Gonium
Encyclopedia
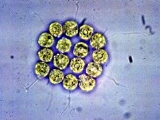
Gonium is a genus of colonial algae
, a member of the order Volvocales
. Typical colonies have 4 to 16 cells, all the same size, arranged in a flat plate, with no anterior-posterior differentiation. In a colony of 16 cells, four are in the center, and the other 12 are on the four sides, three each. A description by G.M. Smith (1920, p. 94):
. The order Volvocales
has long been a well recognized model system for the study of multicellular evolution. Gonium and the genus Tetrabaenecae contain species representative of colony formation among unicells. Gonium's morphology of colonies of alike cells suggest it is more genetically similar to Chlamydomonas
that Volvox
, a fact confirmed by phylogenetic analysis.
The Volvocales
have been hypothesized to have evolved in twelve discrete steps. Gonium represents the first six evolutionary steps of multicellularity; (1) incomplete cytokinesis, (2) partial inversion, (3) rotation of the basal bodies, (4) organismal polarity, (5) transformation of the cell wall into extra-cellular matrix (ECM), (6) genetic control of cell number. Although the exact order and progression through David Kirk's twelve steps of multicellular evolution are probably not necessarily linear and each occurs more dynamically than originally thought.
has a life cycle that is derivative of that of Chlamydomonas
. Gonium cells grow asexually as colonies of either 4, 8 or 16 colonial cells. Cell and colony growth of Gonium is uncoupled from cell division just like Chlamydomonas
and each cell within the colony divides by multiple-fission. Thus, each cell within the colony will divide 2, 3 or 4 times, thus producing 2"n" daughter cells, or 4, 8 or 16 cells within the colony. Unlike Chlamydomonas
where each of the daughter cells separate from each other, Gonium daughter cells remain attached to each other in their ECM.
The sexual cycle of Gonium is also very similar to that of Chlamydomonas
. The sexual program of Gonium is induced by nitrogen deprivation where each vegetative cell within the colony differentiates in gametes. Gonium gametes are isogomous, or equal-sized, and unicellular. Thus unicellular Gonium gametes break apart from the multicellular colonies when the sexual program is initiated. Also like Chlamydomonas
, there are two "sexes", plus or minus controlled by a genes homologous to those found in Chlamydomonas
and Volvox
.
Algae
Algae are a large and diverse group of simple, typically autotrophic organisms, ranging from unicellular to multicellular forms, such as the giant kelps that grow to 65 meters in length. They are photosynthetic like plants, and "simple" because their tissues are not organized into the many...
, a member of the order Volvocales
Volvocales
In taxonomy, the Volvocales, also known as Chlamydomonadales, are an order of flagellate or pseudociliate green algae, specifically of the Chlorophyceae...
. Typical colonies have 4 to 16 cells, all the same size, arranged in a flat plate, with no anterior-posterior differentiation. In a colony of 16 cells, four are in the center, and the other 12 are on the four sides, three each. A description by G.M. Smith (1920, p. 94):
Gonium Mueller 1773: Colonies of 4-8-16 cells arranged in a flat quadrangular plate and embedded in a common gelatinous matrix or connected by broad gelatinous strands. Cells ovoid to pyriform, with a single cup-shaped chloroplast containing one pyrenoid. Each cell with two cilia of equal length, contractile vacuoles at the base of the cilia, and an eyespot. Four- and eight-celled colonies with the cilia on the same side ; sixteencelled colonies with the four central cells having their cilia on the same side and the twelve marginal cells with radially arranged cilia.
Asexual reproduction by simultaneous division of all cells in the colony to form autocolonies, or by a formation of 2-4 zoospores in each cell.
Sexual reproduction isogamous, by a fusion of biciliate zoogametes.
Evolution
The genus Gonium represents species closely related to single celled Chamydomonas and multicellular differentiated VolvoxVolvox
Volvox is a genus of chlorophytes, a type of green algae. It forms spherical colonies of up to 50,000 cells. They live in a variety of freshwater habitats, and were first reported by Antonie van Leeuwenhoek in 1700. Volvox developed its colonial lifestyle .-Description:Volvox is the most developed...
. The order Volvocales
Volvocales
In taxonomy, the Volvocales, also known as Chlamydomonadales, are an order of flagellate or pseudociliate green algae, specifically of the Chlorophyceae...
has long been a well recognized model system for the study of multicellular evolution. Gonium and the genus Tetrabaenecae contain species representative of colony formation among unicells. Gonium's morphology of colonies of alike cells suggest it is more genetically similar to Chlamydomonas
Chlamydomonas
Chlamydomonas is a genus of green algae. They are unicellular flagellates. Chlamydomonas is used as a model organism for molecular biology, especially studies of flagellar motility and chloroplast dynamics, biogenesis, and genetics...
that Volvox
Volvox
Volvox is a genus of chlorophytes, a type of green algae. It forms spherical colonies of up to 50,000 cells. They live in a variety of freshwater habitats, and were first reported by Antonie van Leeuwenhoek in 1700. Volvox developed its colonial lifestyle .-Description:Volvox is the most developed...
