.gif)
Ghost (software)
Encyclopedia
Ghost is a disk cloning
program product sold by Symantec
. Originally developed by Murray Haszard
in 1995 for Binary Research
, the technology was acquired in 1998 by Symantec. The name Ghost is an acronym for General Hardware-Oriented System Transfer.
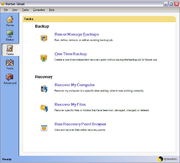
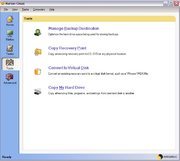 Binary Research developed Ghost in Auckland, New Zealand. After the Symantec acquisition, a few functions (such as translation into other languages) were moved elsewhere, but the main development remained in Auckland until October 2009 at which time much was moved to India.
Binary Research developed Ghost in Auckland, New Zealand. After the Symantec acquisition, a few functions (such as translation into other languages) were moved elsewhere, but the main development remained in Auckland until October 2009 at which time much was moved to India.
Technologies developed by 20/20 Software were integrated into Ghost after their acquisition by Symantec in April 2000.
. On August 2, 2004, Norton Ghost 9.0 was released as a new consumer version of Ghost, which was based on PowerQuest′s Drive Image version 7, and provided Live imaging of a Windows system. Ghost 9 continued to leverage the PowerQuest file format, meaning it wasn′t backward compatible with previous versions of Ghost. However, a version of Ghost 8.0 was included on the Ghost 9 recovery disk to support existing Ghost customers.
Ghost is marketed as a backup program. It comes with an ISO
file that needs to be written to a CD. This provides a recovery environment to perform a full system recovery. There′s also provision to mount a drive & select backed-up files from that drive and recover them to the primary hard disk.
Ghost can copy the contents of one hard drive to another and can convert a hard drive′s contents to a virtual disk format such as VMware
′s VMDK file.
filesystems directly, but it could also copy (although not resize) other filesystems by performing a sector
copy. Ghost added support for the NTFS
filesystem later in 1996, and also provided a program, Ghostwalker (DOS name: ghstwalk.exe), to change the Security ID (SID) that made Windows NT
systems distinguishable from each other. Ghostwalker is also capable of modifying the name of the Windows NT
-based computer from its own interface. Ghost added support for the ext2
filesystem in 1999 and for ext3
subsequently.
technology, following the lead of a competitor, ImageCast. Multicasting allows sending a single backup image simultaneously to other machines without putting greater stress on the network than by sending an image to a single machine. This version also introduced Ghost Explorer, a Windows
program which allowed a user to browse the contents of an image file and extract individual files from it. Explorer was subsequently enhanced to allow users to add and delete files on FAT, later on ext2, ext3 and NTFS filesystems in an image. Until 2007, Ghost Explorer could extract files from NTFS images but not edit NTFS images. Ghost Explorer could work with images from older versions but only slowly; version 4 images contained indexes to find files rapidly. Version 4.0 also moved from real-mode
DOS
to 286 protected-mode
. The additional memory available allowed Ghost to provide several levels of compression
for images, and to provide the file browser. In 1998, Ghost 4.1 allowed for password-protected images.
. The Binary Research logo, two stars revolving around each other, played on the main screen while the program idled. In 1998 Gdisk, a script based partition manager, was integrated in Ghost. Gdisk serves a role similar to Fdisk
, but has greater capabilities.
around 1999, with supported NSS
partitions (although it ran in DOS, like the others).
to refresh the disk of a machine remotely.
As a DOS-based program, Ghost required machines running Windows to reboot to a DOS environment to run it. Ghost 6.0 required a separate DOS partition when used with the Console.
Norton Ghost version 7.0 (retail) was marketed as Norton Ghost 2002 Personal Edition. Help|About reveals version 7.00.
Ghost 7.5 in 2002 created a ‘Virtual Partition’ instead – a DOS partition which actually exists as a file within a normal Windows filesystem. This significantly eased systems management because the user no longer had to set up their own partition tables. Ghost 7.5 could also write images to CD-R drives, and later versions can also write DVDs.
′s bootable CD. The Corporate edition supports Unicast, Multicast and peer-to-peer transfers via TCP/IP. Ghost 8.0 also allows an image to be saved on, or read from, an NTFS filesystem, although NTFS is not normally accessible from a DOS program.
 In 2004, Symantec renamed the Enterprise version of Ghost to Symantec Ghost Solution Suite 1.0. This helped to clarify the difference between the consumer and business lines of the product. This was further defined in February 2006, with the Release of Norton Save And Restore (some packages are labelled Norton Backup And Restore), a standalone backup application based on Ghost 10.0.
