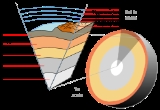
Geothermal gradient
Overview
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun, and the densest and fifth-largest of the eight planets in the Solar System. It is also the largest of the Solar System's four terrestrial planets...
's interior. Away from tectonic plate boundaries, it is 25–30°C per km of depth in most of the world. Strictly speaking, geo-thermal necessarily refers to the Earth
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun, and the densest and fifth-largest of the eight planets in the Solar System. It is also the largest of the Solar System's four terrestrial planets...
but the concept may be applied to other planets. The Earth's internal heat
Internal heat
Internal heat is the heat source from the interior of celestial objects, such as planets, brown dwarfs, and stars, caused by gravity, nuclear fusion and decaying radioactive materials. The amount of internal heating depends on mass; the more massive the object, the more internal heat it has...
comes from a combination of residual heat from planetary accretion
Gravitational binding energy
The gravitational binding energy of an object consisting of loose material, held together by gravity alone, is the amount of energy required to pull all of the material apart, to infinity...
(about 20%) and heat produced through radioactive decay
Radioactive decay
Radioactive decay is the process by which an atomic nucleus of an unstable atom loses energy by emitting ionizing particles . The emission is spontaneous, in that the atom decays without any physical interaction with another particle from outside the atom...
(80%).
Discussions

