
Godfrey Hounsfield
Encyclopedia
Sir Godfrey Newbold Hounsfield CBE
, FRS, (28 August 1919 – 12 August 2004) was an English
electrical engineer who shared the 1979 Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicine with Allan McLeod Cormack
for his part in developing the diagnostic technique of X-ray
computed tomography (CT).
His name is immortalised in the Hounsfield scale
, a quantitative measure of radiodensity
used in evaluating CT scans. The scale is defined in Hounsfield units (symbol HU), running from air at −1000 HU, through water at 0 HU, and up to dense cortical bone at +1000 HU and more.
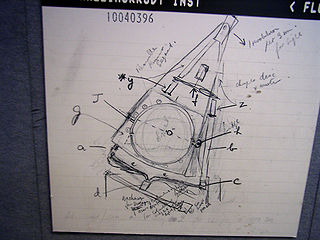 He then set to work constructing a computer that could take input from X-rays at various angles to create an image of the object in "slices". Applying this idea to the medical field led him to propose what is now known as computed tomography. At the time, Hounsfield was not aware of the work that Cormack had done on the theoretical mathematics for such a device.
He then set to work constructing a computer that could take input from X-rays at various angles to create an image of the object in "slices". Applying this idea to the medical field led him to propose what is now known as computed tomography. At the time, Hounsfield was not aware of the work that Cormack had done on the theoretical mathematics for such a device. Hounsfield built a prototype head scanner and tested it first on a preserved human brain
Hounsfield built a prototype head scanner and tested it first on a preserved human brain
, then on a fresh cow brain
from a butcher shop, and later on himself. On October 1, 1971, CT scanning was introduced into medical practice
with a successful scan on a cerebral cyst
patient at Atkinson Morley Hospital
in Wimbledon, London
, United Kingdom
. In 1975, Hounsfield built a whole-body scanner.
(near Newark-on-Trent
), Nottinghamshire
, England
on 28 August 1919. He was the youngest of five children. (Two brothers, Two sisters)
As a child he was fascinated by the electrical gadgets and machinery found all over his parents' farm. Between the ages of eleven and eighteen, he tinkered with his own electrical recording machines, launched himself off haystacks with his own home-made glider
, and almost killed himself by using water filled tar barrels and acetylene to see how high they could be waterjet propelled. He attended the Magnus Grammar School (now Magnus Church of England School) in Newark-on-Trent
and excelled in physics
and arithmetic
.
, he joined the Royal Air Force
as a volunteer reservist where he learned the basics of electronics
and radar
. After the war, he attended Faraday House Electrical Engineering College in London, graduating with the DFH (Diploma of Faraday House). Faraday House was a specialist Electrical Engineering college that provided university level education and was established in 1890, before the advent of most university engineering departments. Faraday House pioneered the use of sandwich courses, combining practical experience with theoretical study.
The suggestion that Hounsfield lacked formal engineering education to the level of a Chartered Engineer
does not reflect the nature of engineering education at the time when Hounsfield was a student, or the esteem in which Faraday House was held within the profession.
s and in 1958, he helped design the first commercially available all-transistor
computer made in Great Britain: the EMIDEC 1100
. Shortly afterwards, he began work on the CT scanner at EMI. He continued to improve CT scanning, introducing a whole-body scanner in 1975, and was senior researcher (and after his retirement in 1984, consultant) to the laboratories.
in 1976 and knight
ed in 1981.
In 1975, he was elected to the Royal Society
. He was awarded the Howard N. Potts Medal in 1977.
Order of the British Empire
The Most Excellent Order of the British Empire is an order of chivalry established on 4 June 1917 by George V of the United Kingdom. The Order comprises five classes in civil and military divisions...
, FRS, (28 August 1919 – 12 August 2004) was an English
England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Scotland to the north and Wales to the west; the Irish Sea is to the north west, the Celtic Sea to the south west, with the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south separating it from continental...
electrical engineer who shared the 1979 Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicine with Allan McLeod Cormack
Allan McLeod Cormack
Allan MacLeod Cormack was a South African-born American physicist who won the 1979 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for his work on X-ray computed tomography ....
for his part in developing the diagnostic technique of X-ray
X-ray
X-radiation is a form of electromagnetic radiation. X-rays have a wavelength in the range of 0.01 to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30 petahertz to 30 exahertz and energies in the range 120 eV to 120 keV. They are shorter in wavelength than UV rays and longer than gamma...
computed tomography (CT).