In 2004, Symantec renamed the Enterprise version of Ghost to Symantec Ghost Solution Suite 1.0. This helped to clarify the difference between the consumer and business lines of the product. This was further defined in February 2006, with the Release of Norton Save And Restore (some packages are labelled Norton Backup And Restore), a standalone backup application based on Ghost 10.0.
Released November 15, 2004
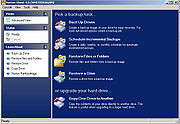 Ghost 9.0 was released August 2, 2004. It represents a significant shift in the consumer product line from Ghost 2003, in several ways:
Ghost 9.0 was released August 2, 2004. It represents a significant shift in the consumer product line from Ghost 2003, in several ways:
Since the DriveImage-based Ghost 9 did not support the older .gho format disk images, a separate CD containing Ghost 2003 was included in the retail packaging for users needing to access those older images.
The limitations of Ghost 9 compared to Ghost 2003 were not well communicated by Symantec, and resulted in many dissatisfied customers who purchased Ghost 9 expecting the previous version′s features (like making images from the bootable Ghost environment, no installation required, and no product activation).
external drives with Maxtor OneTouch buttons.
The Ghost version 10.0 are compatible with previous revisions, but not with future revisions.
, x64 versions of Windows, and GUID Partition Table
(GPT)-based disks (although the software does not yet fully support systems with Extensible Firmware Interface
(EFI)-compliant firmware). Running Live Update from Ghost Explorer will update Ghost to 11.0.2.1573.
support with an updated and more thorough user interface. It allowed for a full system backup & one where individual files or folders can be selected & backed up.
This version also provided a “LightsOut Restore” feature. This restored a system with an on-disk software recovery environment, thereby allowing a recovery without a bootable CD. Upon computer boot-up, a screen will ask which drive to boot from, the regular drive, or the LightsOut restore virtual drive.
LightsOut restore would augment the ISO disk, which came with the Ghost program, that had to be burned to a CD. That contained a recovery environment that allowed one to recover files even if Windows didn′t start up, but the computer could turn on. The latest update to that program was 12.0.5.29804.
This version also supports 32-bit and 64-bit versions of Windows XP and Vista.
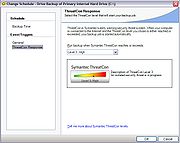 Version 14.0 preserves the features of version 12.0, with the ability to make full Volume Snapshot Service (VSS) backups and the option to make remote backups to an FTP site as another storage option. Ghost also leverages data from ThreatCon, which monitors malware activity around the world, and performs incremental backup
Version 14.0 preserves the features of version 12.0, with the ability to make full Volume Snapshot Service (VSS) backups and the option to make remote backups to an FTP site as another storage option. Ghost also leverages data from ThreatCon, which monitors malware activity around the world, and performs incremental backup
s when a specific threat level is reached. However, this functions only when connected to the Internet, so it will not resist any local attack.
Other features include the ability to back up to Network-attached storage
devices and support of NTFS
partitions up to 16TB. Ghost can manage other installations of version 12.0 or later across a network. Version 14 supports XP and Vista. The latest version is 14.0.5.34587. This version no longer supports opening of older version .gho image files. Rather, it stores images in .v2i format. Incremental backup images created with Norton Ghost saved with the file extension .IV2I on a regular basis after the initial volume backup (.V2I). The .iv2i file must be saved along with the initial .v2i backup file in order to function correctly. Older .gho image files can be restored using Ghost Explorer, a separate utility.
's bootable CD using a PE Builder plug-in for Symantec Ghost 11.
|-
! New Features !! Description
|-
| DeployAnywhere >
| Hot Imaging
| Image Formats
VMware
disk image (VMDK)
Symantec
Backup Exec System Recovery (BESR)
PowerQuest
image (PQi).
>-
| PreOS (boot disk) operating systems
|-
! New Features !! Description
|-
| Improved support for virtual formats>
VMware ESX 3.5i and 4.0i
VMware ESX 3.5 and 4.0
>-
| Improved platform support
Windows 7
Windows Vista with SP2 (includes Home Basic, Home Premium, Business-Retail, and Ultimate)
BitLocker-encrypted volume support
>-
| Create recovery points from within Symantec Recovery Disk
| Convert recovery points to virtual disks using a schedule
| Support for Microsoft Hyper-V
| Support for Blu-ray disc media
| 30-day trial If you choose to delay installation of the product license, all features will not be enabled during the 30-day trial period. The 30-day trial period begins when you do a particular task.
