenditure
seeing as it is a scalable solution depending on bandwidth and quality of service
requirements. Because the interconnection between the visited PLMN and home PLMN uses private GRX networks there is also no need to maintain Internet Protocol Security
(IPsec) tunnels over the public internet.
Roaming
In wireless telecommunications, roaming is a general term referring to the extension of connectivity service in a location that is different from the home location where the service was registered. Roaming ensures that the wireless device is kept connected to the network, without losing the...
users, removing the need for a dedicated link between each GPRS service provider. It was developed to facilitate a more efficient way for operators to interconnect networks, and played a large part in the transition to third-generation systems.
Development
Initially GPRS roaming was based on complicated relationships between individual operators with each operator requiring a dedicated link to each different partner so that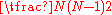 , whereby
, whereby  is the number of global operators that would require a dedicated link. This meant that mobile subscribers who wanted to use GPRS whilst roaming could only do so if their operator had a direct agreement with the operator in the country or area in which they were roaming.
is the number of global operators that would require a dedicated link. This meant that mobile subscribers who wanted to use GPRS whilst roaming could only do so if their operator had a direct agreement with the operator in the country or area in which they were roaming.In 2000 the GSMA (GSM Association) developed the idea of GRX to handle all roaming between public land mobile networks (PLMNs).
Technical implementation
Usually, GRX is based on a private or public IPInternet Protocol
The Internet Protocol is the principal communications protocol used for relaying datagrams across an internetwork using the Internet Protocol Suite...
backbone and uses GPRS Tunnelling Protocol
GPRS Tunnelling Protocol
GPRS Tunneling Protocol is a group of IP-based communications protocols used to carry General Packet Radio Service within GSM, UMTS and LTE networks. In 3GPP architectures, GTP and Proxy Mobile IPv6 based interfaces are specified on various interface points.GTP can be decomposed into separate...
on the session layer
Session layer
The session layer is layer 5 of the seven-layer OSI model of computer networking.The session layer provides the mechanism for opening, closing and managing a session between end-user application processes, i.e., a semi-permanent dialogue. Communication sessions consist of requests and responses...
(OSI
OSI
- General :* OSI Pharmaceuticals, an American pharmaceutical company* OSI Restaurant Partners, the restaurant and entertainment group that includes Outback Steakhouse...
Layer Five) between the visited PLMN(Public Land Mobile Network) and the home PLMN. Each GRX operator will have a network consisting of a set of routers and links connecting to the GPRS networks, moreover the GRX network will have links connecting to other GRX nodes in peer model.
The GRX operator can therefore act as a hub, allowing a GPRS subscriber to interconnect with many roaming partners without the need for dedicated links. For operators this is advantageous in that it allows quicker implementation of roaming partners, faster time to market for new operators and lower capital expenditure
Capital expenditure
Capital expenditures are expenditures creating future benefits. A capital expenditure is incurred when a business spends money either to buy fixed assets or to add to the value of an existing fixed asset with a useful life extending beyond the taxable year...
seeing as it is a scalable solution depending on bandwidth and quality of service
Quality of service
The quality of service refers to several related aspects of telephony and computer networks that allow the transport of traffic with special requirements...
requirements. Because the interconnection between the visited PLMN and home PLMN uses private GRX networks there is also no need to maintain Internet Protocol Security
IPsec
Internet Protocol Security is a protocol suite for securing Internet Protocol communications by authenticating and encrypting each IP packet of a communication session...
(IPsec) tunnels over the public internet.

