
Government of Karnataka
Encyclopedia
The Government of Karnataka
is a democratically elected body with the Governor as the constitutional head. The Governor who is appointed for a period of five years appoints the Chief Minister and his council of ministers. Even though the governor remains the ceremonial head of the state, the day to day running of the government is taken care of by the Chief Minister and his council of ministers in whom a great deal of legislative powers is vested.
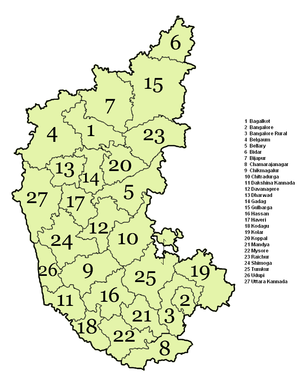
Karnataka State has been divided into four Revenue divisions, 49 sub-divisions, 29 districts, 175 taluks and 745 hoblies/Revenue Circles for administrative purposes.
The State has 27,028 inhabited and 2,362 uninhabited villages, 281 towns and 7 municipal corporations. Bangalore is the sixth largest urban agglomeration out of 23 metropolis, urban agglomerations and cities in India. It is among the fastest growing cities in the world.
and Coorg (Kodagu) were merged with the Kannada-speaking districts of the former states of Bombay
and Hyderabad
, and Madras
. Mysore state was made up of ten districts, Bangalore, Kolar, Tumkur, Mandya, Mysore, Hassan, Chikmagalur (Kadur), Shimoga and Chitradurga; Bellary
had been transferred from Madras state to Mysore in 1953, when the new Andhra State
was created out of Madras' northern districts. Kodagu became a district, and Dakshina Kannada
(South Kanara) district was transferred from Madras state, North Kanara, Dharwad
, Belgaum District
, and Bijapur District from Bombay state, and Bidar District
, Gulbarga District
, and Raichur District
from Hyderabad state.
In 1989, Bangalore Rural district was split from Bangalore and, in 1997, Bagalkot district split from Bijapur, Chamrajnagar district split from Mysore, Gadag district split from Dharwad, Haveri district split from Dharwad, Koppal district split from Raichur, Udupi district split from Dakshina Kannada, and Davanagere district was created from parts of Bellary, Chitradurga, Dharwad, and Shimoga.
In 2008, Bangalore Rural district was split into two and a new district of Ramanagaram was constituted. In the same way district of Chickballapur was carved out of the erstwhile Kolar district.

The State legislature is bicameral and consists of the Legislative Assembly and the Legislative Council. The Legislative Assembly consists of 224 members with one member nominated by the Governor to represent the Anglo-Indian community. The term of office of the members is five years and the term of a member elected to the council is six years. The Legislative Council is a permanent body with one-third of its members retiring every two years.
The Secretariat headed by the secretary to the governor assists the council of ministers. The council of ministers consists of cabinet Ministers, ministers of state and deputy ministers. The chief minister is also assisted by the Chief Secretary, who is the head of the administrative services.
{| class="wikitable sortable"
|-
! style="background:#666; color:white;"|Department(s)
! style="background:#666; color:white;"|Minister
|-
|Chief Minister (Including Finance, Kannada Languages and Cultural, Cabinet Affairs, Personnel and Administrative Reforms, Intelligence Wing, Urban Development, Mines and Geology, Forest)
|DV Sadananda Gowda
|-
|Higher education, Planning, Statistics
|V.S. Acharya
|-
|Law & Parliamentary Affairs, Justice and Municipal Administration
|S.Suresh Kumar
|-
|Energy
|Shobha Karandlaje
|-
|Rural Development, Panchayati Raj, Rural Water Supply & Sanitation
|Jagadish Shettar
|-
|Sugar and Horticulture
|S.A. Ravindranath
|-
|Medical Education
|S.A.Ramadas
|-
|Home, Transport
|R. Ashok
|-
|Social Welfare (Excluding Minority Welfare)
|A.Narayanaswamy
|-
|Small Scale Industries and Sericulture
| Raju Gouda
|-
|Revenue
|
|-
|Tourism and Infrastructure Development
|
|-
|Housing, IT, BT, and BWSSB
|
|-
|Health and Family Welfare (Excluding Medical Education)
|
|-
|Labour
|B.N. Bacche Gowda
|-
|Primary and Secondary Education (Excluding Mass Education and Public Libraries)
|Vishweshwar Hegde Kageri
|-
|Animal Husbandry
|Revu Naik Belamgi
|-
|Ports and Inland Water Transport, Ecology and Environment
|J. Krishna Palemar
|-
|Excise
|M.P. Renukacharya
|-
|Public Works Department (Excluding Ports and Inland Water Transport)
|Udasi Channabasappa Mahalingappa
|-
|Agriculture Marketing & Sugar, Minor Irrigation, Kannada & Culture, Information & Tourism, Textiles and Youth Services
|Govind .M. Karjol
|-
|Medium and Major Irrigation
|Basavaraj Bommai
|-
|Medium and Major Industries
|Murugesh Rudrappa Nirani
|-
|Women & Child Development
|C.C.Patil
|-
|Housing Department (Including Slum Clearance Board)
|V. Somanna
|-
|Co-operation (Excluding Agriculture Marketing)
|Laxman Sangappa Savadi
|-
|Municipalities, Local Bodies and Public Enterprises
| Balachandra Jarkihol
|-
|Fisheries, Science and Technology
| Anand Asnotikar
|-
|Mass Education, Public Libraries, Small Savings and Lotteries
|Revu Naik Belamgi
|-
|Haj, Wakf and Minority Welfare
|Ali Khan
|-
|Forest Department from Forest,Ecology & Enviornment Department
|C. P. Yogishwar
|-
}
are appointed as the highest officers to look after each district.