On April 1, 2010 an updated version of Norton Ghost 15 was released. The current version is 15.0.1.36526.
environment.
Driver selection and configuration within DOS was non-trivial from the beginning, and the limited space available on floppy disks made disk cloning of several different disk controllers a difficult task, where different SCSI, USB, and CD-ROM drives were involved. Mouse support was possible but often left out due to the limited space for drivers on a floppy disk..
Some devices such as USB often did not work using newer features such as USB 2.0, instead only operating at 1.0 speeds and taking hours to do what should have taken only a few minutes. As widespread support for DOS went into decline, it became increasingly difficult to get hardware drivers for DOS for the newer hardware.
Disk imaging competitors to Ghost have dealt with the decline of DOS by moving to Linux
based preboot environments, where they can draw on the driver development for the Linux kernel
to be able to image newer models of disk controllers. Nevertheless the DOS version of Ghost on compatible hardware configurations works much faster than most of the Linux based image and backup tools.
Eventually Ghost was rewritten as Ghost32.exe, a 32-bit version capable of running with the Windows Preinstallation Environment (WinPE), which is a stripped down version of Windows originally used by product manufacturers to set up new computers. Because WinPE was based on the modern 32-bit Windows, it could use the same plug and play hardware drivers as a standard desktop computer, making hardware support for Ghost much simpler.
Ghost32.exe is also compatible with BartPE
(Bart's Preinstalled Environment) a Windows XP based Live CD created using the PE Builder. To integrate Ghost32.exe into BartPE a PE Builder plug-in for Ghost is available.
Disk cloning
Disk cloning is the process of copying the contents of one computer hard disk to another disk or to an "image" file. Often, the contents of the first disk are written to an image file as an intermediate step, and the second disk is loaded with the contents of the image...
program product sold by Symantec
Symantec
Symantec Corporation is the largest maker of security software for computers. The company is headquartered in Mountain View, California, and is a Fortune 500 company and a member of the S&P 500 stock market index.-History:...
. Originally developed by Murray Haszard
Murray Haszard
Murray Hayden Haszard is a New Zealand entrepreneur and businessman who founded the companies B32 Software and Binary Research and is presently the chairman of Ilion Technology.Haszard married Kris MacPherson, and they had two children...
in 1995 for Binary Research
Binary Research
Binary Research Ltd was a company founded in Auckland, New Zealand by Murray Haszard in 1991 after the sale of his previous company, B32 Software.Binary Research initially considered developing competitors to the file transfer programs Blast and Laplink...
, the technology was acquired in 1998 by Symantec. The name Ghost is an acronym for General Hardware-Oriented System Transfer.
History


Technologies developed by 20/20 Software were integrated into Ghost after their acquisition by Symantec in April 2000.
PowerQuest
At the end of 2003, Symantec acquired its largest competitor, PowerQuestPowerQuest
PowerQuest was a software company that produced utility software. It was acquired by Symantec in 2003. PowerQuest's market focus was on management of computer data storage, especially file systems and disk partitions. Their products included PartitionMagic, ServerMagic, and Drive...
. On August 2, 2004, Norton Ghost 9.0 was released as a new consumer version of Ghost, which was based on PowerQuest′s Drive Image version 7, and provided Live imaging of a Windows system. Ghost 9 continued to leverage the PowerQuest file format, meaning it wasn′t backward compatible with previous versions of Ghost. However, a version of Ghost 8.0 was included on the Ghost 9 recovery disk to support existing Ghost customers.
Phantom
The internal project name Phantom designated a complete rewrite of the Ghost cloning engine at Symantec in Auckland. The Phantom project ran for about three years in parallel with the ongoing development of the Ghost code. Some parts of the Phantom code, such as the ability to write to NTFS filesystems from MS-DOS, got folded into the main Ghost product. Symantec released a prototype of Phantom as Ghost for Manufacturing in 2003.Backup software
Although disk cloning programs are not primarily backup programs, they are sometimes used as such. A key feature of a backup program is to allow the retrieval of individual files without needing to restore the entire backup. Disk cloning programs either provide a Windows Explorer-like program to browse image files and extract individual files from them, or allow an image file to be mounted as a read-only filesystem within Windows Explorer.Ghost is marketed as a backup program. It comes with an ISO
ISO image
An ISO image is an archive file of an optical disc, composed of the data contents of every written sector of an optical disc, including the optical disc file system...
file that needs to be written to a CD. This provides a recovery environment to perform a full system recovery. There′s also provision to mount a drive & select backed-up files from that drive and recover them to the primary hard disk.
