
Gallurese
Encyclopedia
Gallurese is a Italo-Dalmatian Romance language
spoken in the northeastern part of Sardinia
. It is often considered as a variety
of Corsican
, or a transitional language between Corsican
and Sardinian
.
The language takes its name from the region of Gallura
.
Grammatical structure, pronunciation and many terms reflect a certain closeness to Corsican
, showing many similarities with the southern Corsican
dialects of Sartene
and Porto-Vecchio
, with which it shared some mutual influences. A substantial part of its vocabulary comes from the Logudorese variety of Sardinian
, which was probably spoken in this area in the Middle Ages
.
The Sassarese language, spoken in the area of Sassari
, also has similar characteristics, even if it is more linked to Logudorese and has a different, both geographical and historical, origin.
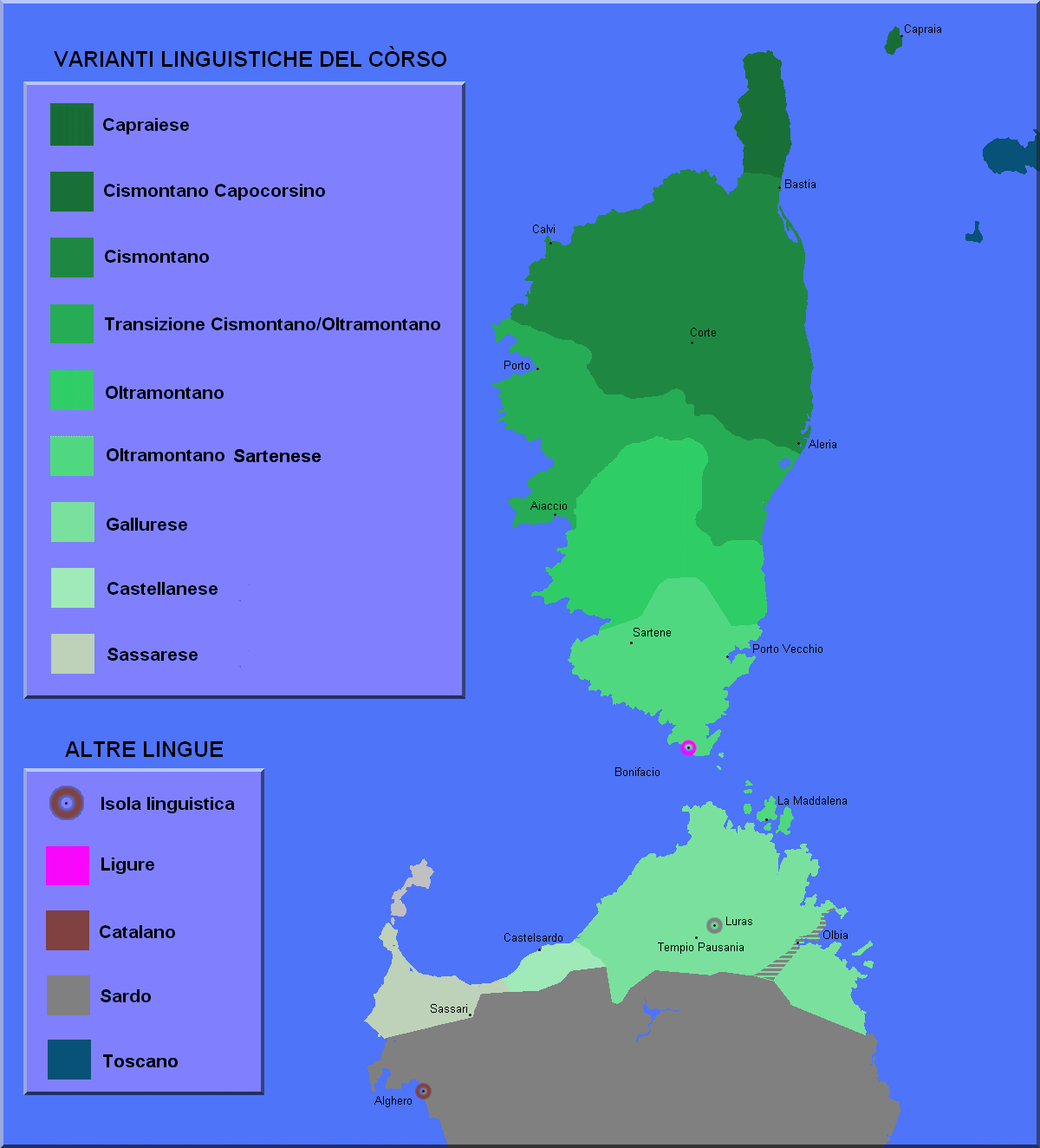
and Gallurese, while there is relatively more distance from the neighbouring Sardinian varieties
.
