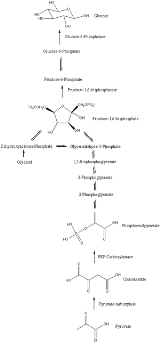
Gluconeogenesis
Overview
Gluconeogenesis is a metabolic pathway
that results in the generation of glucose
from non-carbohydrate
carbon substrates such as lactate
, glycerol
, and glucogenic amino acid
s.
It is one of the two main mechanisms humans and many other animals use to keep blood glucose
levels from dropping too low (hypoglycemia
). The other means of maintaining blood glucose
levels is through the degradation of glycogen
(glycogenolysis
).
Gluconeogenesis is a ubiquitous process, present in plants, animals, fungi, bacteria, and other microorganisms. In animals, gluconeogenesis takes place mainly in the liver
and, to a lesser extent, in the cortex of kidney
s.
Metabolic pathway
In biochemistry, metabolic pathways are series of chemical reactions occurring within a cell. In each pathway, a principal chemical is modified by a series of chemical reactions. Enzymes catalyze these reactions, and often require dietary minerals, vitamins, and other cofactors in order to function...
that results in the generation of glucose
Glucose
Glucose is a simple sugar and an important carbohydrate in biology. Cells use it as the primary source of energy and a metabolic intermediate...
from non-carbohydrate
Carbohydrate
A carbohydrate is an organic compound with the empirical formula ; that is, consists only of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, with a hydrogen:oxygen atom ratio of 2:1 . However, there are exceptions to this. One common example would be deoxyribose, a component of DNA, which has the empirical...
carbon substrates such as lactate
Lactic acid
Lactic acid, also known as milk acid, is a chemical compound that plays a role in various biochemical processes and was first isolated in 1780 by the Swedish chemist Carl Wilhelm Scheele. Lactic acid is a carboxylic acid with the chemical formula C3H6O3...
, glycerol
Glycerol
Glycerol is a simple polyol compound. It is a colorless, odorless, viscous liquid that is widely used in pharmaceutical formulations. Glycerol has three hydroxyl groups that are responsible for its solubility in water and its hygroscopic nature. The glycerol backbone is central to all lipids...
, and glucogenic amino acid
Glucogenic amino acid
A glucogenic amino acid is an amino acid that can be converted into glucose through gluconeogenesis. This is in contrast to the ketogenic amino acids, which are converted into ketone bodies....
s.
It is one of the two main mechanisms humans and many other animals use to keep blood glucose
Glucose
Glucose is a simple sugar and an important carbohydrate in biology. Cells use it as the primary source of energy and a metabolic intermediate...
levels from dropping too low (hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia or hypoglycæmia is the medical term for a state produced by a lower than normal level of blood glucose. The term literally means "under-sweet blood"...
). The other means of maintaining blood glucose
Glucose
Glucose is a simple sugar and an important carbohydrate in biology. Cells use it as the primary source of energy and a metabolic intermediate...
levels is through the degradation of glycogen
Glycogen
Glycogen is a molecule that serves as the secondary long-term energy storage in animal and fungal cells, with the primary energy stores being held in adipose tissue...
(glycogenolysis
Glycogenolysis
Glycogenolysis is the conversion of glycogen polymers to glucose monomers. Glycogen is catabolized by removal of a glucose monomer through cleavage with inorganic phosphate to produce glucose-1-phosphate...
).
Gluconeogenesis is a ubiquitous process, present in plants, animals, fungi, bacteria, and other microorganisms. In animals, gluconeogenesis takes place mainly in the liver
Liver
The liver is a vital organ present in vertebrates and some other animals. It has a wide range of functions, including detoxification, protein synthesis, and production of biochemicals necessary for digestion...
and, to a lesser extent, in the cortex of kidney
Kidney
The kidneys, organs with several functions, serve essential regulatory roles in most animals, including vertebrates and some invertebrates. They are essential in the urinary system and also serve homeostatic functions such as the regulation of electrolytes, maintenance of acid–base balance, and...
s.
Unanswered Questions