Ghost can copy the contents of one hard drive to another and can convert a hard drive′s contents to a virtual disk format such as VMware
VMware
VMware, Inc. is a company providing virtualization software founded in 1998 and based in Palo Alto, California, USA. The company was acquired by EMC Corporation in 2004, and operates as a separate software subsidiary ....
′s VMDK file.
Filesystems
Initially, Ghost supported only FATFile Allocation Table
File Allocation Table is a computer file system architecture now widely used on many computer systems and most memory cards, such as those used with digital cameras. FAT file systems are commonly found on floppy disks, flash memory cards, digital cameras, and many other portable devices because of...
filesystems directly, but it could also copy (although not resize) other filesystems by performing a sector
Disk sector
In computer disk storage, a sector is a subdivision of a track on a magnetic disk or optical disc. Each sector stores a fixed amount of user data. Traditional formatting of these storage media provides space for 512 bytes or 2048 bytes of user-accessible data per sector...
copy. Ghost added support for the NTFS
NTFS
NTFS is the standard file system of Windows NT, including its later versions Windows 2000, Windows XP, Windows Server 2003, Windows Server 2008, Windows Vista, and Windows 7....
filesystem later in 1996, and also provided a program, Ghostwalker (DOS name: ghstwalk.exe), to change the Security ID (SID) that made Windows NT
Windows NT
Windows NT is a family of operating systems produced by Microsoft, the first version of which was released in July 1993. It was a powerful high-level-language-based, processor-independent, multiprocessing, multiuser operating system with features comparable to Unix. It was intended to complement...
systems distinguishable from each other. Ghostwalker is also capable of modifying the name of the Windows NT
Windows NT
Windows NT is a family of operating systems produced by Microsoft, the first version of which was released in July 1993. It was a powerful high-level-language-based, processor-independent, multiprocessing, multiuser operating system with features comparable to Unix. It was intended to complement...
-based computer from its own interface. Ghost added support for the ext2
Ext2
The ext2 or second extended filesystem is a file system for the Linux kernel. It was initially designed by Rémy Card as a replacement for the extended file system ....
filesystem in 1999 and for ext3
Ext3
The ext3 or third extended filesystem is a journaled file system that is commonly used by the Linux kernel. It is the default file system for many popular Linux distributions, including Debian...
subsequently.
Ghost 3.1
The first versions of Ghost supported only the cloning of entire disks, however version 3.1 in 1997 allowed the cloning of individual partitions. Ghost could clone a disk or partition to another disk or partition or to an image file. Ghost allowed for writing a clone or image to a second disk in the same machine, another machine linked by a parallel or network cable, a network drive, or to a tape drive.Ghost 4.0 and 4.1
Version 4.0 of Ghost added multicastMulticast
In computer networking, multicast is the delivery of a message or information to a group of destination computers simultaneously in a single transmission from the source creating copies automatically in other network elements, such as routers, only when the topology of the network requires...
technology, following the lead of a competitor, ImageCast. Multicasting allows sending a single backup image simultaneously to other machines without putting greater stress on the network than by sending an image to a single machine. This version also introduced Ghost Explorer, a Windows
Microsoft Windows
Microsoft Windows is a series of operating systems produced by Microsoft.Microsoft introduced an operating environment named Windows on November 20, 1985 as an add-on to MS-DOS in response to the growing interest in graphical user interfaces . Microsoft Windows came to dominate the world's personal...
program which allowed a user to browse the contents of an image file and extract individual files from it. Explorer was subsequently enhanced to allow users to add and delete files on FAT, later on ext2, ext3 and NTFS filesystems in an image. Until 2007, Ghost Explorer could extract files from NTFS images but not edit NTFS images. Ghost Explorer could work with images from older versions but only slowly; version 4 images contained indexes to find files rapidly. Version 4.0 also moved from real-mode
Real mode
Real mode, also called real address mode, is an operating mode of 80286 and later x86-compatible CPUs. Real mode is characterized by a 20 bit segmented memory address space and unlimited direct software access to all memory, I/O addresses and peripheral hardware...