The Regional Government of Sardinia has recognized Gallurese, along with Sassarese as separate languages, distinct from Sardinian
.
could perhaps stem from the age of Giudicati
, and possibly from the different (direct rather indirect) political control of the Republic of Pisa
over Sardinia.
It could be interesting to investigate if the Tuscan
ingredients of Gallurese effectively came from this domination, because in this case, a Tuscan influence would have presumedly affected a Sardinian version, resulting in a modified Sardinian version (then it still could be a Sardinian version). It would consequently be classified as a Sardinian language for a genetical reason.
In this hypothesis we were considering Sardinian as if Corsican could modify it, but the contrary could be possible, as well, and there could also be a possible Sardinian influence on Corsican. It could also be that Corsican had been influenced by Sardinian. Or it could eventually be that they both were influenced by the same factors, received in their own territories separately and with different actions, finally producing not so distant results. External influences could consent this hypothesis: Sardinia had a wider population, and in its history has been more subject to foreign influences than Corsica. Invasions and taxes would probably have caused an eventual movement in the direction of the minor island, less probably the other way, even if the establishment of a few groups of Corsicans in Sardinia is known. Also, the little distance between Corsica and Tyrrhenic islands would let suppose more frequent practical contacts, while in Sardinia these contacts were more decisive on a point of local administration.
Similarities do exist also with Maremma
, in southern Tuscany-northern Lazio, with which there were no relationships. All this would tend to suggest that a common evolution had interested the areas. Some authors like Maxia believe that, in analogy among themselves, all the coastal areas of Tyrrhenian Sea
should have lived an evolutive moment perhaps at the same time. But the point is not obviously the similarity, because it would not be sufficient to a classification. Current central logudorese Sardinian is not similar, in phonetics, to medieval logudorese Sardinian, although no one would ever deny that it is the same languages.
Italo-Dalmatian languages
The Italo-Dalmatian languages are a group of Romance languages of Italy , Corsica, and, formerly, the Dalmatian Coast of Croatia...
spoken in the northeastern part of Sardinia
Sardinia
Sardinia is the second-largest island in the Mediterranean Sea . It is an autonomous region of Italy, and the nearest land masses are the French island of Corsica, the Italian Peninsula, Sicily, Tunisia and the Spanish Balearic Islands.The name Sardinia is from the pre-Roman noun *sard[],...
. It is often considered as a variety
Variety (linguistics)
In sociolinguistics a variety, also called a lect, is a specific form of a language or language cluster. This may include languages, dialects, accents, registers, styles or other sociolinguistic variation, as well as the standard variety itself...
of Corsican
Corsican language
Corsican is a Italo-Dalmatian Romance language spoken and written on the islands of Corsica and northern Sardinia . Corsican is the traditional native language of the Corsican people, and was long the vernacular language alongside the Italian, official language in Corsica until 1859, which was...
, or a transitional language between Corsican
Corsican language
Corsican is a Italo-Dalmatian Romance language spoken and written on the islands of Corsica and northern Sardinia . Corsican is the traditional native language of the Corsican people, and was long the vernacular language alongside the Italian, official language in Corsica until 1859, which was...
and Sardinian
Sardinian language
Sardinian is a Romance language spoken and written on most of the island of Sardinia . It is considered the most conservative of the Romance languages in terms of phonology and is noted for its Paleosardinian substratum....