His name is immortalised in the Hounsfield scale
Hounsfield scale
The Hounsfield scale, named after Sir Godfrey Newbold Hounsfield, is a quantitative scale for describing radiodensity.-Definition:The Hounsfield unit scale is a linear transformation of the original linear attenuation coefficient measurement into one in which the radiodensity of distilled water at...
, a quantitative measure of radiodensity
Radiodensity
Radiodensity refers to the relative inability of electromagnetic radiation, particularly X-rays, to pass through a particular material. Radiolucency indicates greater transparency or "transradiancy" to X-ray photons...
used in evaluating CT scans. The scale is defined in Hounsfield units (symbol HU), running from air at −1000 HU, through water at 0 HU, and up to dense cortical bone at +1000 HU and more.
Invention of the CT scanner
While on an outing in the country, Hounsfield came up with the idea that one could determine what was inside a box by taking X-ray readings at all angles around the object.

Human brain
The human brain has the same general structure as the brains of other mammals, but is over three times larger than the brain of a typical mammal with an equivalent body size. Estimates for the number of neurons in the human brain range from 80 to 120 billion...
, then on a fresh cow brain
Brain
The brain is the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals—only a few primitive invertebrates such as sponges, jellyfish, sea squirts and starfishes do not have one. It is located in the head, usually close to primary sensory apparatus such as vision, hearing,...
from a butcher shop, and later on himself. On October 1, 1971, CT scanning was introduced into medical practice
Medicine
Medicine is the science and art of healing. It encompasses a variety of health care practices evolved to maintain and restore health by the prevention and treatment of illness....
with a successful scan on a cerebral cyst
Cyst
A cyst is a closed sac, having a distinct membrane and division on the nearby tissue. It may contain air, fluids, or semi-solid material. A collection of pus is called an abscess, not a cyst. Once formed, a cyst could go away on its own or may have to be removed through surgery.- Locations :* Acne...
patient at Atkinson Morley Hospital
Atkinson Morley Hospital
Atkinson Morley Hospital was located at Copse Hill, Wimbledon, London , SW20, England from 1869 until 2003. The hospital was noted as one of the most advanced brain surgery centres in the world, and in particular for the first use of computed tomography on a human being in 1972 by Godfrey...
in Wimbledon, London
Wimbledon, London
Wimbledon is a district in the south west area of London, England, located south of Wandsworth, and east of Kingston upon Thames. It is situated within Greater London. It is home to the Wimbledon Tennis Championships and New Wimbledon Theatre, and contains Wimbledon Common, one of the largest areas...
, United Kingdom
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
. In 1975, Hounsfield built a whole-body scanner.
Childhood and education
Hounsfield was born in Sutton-on-TrentSutton-on-Trent
Sutton-on-Trent is a village in Nottinghamshire. According to the 2001 census it had a population of 1,327.It is located 8 miles north of Newark-on-Trent....
(near Newark-on-Trent
Newark-on-Trent
Newark-on-Trent is a market town in Nottinghamshire in the East Midlands region of England. It stands on the River Trent, the A1 , and the East Coast Main Line railway. The origins of the town are possibly Roman as it lies on an important Roman road, the Fosse Way...
), Nottinghamshire
Nottinghamshire
Nottinghamshire is a county in the East Midlands of England, bordering South Yorkshire to the north-west, Lincolnshire to the east, Leicestershire to the south, and Derbyshire to the west...
, England
England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Scotland to the north and Wales to the west; the Irish Sea is to the north west, the Celtic Sea to the south west, with the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south separating it from continental...
on 28 August 1919. He was the youngest of five children. (Two brothers, Two sisters)
As a child he was fascinated by the electrical gadgets and machinery found all over his parents' farm. Between the ages of eleven and eighteen, he tinkered with his own electrical recording machines, launched himself off haystacks with his own home-made glider
Glider aircraft
Glider aircraft are heavier-than-air craft that are supported in flight by the dynamic reaction of the air against their lifting surfaces, and whose free flight does not depend on an engine. Mostly these types of aircraft are intended for routine operation without engines, though engine failure can...
