
Geography of Laos
Encyclopedia
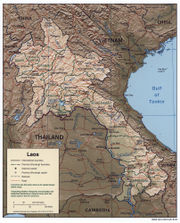
Laos
Laos Lao: ສາທາລະນະລັດ ປະຊາທິປະໄຕ ປະຊາຊົນລາວ Sathalanalat Paxathipatai Paxaxon Lao, officially the Lao People's Democratic Republic, is a landlocked country in Southeast Asia, bordered by Burma and China to the northwest, Vietnam to the east, Cambodia to the south and Thailand to the west...
is a landlocked nation in Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, South-East Asia, South East Asia or Southeastern Asia is a subregion of Asia, consisting of the countries that are geographically south of China, east of India, west of New Guinea and north of Australia. The region lies on the intersection of geological plates, with heavy seismic...
, northeast of Thailand
Thailand
Thailand , officially the Kingdom of Thailand , formerly known as Siam , is a country located at the centre of the Indochina peninsula and Southeast Asia. It is bordered to the north by Burma and Laos, to the east by Laos and Cambodia, to the south by the Gulf of Thailand and Malaysia, and to the...
, west of Vietnam
Vietnam
Vietnam – sometimes spelled Viet Nam , officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam – is the easternmost country on the Indochina Peninsula in Southeast Asia. It is bordered by China to the north, Laos to the northwest, Cambodia to the southwest, and the South China Sea –...
, that covers 236,800 square kilometers in the center of the Southeast Asian peninsula, is surrounded by Burma (Myanmar), Cambodia
Cambodia
Cambodia , officially known as the Kingdom of Cambodia, is a country located in the southern portion of the Indochina Peninsula in Southeast Asia...
, the People's Republic of China
People's Republic of China
China , officially the People's Republic of China , is the most populous country in the world, with over 1.3 billion citizens. Located in East Asia, the country covers approximately 9.6 million square kilometres...
, Thailand
Thailand
Thailand , officially the Kingdom of Thailand , formerly known as Siam , is a country located at the centre of the Indochina peninsula and Southeast Asia. It is bordered to the north by Burma and Laos, to the east by Laos and Cambodia, to the south by the Gulf of Thailand and Malaysia, and to the...
, and Vietnam
Vietnam
Vietnam – sometimes spelled Viet Nam , officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam – is the easternmost country on the Indochina Peninsula in Southeast Asia. It is bordered by China to the north, Laos to the northwest, Cambodia to the southwest, and the South China Sea –...
. Its location has often made it a buffer between more powerful neighboring states, as well as a crossroads for trade and communication. Migration and international conflict have contributed to the present ethnic composition of the country and to the geographic distribution of its ethnic groups.
Geographic coordinates:
18°00′N 105°00′E
Topography
Most of the western border of Laos is demarcated by the Mekong River, which is an important artery for transportation. The Dong falls at the southern end of the country prevent access to the sea, but cargo boats travel along the entire length of the Mekong in Laos during most of the year. Smaller power boats and pirogues provide an important means of transportation on many of the tributaries of the Mekong.
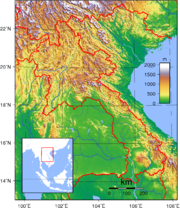
Laos shares its short--only 541 kilometers--southern border with Cambodia, and ancient Khmer ruins at Wat Pho and other southern locations attest to the long history of contact between the Lao and the Khmer. In the north, the country is bounded by a mountainous 423-kilometer border with China and shares the 235-kilometer-long Mekong River border with Burma.
The topography of Laos is largely mountainous, with elevations above 500 meters typically characterized by steep terrain, narrow river valleys, and low agricultural potential. This mountainous landscape extends across most of the north of the country, except for the plain of Vientiane and the Plain of Jars in Xiangkhoang Province. The southern "panhandle" of the country contains large level areas in Savannakhét and Champasak provinces that are well suited for extensive paddy rice cultivation and livestock raising. Much of Khammouan Province and the eastern part of all the southern provinces are mountainous. Together, the alluvial plains and terraces of the Mekong and its tributaries cover only about 20% of the land area.
Only about 4% of the total land area is classified as arable. The forested land area has declined significantly since the 1970s as a result of commercial logging and expanded swidden, or slash-and-burn, farming.
Climate
Luang Prabang
Luang Prabang, or Louangphrabang , is a city located in north central Laos, where the Nam Khan river meets the Mekong River about north of Vientiane. It is the capital of Luang Prabang Province...