.
The language takes its name from the region of Gallura
Gallura
Gallura is a region of northern Sardinia, Italy.The name Gallùra means "area located on high ground".-Geography:...
.
Grammatical structure, pronunciation and many terms reflect a certain closeness to Corsican
Corsican language
Corsican is a Italo-Dalmatian Romance language spoken and written on the islands of Corsica and northern Sardinia . Corsican is the traditional native language of the Corsican people, and was long the vernacular language alongside the Italian, official language in Corsica until 1859, which was...
, showing many similarities with the southern Corsican
Corsican language
Corsican is a Italo-Dalmatian Romance language spoken and written on the islands of Corsica and northern Sardinia . Corsican is the traditional native language of the Corsican people, and was long the vernacular language alongside the Italian, official language in Corsica until 1859, which was...
dialects of Sartene
Sartène
Sartène , is a commune in the Corse-du-Sud department of France on the island of Corsica.Its history dates back to medieval times and granite buildings from the early 16th century still line some of the streets. One of the main incidents in the town's history was an attack by pirates from Algiers...
and Porto-Vecchio
Porto-Vecchio
Porto-Vecchio is a commune in the Corse-du-Sud department of France on the island of Corsica.It is the seat of the canton of Porto-Vecchio, which it shares with Sari-Solenzara, Conca and Lecci. Port-Vecchio is a medium-sized port city placed on a good harbor, the southernmost of the marshy and...
, with which it shared some mutual influences. A substantial part of its vocabulary comes from the Logudorese variety of Sardinian
Sardinian language
Sardinian is a Romance language spoken and written on most of the island of Sardinia . It is considered the most conservative of the Romance languages in terms of phonology and is noted for its Paleosardinian substratum....
, which was probably spoken in this area in the Middle Ages
Middle Ages
The Middle Ages is a periodization of European history from the 5th century to the 15th century. The Middle Ages follows the fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476 and precedes the Early Modern Era. It is the middle period of a three-period division of Western history: Classic, Medieval and Modern...
.
The Sassarese language, spoken in the area of Sassari
Sassari
Sassari is an Italian city. It is the second-largest city of Sardinia in terms of population with about 130,000 inhabitants, or about 300,000 including the greater metropolitan area...
, also has similar characteristics, even if it is more linked to Logudorese and has a different, both geographical and historical, origin.
Typical constitutional elements of Gallurese

- the plural form of nouns in -i (ghjanni or polti 'doors') like in Corsican and Italian, and not in -s like in Sardinian (jannas, portas), French, Spanish, Catalan, etc.
- Latin 'll' has become -dd- (like casteddu, beddu 'castle', 'beautiful'), the same as in Sardinian and southern Corsican (but castellu, bellu in northern Corsican);
- -r- modified to -l- (poltu 'port', while portu in Corsican and Sardinian);
- -chj- and -ghj- sounds (ghjesgia 'church', occhji 'eyes'), like in Corsican, while Sardinian is cresia, ogros.
- articles lu, la, li, like in former Corsican dialects (u, a, i in modern Corsican, su, sa, sos, sas in Sardinian);
Relation to Corsican language
Gallurese is classified by some linguists as a dialect of Corsican, and by others as a dialect of Sardianian. A great deal of similarity exists between Southern Corsican dialectsCorsican language
Corsican is a Italo-Dalmatian Romance language spoken and written on the islands of Corsica and northern Sardinia . Corsican is the traditional native language of the Corsican people, and was long the vernacular language alongside the Italian, official language in Corsica until 1859, which was...
and Gallurese, while there is relatively more distance from the neighbouring Sardinian varieties
Sardo logudorese
Logudorese Sardinian is a standardised variety of Sardinian, often considered the most conservative of all Romance languages. Its ISO 639-3 code is src....
.
The Regional Government of Sardinia has recognized Gallurese, along with Sassarese as separate languages, distinct from Sardinian
Sardinian language
Sardinian is a Romance language spoken and written on most of the island of Sardinia . It is considered the most conservative of the Romance languages in terms of phonology and is noted for its Paleosardinian substratum....
.
Sample of text
An extract from a hymn dedicated to the Virgin Mary.| Gallurese | Corsican Corsican language Corsican is a Italo-Dalmatian Romance language spoken and written on the islands of Corsica and northern Sardinia . Corsican is the traditional native language of the Corsican people, and was long the vernacular language alongside the Italian, official language in Corsica until 1859, which was... |
Logudorese Sardinian Sardinian language Sardinian is a Romance language spoken and written on most of the island of Sardinia . It is considered the most conservative of the Romance languages in terms of phonology and is noted for its Paleosardinian substratum.... |
English translation |
|---|---|---|---|
Tu sei nata par incantu diliziosa elmosùra la meddu di Locusantu la più bedda di Gaddura. Sei bedda chi dugna cori s’innammurigghja di te pa l’occhj mei un fiori ed è la meddu chi c’è. E socu vecchju canutu e socu a tempu passendi parò sempri burrulendi comu m’eti cunnisciutu Cantu campu decu fà sempri onori a Locusantu ch’è la tarra di l’incantu di ca' veni a istragnà. La Patrona di Gaddura l’emu noi in Locusantu incurunata da lu cantu cussì bedda criatura. |
Tu sè nata par incantu diliziosa biddezza a meddu di Locusantu a più bedda di Gaddura. Sè bedda chi ugna cori s’innamurighja di te pa' l’occhj mei un fiori ed è a meddu chi c’è. E socu vecchju canutu e socu a tempu passendu parò sempri burlendu comu m’eti cunisciutu Quantu campu devu fà sempri onori a Locusantu ch’è a tarra di l’incantu di qua' veni a sughjurnà. A' Patrona di Gaddura l’emu noi in Locusantu incurunata da u cantu cusì bedda criatura. |
Tue ses naschida pro incantu delitziosa ermosura sa menzus de Logusantu sa prus bella de Gallura. Ses bella gai chi donzi coro s'innamorat de a tie pro sos ogros meos unu frore e ses sa menzus chi b'est. E seo betzu e canu e su tempus meu est colande però seo semper brullande comente m'azis connottu. Pro cantu bivo appo a depper fàghere semper onore a Logusantu chi est sa terra 'e s'incantu de chie benit a l'abbisitare. Sa patrona de Gallura la tenimus nois in Logusantu coronada de su cantu gai bella creadura. |
You were born from bliss Delightful beauty The best one in Locusant The prettiest of Gallura. You are so pretty that each heart Falls in love with you A flower to my eyes The best one that ever existed. I am old and bald And my time is passing by But I am always cheering up Just like when you met me. No matter how long should I walk I shall always pay tribute to Locusantu For it is the land of bliss To whomever comes to visit it. The Patron Patron saint A patron saint is a saint who is regarded as the intercessor and advocate in heaven of a nation, place, craft, activity, class, clan, family, or person... of Gallura Is here for us in Locusantu Crowned by hymns Such a splendid creature. |
Hypothesis on the development of Gallurese
The split between Gallurese and Sardinian varietiesSardinian language
Sardinian is a Romance language spoken and written on most of the island of Sardinia . It is considered the most conservative of the Romance languages in terms of phonology and is noted for its Paleosardinian substratum....
could perhaps stem from the age of Giudicati
Giudicati
The giudicati were the indigenous kingdoms of Sardinia from about 900 until 1410, when the last fell to the Aragonese. The rulers of the giudicati were giudici , from the Latin iudice , often translates as "judge". The Latin for giudicato was iudicatus The giudicati (singular giudicato) were the...
, and possibly from the different (direct rather indirect) political control of the Republic of Pisa
Republic of Pisa
The Republic of Pisa was a de facto independent state centered on the Tuscan city of Pisa during the late tenth and eleventh centuries. It rose to become an economic powerhouse, a commercial center whose merchants dominated Mediterranean and Italian trade for a century before being surpassed and...
over Sardinia.