, and almost killed himself by using water filled tar barrels and acetylene to see how high they could be waterjet propelled. He attended the Magnus Grammar School (now Magnus Church of England School) in Newark-on-Trent
Newark-on-Trent
Newark-on-Trent is a market town in Nottinghamshire in the East Midlands region of England. It stands on the River Trent, the A1 , and the East Coast Main Line railway. The origins of the town are possibly Roman as it lies on an important Roman road, the Fosse Way...
and excelled in physics
Physics
Physics is a natural science that involves the study of matter and its motion through spacetime, along with related concepts such as energy and force. More broadly, it is the general analysis of nature, conducted in order to understand how the universe behaves.Physics is one of the oldest academic...
and arithmetic
Arithmetic
Arithmetic or arithmetics is the oldest and most elementary branch of mathematics, used by almost everyone, for tasks ranging from simple day-to-day counting to advanced science and business calculations. It involves the study of quantity, especially as the result of combining numbers...
.
Wartime
Shortly before World War IIWorld War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
, he joined the Royal Air Force
Royal Air Force
The Royal Air Force is the aerial warfare service branch of the British Armed Forces. Formed on 1 April 1918, it is the oldest independent air force in the world...
as a volunteer reservist where he learned the basics of electronics
Electronics
Electronics is the branch of science, engineering and technology that deals with electrical circuits involving active electrical components such as vacuum tubes, transistors, diodes and integrated circuits, and associated passive interconnection technologies...
and radar
Radar
Radar is an object-detection system which uses radio waves to determine the range, altitude, direction, or speed of objects. It can be used to detect aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, weather formations, and terrain. The radar dish or antenna transmits pulses of radio...
. After the war, he attended Faraday House Electrical Engineering College in London, graduating with the DFH (Diploma of Faraday House). Faraday House was a specialist Electrical Engineering college that provided university level education and was established in 1890, before the advent of most university engineering departments. Faraday House pioneered the use of sandwich courses, combining practical experience with theoretical study.
The suggestion that Hounsfield lacked formal engineering education to the level of a Chartered Engineer
Chartered Engineer (UK)
In the United Kingdom, a Chartered Engineer is an engineer registered with Engineering Council UK . Contemporary Chartered Engineers are master's degree-qualified and have gained professional competencies through training and experience...
does not reflect the nature of engineering education at the time when Hounsfield was a student, or the esteem in which Faraday House was held within the profession.
EMI and later years
In 1951, Hounsfield began work at EMI Ltd in their Central Research Laboratories in Hayes, Middlesex where he researched guided weapon systems and radar. There, he became interested in computerComputer
A computer is a programmable machine designed to sequentially and automatically carry out a sequence of arithmetic or logical operations. The particular sequence of operations can be changed readily, allowing the computer to solve more than one kind of problem...
s and in 1958, he helped design the first commercially available all-transistor
Transistor
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to amplify and switch electronic signals and power. It is composed of a semiconductor material with at least three terminals for connection to an external circuit. A voltage or current applied to one pair of the transistor's terminals changes the current...
computer made in Great Britain: the EMIDEC 1100
EMIDEC 1100
-External links:**...
. Shortly afterwards, he began work on the CT scanner at EMI. He continued to improve CT scanning, introducing a whole-body scanner in 1975, and was senior researcher (and after his retirement in 1984, consultant) to the laboratories.
Awards
Hounsfield received numerous awards in addition to the Nobel Prize. He was appointed Commander of the British EmpireOrder of the British Empire
The Most Excellent Order of the British Empire is an order of chivalry established on 4 June 1917 by George V of the United Kingdom. The Order comprises five classes in civil and military divisions...
in 1976 and knight
Knight
A knight was a member of a class of lower nobility in the High Middle Ages.By the Late Middle Ages, the rank had become associated with the ideals of chivalry, a code of conduct for the perfect courtly Christian warrior....
ed in 1981.
In 1975, he was elected to the Royal Society
Royal Society
The Royal Society of London for Improving Natural Knowledge, known simply as the Royal Society, is a learned society for science, and is possibly the oldest such society in existence. Founded in November 1660, it was granted a Royal Charter by King Charles II as the "Royal Society of London"...
. He was awarded the Howard N. Potts Medal in 1977.

