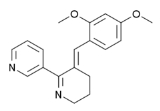
GTS-21
Encyclopedia
GTS-21 is a drug that acts as a partial agonist
at neural nicotinic acetylcholine receptor
s. It binds to both the α4β2
and α7
subtypes, but activates only the α7 to any significant extent.
Both GTS-21 itself and its demethylated active metabolite 4-OH-GTS-21 display nootropic
and neuroprotective effects, and GTS-21 is being investigated for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease
, nicotine dependence, and, most important, for schizophrenia
.
Partial agonist
Partial agonists bind and activate a given receptor, but have only partial efficacy at the receptor relative to a full agonist...
at neural nicotinic acetylcholine receptor
Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor
Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors, or nAChRs, are cholinergic receptors that form ligand-gated ion channels in the plasma membranes of certain neurons and on the postsynaptic side of the neuromuscular junction...
s. It binds to both the α4β2
Alpha-4 beta-2 nicotinic receptor
The alpha-4 beta-2 nicotinic receptor, also known as the α4β2 receptor, is a type of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor, consisting of α4 and β2 subunits...
and α7
Alpha-7 nicotinic receptor
The alpha-7 nicotinic receptor, also known as the α7 receptor, is a type of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor, consisting entirely of α7 subunits....
subtypes, but activates only the α7 to any significant extent.
Both GTS-21 itself and its demethylated active metabolite 4-OH-GTS-21 display nootropic
Nootropic
Nootropics , also referred to as smart drugs, brain steroids, memory enhancers, cognitive enhancers, and intelligence enhancers, are drugs, supplements, nutraceuticals, and functional foods that improve mental functions such as cognition, memory, intelligence, motivation, attention, and concentration...
and neuroprotective effects, and GTS-21 is being investigated for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease
Alzheimer's disease
Alzheimer's disease also known in medical literature as Alzheimer disease is the most common form of dementia. There is no cure for the disease, which worsens as it progresses, and eventually leads to death...
, nicotine dependence, and, most important, for schizophrenia
Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is a mental disorder characterized by a disintegration of thought processes and of emotional responsiveness. It most commonly manifests itself as auditory hallucinations, paranoid or bizarre delusions, or disorganized speech and thinking, and it is accompanied by significant social...
.