) receives about 1360 millimetres (53.5 in). Rainfall is not always adequate for rice cultivation, however, and the relatively high average precipitation conceals years where rainfall may be only half or less of the norm, causing significant declines in rice yields. Such droughts often are regional, leaving production in other parts of the country unaffected. Temperatures range from highs around 40 °C (104 °F) along the Mekong in March and April to lows of 5 °C (41 °F) or less in the uplands of Xiangkhoang and Phôngsali in January.
Transportation routes
Because of its mountainous topography and lack of development, Laos has few reliable transportation routes. This inaccessibility has historically limited the ability of any government to maintain a presence in areas distant from the national or provincial capitals and has limited interchange and communication among villages and ethnic groups. The MekongMekong
The Mekong is a river that runs through China, Burma, Laos, Thailand, Cambodia and Vietnam. It is the world's 10th-longest river and the 7th-longest in Asia. Its estimated length is , and it drains an area of , discharging of water annually....
and Nam Ou
Nam Ou
The Nam Ou is one of the most important rivers of Laos. It runs 448 km from Phongsaly Province to Luang Prabang Province. Along with the Mekong, the Nam Ou is the only natural channel suitable for large-draft boat transportation. Near its confluence with the Mekong are the Pak Ou Caves,...
are the only natural channels suitable for large-draft boat transportation, and from December through May low water limits the size of the craft that may be used over many routes. Laotians in lowland villages located on the banks of smaller rivers have traditionally traveled in pirogues for fishing, trading, and visiting up and down the river for limited distances. Otherwise, travel is by ox-cart over level terrain or by foot. The steep mountains and lack of roads have caused upland ethnic groups to rely entirely on pack baskets and horse packing for transportation.
Natural resources
The road system is not extensive. However, a rudimentary network begun under French colonial rule and continued from the 1950s has provided an important means of increased intervillage communication, movement of market goods, and a focus for new settlements. In mid-1994, travel in most areas was difficult and expensive, and most Laotians traveled only limited distances, if at all. As a result of ongoing improvements in the road system during the early 1990s, however, it is expected that in the future villagers will more easily be able to seek medical care, send children to schools at district centers, and work outside the village.Expanding commercial exploitation of forests, plans for additional hydroelectric facilities, foreign demands for wild animals and nonwood forest products for food and traditional medicines, and a growing population have brought new and increasing attention to the forests. Traditionally, forests have been important sources of wild foods, herbal medicines, and timber for house construction. Even into the 1990s, the government viewed the forest as a valued reserve of natural products for noncommercial household consumption. Government efforts to preserve valuable hardwoods for commercial extraction have led to measures to prohibit swidden cultivation throughout the country. Further, government restrictions on clearing forestland for swidden cropping in the late 1980s, along with attempts to gradually resettle upland swidden farming villages (ban) to lowland locations suitable for paddy rice cultivation, had significant effects on upland villages. Traditionally, villages rely on forest products as a food reserve during years of poor rice harvest and as a regular source of fruits and vegetables. By the 1990s, however, these gathering systems were breaking down in many areas. At the same time, international concern about environmental degradation and the loss of many wildlife species unique to Laos has also prompted the government to consider the implications of these developments.
Natural resources: timber
Timber
Timber may refer to:* Timber, a term common in the United Kingdom and Australia for wood materials * Timber, Oregon, an unincorporated community in the U.S...
, hydropower
Hydropower
Hydropower, hydraulic power, hydrokinetic power or water power is power that is derived from the force or energy of falling water, which may be harnessed for useful purposes. Since ancient times, hydropower has been used for irrigation and the operation of various mechanical devices, such as...
, gypsum
Gypsum
Gypsum is a very soft sulfate mineral composed of calcium sulfate dihydrate, with the chemical formula CaSO4·2H2O. It is found in alabaster, a decorative stone used in Ancient Egypt. It is the second softest mineral on the Mohs Hardness Scale...
, tin
Tin
Tin is a chemical element with the symbol Sn and atomic number 50. It is a main group metal in group 14 of the periodic table. Tin shows chemical similarity to both neighboring group 14 elements, germanium and lead and has two possible oxidation states, +2 and the slightly more stable +4...
, gold
Gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au and an atomic number of 79. Gold is a dense, soft, shiny, malleable and ductile metal. Pure gold has a bright yellow color and luster traditionally considered attractive, which it maintains without oxidizing in air or water. Chemically, gold is a...
, gemstones
Gemstones
Gemstones is the third solo album by Adam Green, released in 2005. The album is characterised by the heavy presence of Wurlitzer piano, whereas its predecessor relied on a string section in its instrumentation.-Track listing:#Gemstones – 2:24...
Land use:
arable land: 3%
permanent crops: 0%
permanent pastures: 3%
forests and woodland: 54%
other: 40% (1993 est.)