, a fact confirmed by phylogenetic analysis.
The Volvocales
Volvocales
In taxonomy, the Volvocales, also known as Chlamydomonadales, are an order of flagellate or pseudociliate green algae, specifically of the Chlorophyceae...
have been hypothesized to have evolved in twelve discrete steps. Gonium represents the first six evolutionary steps of multicellularity; (1) incomplete cytokinesis, (2) partial inversion, (3) rotation of the basal bodies, (4) organismal polarity, (5) transformation of the cell wall into extra-cellular matrix (ECM), (6) genetic control of cell number. Although the exact order and progression through David Kirk's twelve steps of multicellular evolution are probably not necessarily linear and each occurs more dynamically than originally thought.
Life cycle
Gonium being evolutionarily related to ChlamydomonasChlamydomonas
Chlamydomonas is a genus of green algae. They are unicellular flagellates. Chlamydomonas is used as a model organism for molecular biology, especially studies of flagellar motility and chloroplast dynamics, biogenesis, and genetics...
has a life cycle that is derivative of that of Chlamydomonas
Chlamydomonas
Chlamydomonas is a genus of green algae. They are unicellular flagellates. Chlamydomonas is used as a model organism for molecular biology, especially studies of flagellar motility and chloroplast dynamics, biogenesis, and genetics...
. Gonium cells grow asexually as colonies of either 4, 8 or 16 colonial cells. Cell and colony growth of Gonium is uncoupled from cell division just like Chlamydomonas
Chlamydomonas
Chlamydomonas is a genus of green algae. They are unicellular flagellates. Chlamydomonas is used as a model organism for molecular biology, especially studies of flagellar motility and chloroplast dynamics, biogenesis, and genetics...
and each cell within the colony divides by multiple-fission. Thus, each cell within the colony will divide 2, 3 or 4 times, thus producing 2"n" daughter cells, or 4, 8 or 16 cells within the colony. Unlike Chlamydomonas
Chlamydomonas
Chlamydomonas is a genus of green algae. They are unicellular flagellates. Chlamydomonas is used as a model organism for molecular biology, especially studies of flagellar motility and chloroplast dynamics, biogenesis, and genetics...
where each of the daughter cells separate from each other, Gonium daughter cells remain attached to each other in their ECM.
The sexual cycle of Gonium is also very similar to that of Chlamydomonas
Chlamydomonas
Chlamydomonas is a genus of green algae. They are unicellular flagellates. Chlamydomonas is used as a model organism for molecular biology, especially studies of flagellar motility and chloroplast dynamics, biogenesis, and genetics...
. The sexual program of Gonium is induced by nitrogen deprivation where each vegetative cell within the colony differentiates in gametes. Gonium gametes are isogomous, or equal-sized, and unicellular. Thus unicellular Gonium gametes break apart from the multicellular colonies when the sexual program is initiated. Also like Chlamydomonas
Chlamydomonas
Chlamydomonas is a genus of green algae. They are unicellular flagellates. Chlamydomonas is used as a model organism for molecular biology, especially studies of flagellar motility and chloroplast dynamics, biogenesis, and genetics...
, there are two "sexes", plus or minus controlled by a genes homologous to those found in Chlamydomonas
Chlamydomonas
Chlamydomonas is a genus of green algae. They are unicellular flagellates. Chlamydomonas is used as a model organism for molecular biology, especially studies of flagellar motility and chloroplast dynamics, biogenesis, and genetics...
and Volvox
Volvox
Volvox is a genus of chlorophytes, a type of green algae. It forms spherical colonies of up to 50,000 cells. They live in a variety of freshwater habitats, and were first reported by Antonie van Leeuwenhoek in 1700. Volvox developed its colonial lifestyle .-Description:Volvox is the most developed...
.
External links
- Gonium - Description with pictures
- Michod Lab - Research overview of Dr. Richard Michod at the University of Arizona who studies multicellular evolution and whose lab published a detailed phylogenetic tree of the VolvocalesVolvocalesIn taxonomy, the Volvocales, also known as Chlamydomonadales, are an order of flagellate or pseudociliate green algae, specifically of the Chlorophyceae...
- VIP - The Volvocales Information Project lead by Dr. Aurora M. Nedelcu at University of New Brunswick
- Olson Lab - Dr. Bradley Olson at Kansas State University who studies multicellular evolution with methods for growing Gonium
- Nozaki Lab - Dr. Hisayoshi Nozaki at the University of Tokoyo who studies multicellular evolution and has cultured many VolvocalesVolvocalesIn taxonomy, the Volvocales, also known as Chlamydomonadales, are an order of flagellate or pseudociliate green algae, specifically of the Chlorophyceae...
strains, including Gonium - Hallman Lab - Dr. Armin Hallman at Bielefeld University whose lab developed a method for transforming Gonium
- UTEX - The UTEX algal culture collection which houses many Gonium strains including pictures
- CCAP - The CCAP algal culture collection which houses many Gonium strains including pictures

