
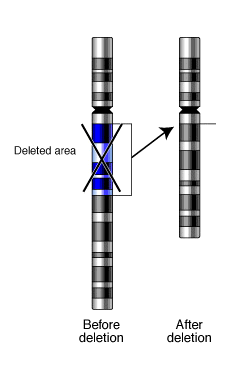
Genetic deletion
Encyclopedia
Genetics
Genetics , a discipline of biology, is the science of genes, heredity, and variation in living organisms....
, a deletion (also called gene deletion, deficiency, or deletion mutation) (sign: Δ
Delta (letter)
Delta is the fourth letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals it has a value of 4. It was derived from the Phoenician letter Dalet...
) is a mutation
Mutation
In molecular biology and genetics, mutations are changes in a genomic sequence: the DNA sequence of a cell's genome or the DNA or RNA sequence of a virus. They can be defined as sudden and spontaneous changes in the cell. Mutations are caused by radiation, viruses, transposons and mutagenic...
(a genetic aberration) in which a part of a chromosome
Chromosome
A chromosome is an organized structure of DNA and protein found in cells. It is a single piece of coiled DNA containing many genes, regulatory elements and other nucleotide sequences. Chromosomes also contain DNA-bound proteins, which serve to package the DNA and control its functions.Chromosomes...
or a sequence of DNA
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid is a nucleic acid that contains the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms . The DNA segments that carry this genetic information are called genes, but other DNA sequences have structural purposes, or are involved in...
is missing. Deletion is the loss of genetic material. Any number of nucleotide
Nucleotide
Nucleotides are molecules that, when joined together, make up the structural units of RNA and DNA. In addition, nucleotides participate in cellular signaling , and are incorporated into important cofactors of enzymatic reactions...
s can be deleted, from a single base to an entire piece of chromosome. Deletions can be caused by errors in chromosomal crossover
Chromosomal crossover
Chromosomal crossover is an exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes. It is one of the final phases of genetic recombination, which occurs during prophase I of meiosis in a process called synapsis. Synapsis begins before the synaptonemal complex develops, and is not completed...
during meiosis
Meiosis
Meiosis is a special type of cell division necessary for sexual reproduction. The cells produced by meiosis are gametes or spores. The animals' gametes are called sperm and egg cells....
. This causes several serious genetic diseases.
Deletion also causes frameshift.
Causes
Causes include the following:- Losses from translocationTranslocationTranslocation may refer to:* Chromosomal translocation, in genetics* Translocation in plants, transport of food or pesticides through phloem or xylem* Protein translocation or protein targeting, a process in protein biosynthesis...
- Chromosomal crossoverChromosomal crossoverChromosomal crossover is an exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes. It is one of the final phases of genetic recombination, which occurs during prophase I of meiosis in a process called synapsis. Synapsis begins before the synaptonemal complex develops, and is not completed...
s within a chromosomal inversionChromosomal inversionAn inversion is a chromosome rearrangement in which a segment of a chromosome is reversed end to end. An inversion occurs when a single chromosome undergoes breakage and rearrangement within itself. Inversions are of two types: paracentric and pericentric.Paracentric inversions do not include the... - Unequal crossing over
- Breaking without rejoining
For synapsis
Synapsis
Synapsis is the pairing of two homologous chromosomes that occurs during meiosis. It allows matching-up of homologous pairs prior to their segregation, and possible chromosomal crossover between them. Synapsis takes place during prophase I. When homologous chromosomes synapse, their ends are...
to occur between a chromosome with a large intercalary deficiency and a normal complete homolog, the unpaired region of the normal homolog must loop out of the linear structure into a deletion or compensation loop.
Types
Types of deletion include the following:- Terminal Deletion - a deletion that occurs towards the end of a chromosome.
- Intercalary Deletion / Interstitial Deletion - a deletion that occurs from the interior of a chromosome.
Effects
Small deletions are less likely to be fatal; large deletions are usually fatal - there are always variations based on which genes are lost. Some medium-sized deletions lead to recognizable human disorders.Deletion of a number of base pairs that is not evenly divisible by three will lead to a frameshift mutation
Frameshift mutation
A frameshift mutation is a genetic mutation caused by indels of a number of nucleotides that is not evenly divisible by three from a DNA sequence...
, causing all of the codons occurring after the deletion to be read incorrectly during translation
Translation (genetics)
In molecular biology and genetics, translation is the third stage of protein biosynthesis . In translation, messenger RNA produced by transcription is decoded by the ribosome to produce a specific amino acid chain, or polypeptide, that will later fold into an active protein...
, producing a severely altered and potentially nonfunctional protein
Protein
Proteins are biochemical compounds consisting of one or more polypeptides typically folded into a globular or fibrous form, facilitating a biological function. A polypeptide is a single linear polymer chain of amino acids bonded together by peptide bonds between the carboxyl and amino groups of...
. In contrast, a deletion that is evenly divisible by three is called an in-frame deletion.
Deletions are responsible for an array of genetic disorders, including some cases of male infertility
Infertility
Infertility primarily refers to the biological inability of a person to contribute to conception. Infertility may also refer to the state of a woman who is unable to carry a pregnancy to full term...
and two thirds of cases of Duchenne muscular dystrophy
Muscular dystrophy
Muscular dystrophy is a group of muscle diseases that weaken the musculoskeletal system and hamper locomotion. Muscular dystrophies are characterized by progressive skeletal muscle weakness, defects in muscle proteins, and the death of muscle cells and tissue.In the 1860s, descriptions of boys who...
. Deletion of part of the short arm of chromosome 5 results in a syndrome called Cri du chat
Cri du chat
Cri du chat syndrome, also known as chromosome 5p deletion syndrome, 5p minus syndrome or Lejeune’s syndrome, is a rare genetic disorder due to a missing part of chromosome 5. Its name is a French term referring to the characteristic cat-like cry of affected children. It was first described by...
, French for "cry of the cat" syndrome. It is found in approximately 1 in 50,000 live births. The surviving infants have a distinctive cry, severe mental retardation, and shortened life span.
Detection
The introduction of molecular techniques in conjunction with classical cytogenetic methods has in recent years greatly improved the diagnostic potential for chromosomal abnormalities. In particular, microarray-comparative genomic hybridization (CGH) based on the use of BAC clones promises a sensitive strategy for the detection of DNA copy-number changes on a genome-wide scale. The resolution of detection could as high as >30,000 "bands" and the size of chromosomal deletion detected could as small as 5–20 kb in length.See also
- IndelIndelIndel is a molecular biology term that has different definitions in different fields:*In evolutionary studies, indel is used to mean an insertion or a deletion and indels simply refers to the mutation class that includes both insertions, deletions, and the combination thereof, including insertion...
- Chromosome abnormalitiesChromosome abnormalitiesA chromosome anomaly, abnormality or aberration reflects an atypical number of chromosomes or a structural abnormality in one or more chromosomes. A Karyotype refers to a full set of chromosomes from an individual which can be compared to a "normal" Karyotype for the species via genetic testing. A...
- Null alleleNull alleleA null allele is a mutant copy of a gene that completely lacks that gene's normal function. This can be the result of the complete absence of the gene product at the molecular level, or the expression of a non-functional gene product...
- List of genetic disorders
- Medical geneticsMedical geneticsMedical genetics is the specialty of medicine that involves the diagnosis and management of hereditary disorders. Medical genetics differs from Human genetics in that human genetics is a field of scientific research that may or may not apply to medicine, but medical genetics refers to the...

