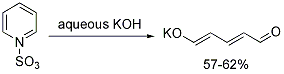Glutaconaldehyde
Encyclopedia
Glutaconaldehyde is an organic compound
with the formula
C5H6O2. It is an unsaturated dialdehyde as is related to glutaraldehyde
and glutaconic acid
, but exists in its enol
form due to the conjugation
with the double bond.
Both the sodium and potassium salts of glutaconaldehyde are known. They are efficiently synthesized from pyridine sulfonate.
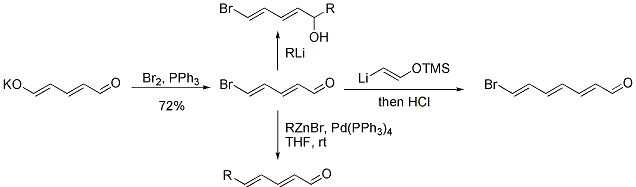
The reaction of the glutaconaldehyde anion with acid chlorides
gives the corresponding enol esters. Glutaconaldehyde can also be converted to the corresponding vinyl bromide
as shown below. This product can be reacted with nucleophiles, cross-coupled
using palladium
, or homologated
by two carbons.
Organic compound
An organic compound is any member of a large class of gaseous, liquid, or solid chemical compounds whose molecules contain carbon. For historical reasons discussed below, a few types of carbon-containing compounds such as carbides, carbonates, simple oxides of carbon, and cyanides, as well as the...
with the formula
Chemical formula
A chemical formula or molecular formula is a way of expressing information about the atoms that constitute a particular chemical compound....
C5H6O2. It is an unsaturated dialdehyde as is related to glutaraldehyde
Glutaraldehyde
Glutaraldehyde is an organic compound with the formula CH22. A pungent colorless oily liquid, glutaraldehyde is used to disinfect medical and dental equipment...
and glutaconic acid
Glutaconic acid
trans-Glutaconic acid is an organic compound with formula HO2CCH=CHCH2CO2H. This dicarboxylic acid exists as a colorless solid and is related to the saturated chemical glutaric acid, HO2CC3CO2H. Esters and salts of glutaconic acid are called glutaconates.-Related compounds:The geometric isomer,...
, but exists in its enol
Enol
Enols are alkenes with a hydroxyl group affixed to one of the carbon atoms composing the double bond. Alkenes with a hydroxyl group on both sides of the double bond are called enediols. Deprotonated anions of enols are called enolates...
form due to the conjugation
Conjugated system
In chemistry, a conjugated system is a system of connected p-orbitals with delocalized electrons in compounds with alternating single and multiple bonds, which in general may lower the overall energy of the molecule and increase stability. Lone pairs, radicals or carbenium ions may be part of the...
with the double bond.
Both the sodium and potassium salts of glutaconaldehyde are known. They are efficiently synthesized from pyridine sulfonate.
The reaction of the glutaconaldehyde anion with acid chlorides
Acyl chloride
In organic chemistry, an acyl chloride is an organic compound with the functional group -CO-Cl. Their formula is usually written RCOCl, where R is a side chain. They are usually considered to be reactive derivatives of carboxylic acids. A specific example of an acyl chloride is acetyl chloride,...
gives the corresponding enol esters. Glutaconaldehyde can also be converted to the corresponding vinyl bromide
Vinyl halide
In organic chemistry, a vinyl halide is any alkene with at least one halide substituent bonded directly on one of the unsaturated carbons. Vinyl chloride is one such substance....
as shown below. This product can be reacted with nucleophiles, cross-coupled
Coupling reaction
A coupling reaction in organic chemistry is a catch-all term for a variety of reactions where two hydrocarbon fragments are coupled with the aid of a metal catalyst...
using palladium
Palladium
Palladium is a chemical element with the chemical symbol Pd and an atomic number of 46. It is a rare and lustrous silvery-white metal discovered in 1803 by William Hyde Wollaston. He named it after the asteroid Pallas, which was itself named after the epithet of the Greek goddess Athena, acquired...
, or homologated
Homologation reaction
A homologation reaction, also known as homologization, is any chemical reaction that converts the reactant into the next member of the homologous series. A Homologous series is a group of compounds that differ by a constant unit, generally a group. The reactants undergo a homologation when the...
by two carbons.