
Glycerol phosphate shuttle
Encyclopedia
The glycerol-3-phosphate shuttle is a mechanism that regenerates NAD+ from NADH, a by-product of glycolysis
. Its importance in transporting reducing equivalents is secondary to the malate-aspartate shuttle
.
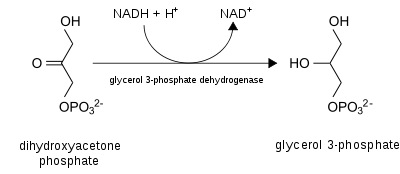
(GPD) converts dihydroxyacetone phosphate (2) to glycerol 3-phosphate
(1) by oxidizing one molecule of NADH to NAD+ as in the following reaction:
, this time reducing one molecule of enzyme-bound flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) to FADH2. FADH2 then reduces coenzyme Q
(ubiquinone to ubiquinol) which enters into oxidative phosphorylation
. This reaction is irreversible.
pathway in the mitochondria to generate ATP. It has been found in animals, fungi, and plants.
Glycolysis
Glycolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose C6H12O6, into pyruvate, CH3COCOO− + H+...
. Its importance in transporting reducing equivalents is secondary to the malate-aspartate shuttle
Malate-aspartate shuttle
The malate-aspartate shuttle is a biochemical system for translocating electrons produced during glycolysis across the semipermeable inner membrane of the mitochondrion for oxidative phosphorylation in eukaryotes. These electrons enter the electron transport chain of the mitochondria via reduction...
.
Reaction
In this shuttle, the enzyme called cytoplasmic glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenaseGlycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase
Glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase is an enzyme that catalyzes the reversible redox conversion of dihydroxyacetone phosphate to sn-glycerol 3-phosphate....
(GPD) converts dihydroxyacetone phosphate (2) to glycerol 3-phosphate
Glycerol 3-phosphate
Glycerol 3-phosphate is an organophosphate derived from the reaction catalysed by glycerol kinase where ATP + glycerol ADP + sn-glycerol 3-phosphate. It is a component of glycerophospholipids. It should not be confused with the similarly named glycerate 3-phosphate or glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate...
(1) by oxidizing one molecule of NADH to NAD+ as in the following reaction:

Reverse path
Glycerol-3-phosphate gets converted back to dihydroxyacetone phosphate by a membrane-bound mitochondrial glycerol-3-phosphate oxidaseGlycerol-3-phosphate oxidase
In enzymology, a glycerol-3-phosphate oxidase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reactionThus, the two substrates of this enzyme are sn-glycerol 3-phosphate and O2, whereas its two products are glycerone phosphate and H2O2....
, this time reducing one molecule of enzyme-bound flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) to FADH2. FADH2 then reduces coenzyme Q
Coenzyme Q
Coenzyme Q10, also known as ubiquinone, ubidecarenone, coenzyme Q, and abbreviated at times to CoQ10 , CoQ, Q10, or Q, is a 1,4-benzoquinone, where Q refers to the quinone chemical group, and 10 refers to the number of isoprenyl chemical subunits in its tail.This oil-soluble, vitamin-like substance...
(ubiquinone to ubiquinol) which enters into oxidative phosphorylation
Oxidative phosphorylation
Oxidative phosphorylation is a metabolic pathway that uses energy released by the oxidation of nutrients to produce adenosine triphosphate . Although the many forms of life on earth use a range of different nutrients, almost all aerobic organisms carry out oxidative phosphorylation to produce ATP,...
. This reaction is irreversible.
Function
The glycerol-3-phosphate shuttle allows the NADH synthesized in the cytosol by glycolysis to contribute to the oxidative phosphorylationOxidative phosphorylation
Oxidative phosphorylation is a metabolic pathway that uses energy released by the oxidation of nutrients to produce adenosine triphosphate . Although the many forms of life on earth use a range of different nutrients, almost all aerobic organisms carry out oxidative phosphorylation to produce ATP,...
pathway in the mitochondria to generate ATP. It has been found in animals, fungi, and plants.
External links
- http://www.elmhurst.edu/~chm/vchembook/601glycolysissum.html (describes the shuttle in the context of glycolysis)