It could be interesting to investigate if the Tuscan
Tuscan dialect
The Tuscan language , or the Tuscan dialect is an Italo-Dalmatian language spoken in Tuscany, Italy.Standard Italian is based on Tuscan, specifically on its Florentine variety...
ingredients of Gallurese effectively came from this domination, because in this case, a Tuscan influence would have presumedly affected a Sardinian version, resulting in a modified Sardinian version (then it still could be a Sardinian version). It would consequently be classified as a Sardinian language for a genetical reason.
In this hypothesis we were considering Sardinian as if Corsican could modify it, but the contrary could be possible, as well, and there could also be a possible Sardinian influence on Corsican. It could also be that Corsican had been influenced by Sardinian. Or it could eventually be that they both were influenced by the same factors, received in their own territories separately and with different actions, finally producing not so distant results. External influences could consent this hypothesis: Sardinia had a wider population, and in its history has been more subject to foreign influences than Corsica. Invasions and taxes would probably have caused an eventual movement in the direction of the minor island, less probably the other way, even if the establishment of a few groups of Corsicans in Sardinia is known. Also, the little distance between Corsica and Tyrrhenic islands would let suppose more frequent practical contacts, while in Sardinia these contacts were more decisive on a point of local administration.
Similarities do exist also with Maremma
Maremma
The Maremma is a vast area in Italy bordering the Tyrrhenian Sea, consisting of part of south-western Tuscany - Maremma Livornese and Maremma Grossetana , and part of northern Lazio - Maremma Laziale .The poet Dante Alighieri in his Divina Commedia places the...
, in southern Tuscany-northern Lazio, with which there were no relationships. All this would tend to suggest that a common evolution had interested the areas. Some authors like Maxia believe that, in analogy among themselves, all the coastal areas of Tyrrhenian Sea
Tyrrhenian Sea
The Tyrrhenian Sea is part of the Mediterranean Sea off the western coast of Italy.-Geography:The sea is bounded by Corsica and Sardinia , Tuscany, Lazio, Campania, Basilicata and Calabria and Sicily ....
should have lived an evolutive moment perhaps at the same time. But the point is not obviously the similarity, because it would not be sufficient to a classification. Current central logudorese Sardinian is not similar, in phonetics, to medieval logudorese Sardinian, although no one would ever deny that it is the same languages.
See also
- CorsicanCorsican languageCorsican is a Italo-Dalmatian Romance language spoken and written on the islands of Corsica and northern Sardinia . Corsican is the traditional native language of the Corsican people, and was long the vernacular language alongside the Italian, official language in Corsica until 1859, which was...
- SardiniaSardiniaSardinia is the second-largest island in the Mediterranean Sea . It is an autonomous region of Italy, and the nearest land masses are the French island of Corsica, the Italian Peninsula, Sicily, Tunisia and the Spanish Balearic Islands.The name Sardinia is from the pre-Roman noun *sard[],...
- SardinianSardinian languageSardinian is a Romance language spoken and written on most of the island of Sardinia . It is considered the most conservative of the Romance languages in terms of phonology and is noted for its Paleosardinian substratum....
- SassareseSassareseSassarese is an Italo-Dalmatian language and transitional between Corsican and Sardinian. It is regarded as a Corsican–Sardinian language because of Sassari's historic ties with Tuscany and Corsica...
External links
- http://interromania.free.fr/media/pdf/maxia/studii_storici_sui_dialetti_della_sardegna.pdf
- Ethnologue report for Gallurese
- http://web.tiscali.it/consultagallurese/index.html
- http://web.tiscali.it/consultagallurese/attivita.htm
- http://www.uniud.it/cip/min_tutelate_scheda.htm
- http://eiha.crs4.it/cultura/opereWord/lingua/lingua.doc
- Walther von WARTBURGWalther von WartburgWalther von Wartburg was a Swiss philologist and lexicographer. He was the author of the Französisches Etymologisches Wörterbuch ....
"La fragmentation linguistique de la Romania", Paris, Librairie C. Klincksieck, 1967.

