German federal election, 1983
Encyclopedia
The tenth German federal election was conducted on March 6, 1983, to elect members to the Bundestag
(parliament) of the Federal Republic of Germany
.
was elected Chancellor by a CDU/CSU and FDP majority in the Bundestag, while the FDP in 1980 still was on the side of the SPD. Early elections were arranged. The SPD encountered difficulties because on the left a new party was emerging, the Greens.
A major issue in this election was the armament question after the NATO Double-Track Decision
.
as Chancellor. This was the first election in which the Greens secured representation in the Bundestag, and the first which saw a fourth (fifth) party in the parliament since 1960.
Bundestag
The Bundestag is a federal legislative body in Germany. In practice Germany is governed by a bicameral legislature, of which the Bundestag serves as the lower house and the Bundesrat the upper house. The Bundestag is established by the German Basic Law of 1949, as the successor to the earlier...
(parliament) of the Federal Republic of Germany
West Germany
West Germany is the common English, but not official, name for the Federal Republic of Germany or FRG in the period between its creation in May 1949 to German reunification on 3 October 1990....
.
Issues and campaign
In October 1982 CDU chairman Helmut KohlHelmut Kohl
Helmut Josef Michael Kohl is a German conservative politician and statesman. He was Chancellor of Germany from 1982 to 1998 and the chairman of the Christian Democratic Union from 1973 to 1998...
was elected Chancellor by a CDU/CSU and FDP majority in the Bundestag, while the FDP in 1980 still was on the side of the SPD. Early elections were arranged. The SPD encountered difficulties because on the left a new party was emerging, the Greens.
A major issue in this election was the armament question after the NATO Double-Track Decision
NATO Double-Track Decision
The NATO Double-Track Decision is the decision of NATO from December 12, 1979 to offer the Warsaw Pact a mutual limitation of Medium-range ballistic missiles and Intermediate-range ballistic missiles combined with the threat that in case of disagreement NATO would deploy more middle range nuclear...
.
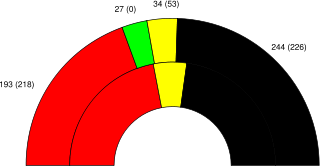
Results
| Party | Party List votes | Vote percentage (change) | Total Seats (change) | Seat percentage | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Christian Democratic Union (CDU) | 14,857,680 | 38.1% | +3.9% | 191 | +17 | 38.4% | |
| Christian Social Union (CSU) | 4,140,865 | 10.6% | +0.3% | 53 | +1 | 10.6% | |
| Free Democratic Party Free Democratic Party (Germany) The Free Democratic Party , abbreviated to FDP, is a centre-right classical liberal political party in Germany. It is led by Philipp Rösler and currently serves as the junior coalition partner to the Union in the German federal government... (FDP) |
2,706,942 | 6.9% | -3.7% | 34 | -19 | 6.8% | |
| Social Democratic Party Social Democratic Party of Germany The Social Democratic Party of Germany is a social-democratic political party in Germany... |
14,865,807 | 38.2% | -4.7% | 193 | -25 | 38.8% | |
| The Greens Alliance '90/The Greens Alliance '90/The Greens is a green political party in Germany, formed from the merger of the German Green Party and Alliance 90 in 1993. Its leaders are Claudia Roth and Cem Özdemir... |
2,167,431 | 5.6% | +4.1% | 27 | +27 | 5.4% | |
| All Others | 201,962 | 0.5% | 0 | 0.0% | |||
| Totals | 38,940,687 | 100.0% | 498 | +1 | 100.0% | ||

Post-election
The coalition between the CDU/CSU and the FDP returned to government, with Helmut KohlHelmut Kohl
Helmut Josef Michael Kohl is a German conservative politician and statesman. He was Chancellor of Germany from 1982 to 1998 and the chairman of the Christian Democratic Union from 1973 to 1998...
as Chancellor. This was the first election in which the Greens secured representation in the Bundestag, and the first which saw a fourth (fifth) party in the parliament since 1960.