Irrigated land: 1,250 km² (1993 est.)
note: rainy season irrigation - 2,169 km²; dry season irrigation - 750 km² (1998 est.)
Area and boundaries
Area:total: 236,800 km²
land: 230,800 km²
water: 6,000 km²
Area - comparative: slightly larger than Utah
Utah
Utah is a state in the Western United States. It was the 45th state to join the Union, on January 4, 1896. Approximately 80% of Utah's 2,763,885 people live along the Wasatch Front, centering on Salt Lake City. This leaves vast expanses of the state nearly uninhabited, making the population the...
Land boundaries:
total: 5,083 km
border countries: Burma
Myanmar
Burma , officially the Republic of the Union of Myanmar , is a country in Southeast Asia. Burma is bordered by China on the northeast, Laos on the east, Thailand on the southeast, Bangladesh on the west, India on the northwest, the Bay of Bengal to the southwest, and the Andaman Sea on the south....
235 km, Cambodia
Cambodia
Cambodia , officially known as the Kingdom of Cambodia, is a country located in the southern portion of the Indochina Peninsula in Southeast Asia...
541 km, the People's Republic of China
People's Republic of China
China , officially the People's Republic of China , is the most populous country in the world, with over 1.3 billion citizens. Located in East Asia, the country covers approximately 9.6 million square kilometres...
423 km, Thailand 1,754 km, Vietnam 2,130 km
Coastline: 0 km (landlocked
Landlocked
A landlocked country is a country entirely enclosed by land, or whose only coastlines lie on closed seas. There are 48 landlocked countries in the world, including partially recognized states...
)
Maritime claims: none (landlocked)
Elevation extremes:
lowest point: Mekong River
Mekong
The Mekong is a river that runs through China, Burma, Laos, Thailand, Cambodia and Vietnam. It is the world's 10th-longest river and the 7th-longest in Asia. Its estimated length is , and it drains an area of , discharging of water annually....
70 m
highest point: Phou Bia
Phou Bia
Phou Bia is the highest mountain in Laos and is located in the Annamese Cordillera, in the Phou Ane Plateau in Xiangkhouang Province.It is in a restricted military area near the abandoned Long Chen air base, and for this reason sees extremely few outside visitors. Unexploded ordnance further...
2,817 m
Environmental concerns
Natural hazards: floodFlood
A flood is an overflow of an expanse of water that submerges land. The EU Floods directive defines a flood as a temporary covering by water of land not normally covered by water...
s, drought
Drought
A drought is an extended period of months or years when a region notes a deficiency in its water supply. Generally, this occurs when a region receives consistently below average precipitation. It can have a substantial impact on the ecosystem and agriculture of the affected region...
s, blight
Blight
Blight refers to a specific symptom affecting plants in response to infection by a pathogenic organism. It is simply a rapid and complete chlorosis, browning, then death of plant tissues such as leaves, branches, twigs, or floral organs. Accordingly, many diseases that primarily exhibit this...
and earthquake
Earthquake
An earthquake is the result of a sudden release of energy in the Earth's crust that creates seismic waves. The seismicity, seismism or seismic activity of an area refers to the frequency, type and size of earthquakes experienced over a period of time...
s in the northern areas.
Air pollution agricultural burning ("slash and burn"), garbage burning
Environment - current issues: unexploded ordnance
Unexploded ordnance
Unexploded ordnance are explosive weapons that did not explode when they were employed and still pose a risk of detonation, potentially many decades after they were used or discarded.While "UXO" is widely and informally used, munitions and explosives of...
; deforestation
Deforestation
Deforestation is the removal of a forest or stand of trees where the land is thereafter converted to a nonforest use. Examples of deforestation include conversion of forestland to farms, ranches, or urban use....
; soil erosion; a majority of the population does not have access to potable water
Environment - international agreements:
party to: Biodiversity
Biodiversity
Biodiversity is the degree of variation of life forms within a given ecosystem, biome, or an entire planet. Biodiversity is a measure of the health of ecosystems. Biodiversity is in part a function of climate. In terrestrial habitats, tropical regions are typically rich whereas polar regions...
, Climate Change
United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change
The United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change is an international environmental treaty produced at the United Nations Conference on Environment and Development , informally known as the Earth Summit, held in Rio de Janeiro from June 3 to 14, 1992...
, Desertification
Desertification
Desertification is the degradation of land in drylands. Caused by a variety of factors, such as climate change and human activities, desertification is one of the most significant global environmental problems.-Definitions:...
, Environmental Modification, Law of the Sea
Law of the sea
Law of the sea may refer to:* United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea* Admiralty law* The Custom of the Sea...
, Nuclear Test Ban, Ozone Layer Protection
signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements

