
GRB 080319B
Encyclopedia
GRB 080319B was a remarkable gamma-ray burst (GRB) detected by the Swift
satellite at 06:12 UTC
on March 19, 2008. The burst set a new record for the farthest object that could be seen with the naked eye
; it had a peak apparent magnitude
of 5.8 and remained visible to human eyes for approximately 30 seconds. The magnitude was brighter than 9.0 for some 60 seconds.
 The GRB's redshift
The GRB's redshift
was measured to be 0.937, which means that the explosion occurred about 7.5 billion (7.5×109) years ago, and it took the light that long to reach Earth. This is roughly half the time since the Big Bang
. The first scientific paper submitted on the event, suggested that the GRB could have easily been seen to a redshift
of 16 (essentially to the time in the universe when stars were just being formed, well into the age of reionization
) from a sub-meter sized telescope
equipped with near-infrared
filters.
The afterglow of the burst set a new record for the "most intrinsically bright object ever observed by humans in the universe",
2.5 million times brighter than the brightest supernova to date, SN 2005ap
.
Evidence suggests that the afterglow was particularly bright due to the gamma jet focusing exactly at the line of sight to Earth. This allowed an unprecedented examination of the jet structure, which appears to have consisted of a narrowly focused cone and a secondary wider one. If this is the norm for GRB jets, it follows that most GRB detections only capture the fainter wide cone, which means that most distant GRBs are too faint to detect with current telescopes. This would imply that GRBs are a far more common phenomenon than so far assumed.
A record for the number of observed bursts with the same satellite on one day, four, was also set. This burst was named with the suffix B since it was the second burst detected that day. In fact, there were 5 GRBs detected in a 24 hour period, including GRB 080320.
Until this gamma-ray burst event, the Triangulum Galaxy
, at a distance of about 2.9 million light years, was the most distant object visible to the naked eye. The galaxy remains the most distant permanent object viewable without aid.
It was soon suggested that this spectacle be named the Clarke Event, as it was recorded just hours after the death was announced of Arthur C. Clarke
. who was the 1956 Hugo Award
winner for his 1955 science fiction short story, The Star
.
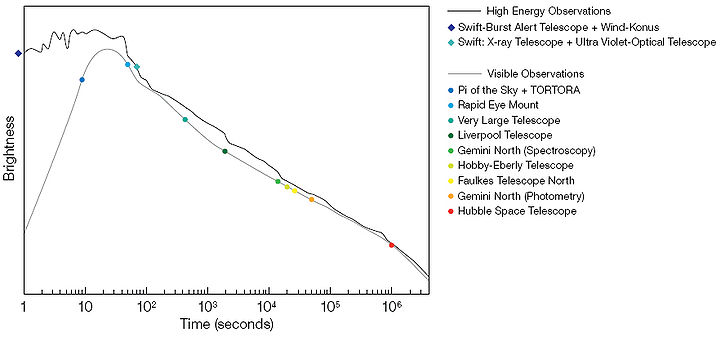
The plot below shows the brightness in both the optical and at higher energy for the event. The first optical exposure started about 2 seconds before the source was first observed by the SWIFT telescope and lasted for 10 seconds. The emission in both curves then peaks at around 60 seconds before a long exponential decay.
Swift Gamma-Ray Burst Mission
The Swift Gamma-Ray Burst Mission consists of a robotic spacecraft called Swift, which was launched into orbit on 20 November 2004, 17:16:00 UTC on a Delta II 7320-10C expendable launch vehicle. Swift is managed by the NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, and was developed by an international...
satellite at 06:12 UTC
Coordinated Universal Time
Coordinated Universal Time is the primary time standard by which the world regulates clocks and time. It is one of several closely related successors to Greenwich Mean Time. Computer servers, online services and other entities that rely on having a universally accepted time use UTC for that purpose...
on March 19, 2008. The burst set a new record for the farthest object that could be seen with the naked eye
Naked eye
The naked eye is a figure of speech referring to human visual perception unaided by a magnifying or light-collecting optical device, such as a telescope or microscope. Vision corrected to normal acuity using corrective lenses is considered "naked"...
; it had a peak apparent magnitude
Apparent magnitude
The apparent magnitude of a celestial body is a measure of its brightness as seen by an observer on Earth, adjusted to the value it would have in the absence of the atmosphere...
of 5.8 and remained visible to human eyes for approximately 30 seconds. The magnitude was brighter than 9.0 for some 60 seconds.
Overview

Redshift
In physics , redshift happens when light seen coming from an object is proportionally increased in wavelength, or shifted to the red end of the spectrum...
was measured to be 0.937, which means that the explosion occurred about 7.5 billion (7.5×109) years ago, and it took the light that long to reach Earth. This is roughly half the time since the Big Bang
Big Bang
The Big Bang theory is the prevailing cosmological model that explains the early development of the Universe. According to the Big Bang theory, the Universe was once in an extremely hot and dense state which expanded rapidly. This rapid expansion caused the young Universe to cool and resulted in...
. The first scientific paper submitted on the event, suggested that the GRB could have easily been seen to a redshift
Redshift
In physics , redshift happens when light seen coming from an object is proportionally increased in wavelength, or shifted to the red end of the spectrum...
of 16 (essentially to the time in the universe when stars were just being formed, well into the age of reionization
Reionization
In Big Bang cosmology, reionization is the process that reionized the matter in the universe after the "dark ages," and is the second of two major phase changes of gas in the universe. As the majority of baryonic matter is in the form of hydrogen, reionization usually refers to the reionization of...
) from a sub-meter sized telescope
Telescope
A telescope is an instrument that aids in the observation of remote objects by collecting electromagnetic radiation . The first known practical telescopes were invented in the Netherlands at the beginning of the 1600s , using glass lenses...
equipped with near-infrared
Infrared
Infrared light is electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength longer than that of visible light, measured from the nominal edge of visible red light at 0.74 micrometres , and extending conventionally to 300 µm...
filters.
The afterglow of the burst set a new record for the "most intrinsically bright object ever observed by humans in the universe",
2.5 million times brighter than the brightest supernova to date, SN 2005ap
SN 2005ap
SN 2005ap was an extremely energetic type II supernova. It is reported to be the brightest supernova yet recorded, twice as bright as the previous record holder, SN 2006gy...
.
Evidence suggests that the afterglow was particularly bright due to the gamma jet focusing exactly at the line of sight to Earth. This allowed an unprecedented examination of the jet structure, which appears to have consisted of a narrowly focused cone and a secondary wider one. If this is the norm for GRB jets, it follows that most GRB detections only capture the fainter wide cone, which means that most distant GRBs are too faint to detect with current telescopes. This would imply that GRBs are a far more common phenomenon than so far assumed.
A record for the number of observed bursts with the same satellite on one day, four, was also set. This burst was named with the suffix B since it was the second burst detected that day. In fact, there were 5 GRBs detected in a 24 hour period, including GRB 080320.
Until this gamma-ray burst event, the Triangulum Galaxy
Triangulum Galaxy
The Triangulum Galaxy is a spiral galaxy approximately 3 million light years from Earth in the constellation Triangulum. It is catalogued as Messier 33 or NGC 598, and is sometimes informally referred to as the Pinwheel Galaxy, a nickname it shares with Messier 101...
, at a distance of about 2.9 million light years, was the most distant object visible to the naked eye. The galaxy remains the most distant permanent object viewable without aid.
It was soon suggested that this spectacle be named the Clarke Event, as it was recorded just hours after the death was announced of Arthur C. Clarke
Arthur C. Clarke
Sir Arthur Charles Clarke, CBE, FRAS was a British science fiction author, inventor, and futurist, famous for his short stories and novels, among them 2001: A Space Odyssey, and as a host and commentator in the British television series Mysterious World. For many years, Robert A. Heinlein,...
. who was the 1956 Hugo Award
Hugo Award
The Hugo Awards are given annually for the best science fiction or fantasy works and achievements of the previous year. The award is named after Hugo Gernsback, the founder of the pioneering science fiction magazine Amazing Stories, and was officially named the Science Fiction Achievement Awards...
winner for his 1955 science fiction short story, The Star
The Star (short story)
"The Star" is a science fiction short story by English writer Arthur C. Clarke. It appeared in the science fiction magazine Infinity Science Fiction in 1955 and won the Hugo award in 1956. The story was also published as "Star of Bethlehem"...
.
The plot below shows the brightness in both the optical and at higher energy for the event. The first optical exposure started about 2 seconds before the source was first observed by the SWIFT telescope and lasted for 10 seconds. The emission in both curves then peaks at around 60 seconds before a long exponential decay.