DOS
DOS
DOS, short for "Disk Operating System", is an acronym for several closely related operating systems that dominated the IBM PC compatible market between 1981 and 1995, or until about 2000 if one includes the partially DOS-based Microsoft Windows versions 95, 98, and Millennium Edition.Related...
to 286 protected-mode
Protected mode
In computing, protected mode, also called protected virtual address mode, is an operational mode of x86-compatible central processing units...
. The additional memory available allowed Ghost to provide several levels of compression
Data compression
In computer science and information theory, data compression, source coding or bit-rate reduction is the process of encoding information using fewer bits than the original representation would use....
for images, and to provide the file browser. In 1998, Ghost 4.1 allowed for password-protected images.
Ghost 5.0
Version 5.0 moved to 386 protected mode. Unlike the character-based user interface of earlier versions, 5.0 used a GUIGui
Gui or guee is a generic term to refer to grilled dishes in Korean cuisine. These most commonly have meat or fish as their primary ingredient, but may in some cases also comprise grilled vegetables or other vegetarian ingredients. The term derives from the verb, "gupda" in Korean, which literally...
. The Binary Research logo, two stars revolving around each other, played on the main screen while the program idled. In 1998 Gdisk, a script based partition manager, was integrated in Ghost. Gdisk serves a role similar to Fdisk
Fdisk
On personal computer operating systems, fdisk is a commonly used name for a command-line utility that provides disk partitioning functions...
, but has greater capabilities.
Ghost for NetWare
There was also a Norton Ghost version (called 2.0) for Novell NetWareNovell NetWare
NetWare is a network operating system developed by Novell, Inc. It initially used cooperative multitasking to run various services on a personal computer, with network protocols based on the archetypal Xerox Network Systems stack....
around 1999, with supported NSS
Novell Storage Services
Novell Storage Services is a file system used by the Novell NetWare operating system. Recently support of NSS was introduced to SUSE Linux via low-level network NCPFS protocol...
partitions (although it ran in DOS, like the others).
Ghost 6.0 (Ghost 2001)
Ghost 6.0 included a Console application in 2000 to simplify the management of large numbers of machines. The Console communicates with client software on managed computers to allow a system administratorSystem administrator
A system administrator, IT systems administrator, systems administrator, or sysadmin is a person employed to maintain and operate a computer system and/or network...
to refresh the disk of a machine remotely.
As a DOS-based program, Ghost required machines running Windows to reboot to a DOS environment to run it. Ghost 6.0 required a separate DOS partition when used with the Console.
Ghost 7.0 / Ghost 2002
Released March 31, 2001Norton Ghost version 7.0 (retail) was marketed as Norton Ghost 2002 Personal Edition. Help|About reveals version 7.00.
Ghost 7.5
Released December 14, 2001Ghost 7.5 in 2002 created a ‘Virtual Partition’ instead – a DOS partition which actually exists as a file within a normal Windows filesystem. This significantly eased systems management because the user no longer had to set up their own partition tables. Ghost 7.5 could also write images to CD-R drives, and later versions can also write DVDs.
Symantec Ghost 8.0
Ghost 8.0 includes a standalone executable (filename: ghost32.exe) that runs directly from Windows, without the need to reboot. It is very well-suited for placement on bootable media, such as BartPEBartPE
BartPE is a lightweight variant of the 32-bit version of Microsoft Windows XP or Windows Server 2003, similar to Windows Preinstallation Environment, which can be run from a Live CD or Live USB drive....
′s bootable CD. The Corporate edition supports Unicast, Multicast and peer-to-peer transfers via TCP/IP. Ghost 8.0 also allows an image to be saved on, or read from, an NTFS filesystem, although NTFS is not normally accessible from a DOS program.
Norton Ghost 2003
Norton Ghost 2003, a consumer edition of Ghost, was released on September 6, 2002. Available as an independent product, Norton Ghost 2003 was also included as a component of Norton SystemWorks 2003 Professional. A simpler, non-corporate version of Ghost, Norton Ghost 2003 does not include the Console but has a Windows front-end to script Ghost operations and create a bootable Ghost diskette (third-party CD burning software can be used to create a bootable Ghost CD based on a bootable Ghost diskette). The machine still needs to reboot to the Virtual Partition, but the user doesn′t need to interact with DOS. Symantec deprecated LiveUpdate support for Norton Ghost 2003 in early 2006. Two Symantec knowledge base articles (Updates to Norton Ghost 2003 How to obtain the programs updates that are archived on Symantec LiveUpdate server) provide step-by-step instructions detailing how to obtain Norton Ghost 2003 updates from the LiveUpdate Archive. As of April 24, 2008, the latest version available from the archive is 2003.793. Older versions of Norton Ghost 2003 can be also updated from a system with a newer version of Norton Ghost 2003 by copying program directory from newer to older. Reliable support for SATA drives was also provided in 2003.793.Symantec Ghost Solution Suite 1.0 (Ghost 8.2)

Released November 15, 2004
Symantec Ghost Solution Suite 1.1 (Ghost 8.3)
Ghost Solution Suite 1.1 was released December 2005. Some of the new features include the ability to create an image file that is larger than 2 GB (in Ghost 8.2 or earlier versions, such image files are automatically split into two or more segments, so that each segment has a maximum size of 2 GB), more comprehensive manufacturing tools, and the ability to create a universal boot disk. Ghost Solution Suite is a bundle of an updated version of Ghost, Symantec Client Migration (a user data and settings migration tool) and the former PowerQuest equivalent, DeployCenter (using PQI images).Norton Ghost 9.0 (includes Ghost 2003)

- It uses a totally different code base, based on the DriveImageDriveImageDrive Image is a software disk cloning package for Intel-based computers. The software was developed and distributed by the former PowerQuest Corporation. Drive Image version 7 became the basis for Norton Ghost 9.0, which was released to retail markets in August 2004. Ghost was a competing...
/V2i Protector product via Symantec′s acquisition of PowerQuestPowerQuestPowerQuest was a software company that produced utility software. It was acquired by Symantec in 2003. PowerQuest's market focus was on management of computer data storage, especially file systems and disk partitions. Their products included PartitionMagic, ServerMagic, and Drive...
. - The main product is a Windows-based application that must be installed on the target system.
- Images of the system can be made while Windows is running, rather than only when booted directly into DOS-mode Ghost.
- IncrementalIncremental backupAn incremental backup preserves data by not creating multiple copies that are based on the differences in those data: a successive copy of the data contains only that portion which has changed since the preceding copy has been created.-Incremental:...
images (containing only changes since the last image) are supported. - The Windows application requires Product ActivationProduct activationProduct activation is a license validation procedure required by some proprietary computer software programs. In one form, product activation refers to a method invented by Ric Richardson and patented by Uniloc where a software application hashes hardware serial numbers and an ID number specific...
in order to function fully. - The bootable environment on the Ghost 9 CD is only useful for recovery of existing backups – it cannot be used to create new images.
Since the DriveImage-based Ghost 9 did not support the older .gho format disk images, a separate CD containing Ghost 2003 was included in the retail packaging for users needing to access those older images.
The limitations of Ghost 9 compared to Ghost 2003 were not well communicated by Symantec, and resulted in many dissatisfied customers who purchased Ghost 9 expecting the previous version′s features (like making images from the bootable Ghost environment, no installation required, and no product activation).
Norton Ghost 10.0
Supported media CDR/RW and DVD+-R/RW drives, USB and FireWire (IEEE 1394) devices, and Iomega Zip and Jaz drives. Enables the encryption of backups and support for MaxtorMaxtor
Maxtor Corporation, founded in 1982 and acquired by Seagate Technology in 2006, was an American manufacturer of computer hard disk drives, the third largest in the world immediately prior to acquisition...
external drives with Maxtor OneTouch buttons.
The Ghost version 10.0 are compatible with previous revisions, but not with future revisions.
Norton Save And Restore 1.0 (Ghost 10.0)
Norton Save And Restore 1.0, released February 2006, was the renamed consumer version of Ghost. The system utilized Ghost 10.0′s engine, with the addition of features to allow backup and restoration of individual files.Symantec Ghost Solution Suite 2.0 (Ghost 11.0)
Ghost Solution Suite 2.0 was released in November 2006. This version provides significant improvements in performance, as well as the ability to edit NTFS images. This version also adds support for Windows VistaWindows Vista
Windows Vista is an operating system released in several variations developed by Microsoft for use on personal computers, including home and business desktops, laptops, tablet PCs, and media center PCs...
, x64 versions of Windows, and GUID Partition Table
GUID Partition Table
In computer hardware, GUID Partition Table is a standard for the layout of the partition table on a physical hard disk. Although it forms a part of the Extensible Firmware Interface standard , it is also used on some BIOS systems because of the limitations of MBR partition tables, which restrict...
(GPT)-based disks (although the software does not yet fully support systems with Extensible Firmware Interface
Extensible Firmware Interface
The Unified Extensible Firmware Interface is a specification that defines a software interface between an operating system and platform firmware...
(EFI)-compliant firmware). Running Live Update from Ghost Explorer will update Ghost to 11.0.2.1573.
| Ghost 11.0 supported image formats to save and restore: | *.GHO, *.GHS, *.IMG, *.RAW |
Norton Ghost 12.0
Ghost 12.0 includes Windows VistaWindows Vista
Windows Vista is an operating system released in several variations developed by Microsoft for use on personal computers, including home and business desktops, laptops, tablet PCs, and media center PCs...
support with an updated and more thorough user interface. It allowed for a full system backup & one where individual files or folders can be selected & backed up.
This version also provided a “LightsOut Restore” feature. This restored a system with an on-disk software recovery environment, thereby allowing a recovery without a bootable CD. Upon computer boot-up, a screen will ask which drive to boot from, the regular drive, or the LightsOut restore virtual drive.
LightsOut restore would augment the ISO disk, which came with the Ghost program, that had to be burned to a CD. That contained a recovery environment that allowed one to recover files even if Windows didn′t start up, but the computer could turn on. The latest update to that program was 12.0.5.29804.
Norton Save & Restore 2.0 (Ghost 13.0)
NSR 2.0 has fewer features when compared to Norton Ghost 12. NSR 2.0 offers one-time backups, file and folder backup, simplified schedule editor, Maxtor OneTouch integration and modifiable Symantec recovery disc.This version also supports 32-bit and 64-bit versions of Windows XP and Vista.
Norton Ghost 14.0

Incremental backup
An incremental backup preserves data by not creating multiple copies that are based on the differences in those data: a successive copy of the data contains only that portion which has changed since the preceding copy has been created.-Incremental:...
s when a specific threat level is reached. However, this functions only when connected to the Internet, so it will not resist any local attack.
Other features include the ability to back up to Network-attached storage
Network-attached storage
Network-attached storage is file-level computer data storage connected to a computer network providing data access to heterogeneous clients. NAS not only operates as a file server, but is specialized for this task either by its hardware, software, or configuration of those elements...
devices and support of NTFS
NTFS
NTFS is the standard file system of Windows NT, including its later versions Windows 2000, Windows XP, Windows Server 2003, Windows Server 2008, Windows Vista, and Windows 7....
partitions up to 16TB. Ghost can manage other installations of version 12.0 or later across a network. Version 14 supports XP and Vista. The latest version is 14.0.5.34587. This version no longer supports opening of older version .gho image files. Rather, it stores images in .v2i format. Incremental backup images created with Norton Ghost saved with the file extension .IV2I on a regular basis after the initial volume backup (.V2I). The .iv2i file must be saved along with the initial .v2i backup file in order to function correctly. Older .gho image files can be restored using Ghost Explorer, a separate utility.
Symantec Ghost Solution Suite 2.5
This is the current version of the enterprise software, and includes Ghost 11.5. It was released in May 2008. New features include DeployAnywhere, Hot Imaging, logical volume support, additional image formats, and new PreOS (boot disk) operating systems. As of January 6, 2010, the latest build from Live Update is 11.5.1.2266 (Live Update 5 (LU5)). This update provides support for Windows 7 and 2008 R2. Furthermore Ghost 11.5 is compatible with BartPEBartPE
BartPE is a lightweight variant of the 32-bit version of Microsoft Windows XP or Windows Server 2003, similar to Windows Preinstallation Environment, which can be run from a Live CD or Live USB drive....
's bootable CD using a PE Builder plug-in for Symantec Ghost 11.
| Ghost 11.5 supported image formats to save: | *.GHO, *.GHS, *.VMDK VMDK The VMDK file format is a type of virtual appliance developed for VMware products. The format is open/documented.-Products that use the format:* VMware Workstation* VMware Player* VMware Server* VMware Fusion... |
| Ghost 11.5 supported image formats to restore: | *.GHO, *.GHS, *.VMDK VMDK The VMDK file format is a type of virtual appliance developed for VMware products. The format is open/documented.-Products that use the format:* VMware Workstation* VMware Player* VMware Server* VMware Fusion... , *.V2I, *.IV2I, *.PQI |
- Improved support for virtual formats
! New Features !! Description
|-
| DeployAnywhere >
| Hot Imaging
| Image Formats
VMware
VMware, Inc. is a company providing virtualization software founded in 1998 and based in Palo Alto, California, USA. The company was acquired by EMC Corporation in 2004, and operates as a separate software subsidiary ....
disk image (VMDK)
Symantec
Symantec Corporation is the largest maker of security software for computers. The company is headquartered in Mountain View, California, and is a Fortune 500 company and a member of the S&P 500 stock market index.-History:...
Backup Exec System Recovery (BESR)
PowerQuest
PowerQuest was a software company that produced utility software. It was acquired by Symantec in 2003. PowerQuest's market focus was on management of computer data storage, especially file systems and disk partitions. Their products included PartitionMagic, ServerMagic, and Drive...
image (PQi).
>-
| PreOS (boot disk) operating systems
- 32-bit Windows PE with greatly enhanced driver set
- Linux (based on ThinstationThinstationThinstation is a free and open source Linux implementation of a thin client operating system. It only requires standard 32-bit x86 PC hardware and can boot directly from the network via PXE or Etherboot from a TFTP server, or from local devices such as Hard disks, CompactFlash drives, USB keyrings...
)
Norton Ghost 15.0
Ghost was updated in November 2009 to v15.0.0.35659. According to the [ftp://ftp.symantec.com/public/english_us_canada/products/ghost/15/manuals/ngh_15_user_guide.pdf manual] on Symantec′s site, the following features are available in Ghost 15:! New Features !! Description
|-
| Improved support for virtual formats>
>-
| Improved platform support
>-
| Create recovery points from within Symantec Recovery Disk
| Convert recovery points to virtual disks using a schedule
| Support for Microsoft Hyper-V
| Support for Blu-ray disc media
| 30-day trial
On April 1, 2010 an updated version of Norton Ghost 15 was released. The current version is 15.0.1.36526.
Transition away from DOS
The off-line version of Ghost, which runs from bootable media in place of the installed operating system, originally faced a number of driver support difficulties due to limitations of the increasingly obsolete 16-bit DOSDOS
DOS, short for "Disk Operating System", is an acronym for several closely related operating systems that dominated the IBM PC compatible market between 1981 and 1995, or until about 2000 if one includes the partially DOS-based Microsoft Windows versions 95, 98, and Millennium Edition.Related...
environment.
Driver selection and configuration within DOS was non-trivial from the beginning, and the limited space available on floppy disks made disk cloning of several different disk controllers a difficult task, where different SCSI, USB, and CD-ROM drives were involved. Mouse support was possible but often left out due to the limited space for drivers on a floppy disk..
Some devices such as USB often did not work using newer features such as USB 2.0, instead only operating at 1.0 speeds and taking hours to do what should have taken only a few minutes. As widespread support for DOS went into decline, it became increasingly difficult to get hardware drivers for DOS for the newer hardware.
Disk imaging competitors to Ghost have dealt with the decline of DOS by moving to Linux
Linux
Linux is a Unix-like computer operating system assembled under the model of free and open source software development and distribution. The defining component of any Linux system is the Linux kernel, an operating system kernel first released October 5, 1991 by Linus Torvalds...
based preboot environments, where they can draw on the driver development for the Linux kernel
Linux kernel
The Linux kernel is an operating system kernel used by the Linux family of Unix-like operating systems. It is one of the most prominent examples of free and open source software....
to be able to image newer models of disk controllers. Nevertheless the DOS version of Ghost on compatible hardware configurations works much faster than most of the Linux based image and backup tools.
Eventually Ghost was rewritten as Ghost32.exe, a 32-bit version capable of running with the Windows Preinstallation Environment (WinPE), which is a stripped down version of Windows originally used by product manufacturers to set up new computers. Because WinPE was based on the modern 32-bit Windows, it could use the same plug and play hardware drivers as a standard desktop computer, making hardware support for Ghost much simpler.
Ghost32.exe is also compatible with BartPE
BartPE
BartPE is a lightweight variant of the 32-bit version of Microsoft Windows XP or Windows Server 2003, similar to Windows Preinstallation Environment, which can be run from a Live CD or Live USB drive....
(Bart's Preinstalled Environment) a Windows XP based Live CD created using the PE Builder. To integrate Ghost32.exe into BartPE a PE Builder plug-in for Ghost is available.
External links
- Symantec Ghost – Solution suite (previously Norton Ghost Enterprise Edition) product page
- Norton Ghost home page
- Brief overview of Symantec Ghost and Norton Ghost versions
- Symantec News
- Symantec Ghost Release Details (Dates seems somewhat questionable based on press releases)
- Symantec Ghost Solution Suite Release Details (Dates seem somewhat questionable based on press releases)