All the three institutions will have elected representatives and there is no provision for nomination by the Government to any of these councils. Karnataka is the first in the country to enact new Panchayat Raj Act. Incorporating all provisions of 73rd Amendment to the Constitution.
or District Magistrate, an officer belonging to the Indian Administrative Service
. The district magistrate or the deputy commissioner is assisted by a number of officers belonging to Karnataka Civil Service and other Karnataka state services.
A Deputy Commissioner of Police, an officer belonging to the Indian Police Service
is entrusted with the responsibility of maintaining law and order and related issues of the district. He is assisted by the officers of the Karnataka Police Service and other Karnataka Police officials. A Deputy Conservator of Forests
, an officer belonging to the Indian Forest Service
is responsible for managing the Forests, environment and wild-life related issues of the district. He is assisted by the officers of the Karnataka Forest Service and other Karnataka Forest officials and Karnataka Wild-Life officials. Sectoral development is looked after by the district head of each development department such as PWD, Health, Education, Agriculture, Animal husbandry, etc. These officers belong to the various State Services.
Units that assist the state in law and order include Criminal Investigation Department (Forest Cell, Anti-Dowry Cell, etc.), Dog Squad, Civil Rights Enforcement Wing, Police Wireless and Police Motor Transport Organization and Special units. Also Village Defence Parties protect persons and property in the village and assist the police when necessary. The Police force is at times supplemented by Home Guards.
(INC), Janata Dal (Secular)
(JDS) and the Bharatiya Janata Party
(BJP).
The previous government was a coalition government
of JDS and BJP. The Chief Minister for an initial term of 20 months was H. D. Kumaraswamy
of JDS and the post was supposed to subsequently be transferred to BJP's B. S. Yeddyurappa. A political fall out due to the failure in transfer of power to Yedurappa broke the coalition. The state was then under President's rule until the elections
in May 2008. As a result of the BJP victory in those elections B. S. Yeddyurappa became chief minister of Karnataka.
Karnataka
Karnataka , the land of the Kannadigas, is a state in South West India. It was created on 1 November 1956, with the passing of the States Reorganisation Act and this day is annually celebrated as Karnataka Rajyotsava...
is a democratically elected body with the Governor as the constitutional head. The Governor who is appointed for a period of five years appoints the Chief Minister and his council of ministers. Even though the governor remains the ceremonial head of the state, the day to day running of the government is taken care of by the Chief Minister and his council of ministers in whom a great deal of legislative powers is vested.
Administrative divisions

Karnataka State has been divided into four Revenue divisions, 49 sub-divisions, 29 districts, 175 taluks and 745 hoblies/Revenue Circles for administrative purposes.
The State has 27,028 inhabited and 2,362 uninhabited villages, 281 towns and 7 municipal corporations. Bangalore is the sixth largest urban agglomeration out of 23 metropolis, urban agglomerations and cities in India. It is among the fastest growing cities in the world.
Political and administrative reorganisation
Karnataka took its present shape in 1956, when the states of MysoreMysore State
The Kingdom of Mysore was one of the three largest princely states within the erstwhile British Empire of India. Upon India gaining its independence in 1947, the Maharaja of Mysore merged his realm with the Union of India...
and Coorg (Kodagu) were merged with the Kannada-speaking districts of the former states of Bombay
Bombay State
The Bombay State was a state of India, dissolved with the formation of Maharashtra and Gujarat states on May 1, 1960.-History:During British rule, portions of the western coast of India under direct British rule were part of the Bombay Presidency...
and Hyderabad
Hyderabad State
-After Indian independence :When India gained independence in 1947 and Pakistan came into existence in 1947, the British left the local rulers of the princely states the choice of whether to join one of the new dominions or to remain independent...
, and Madras
Madras State
Madras State was the name by which the Indian districts in Tamil Nadu, Andhra, Northern Kerala, Bellary and Dakshina Kannada were collectively known as from 1950 to 1953....
. Mysore state was made up of ten districts, Bangalore, Kolar, Tumkur, Mandya, Mysore, Hassan, Chikmagalur (Kadur), Shimoga and Chitradurga; Bellary
Bellary
Bellary is a historic city in Bellary District in Karnataka state, India.-Origins of the city's name:There are several legends about how Bellary got its name....
had been transferred from Madras state to Mysore in 1953, when the new Andhra State
Andhra State
Andhra State was a state in India created on October 1, 1953 from the Telugu-speaking northern districts of Madras Presidency. On November 1, 1956 it was merged with the Telangana region of Hyderabad State to form the united Telugu-speaking state of Andhra Pradesh.- Madras Manade movement :In 1953,...
was created out of Madras' northern districts. Kodagu became a district, and Dakshina Kannada
Dakshina Kannada
- Geography :The district geography consists of sea shore in the west and Western Ghats in the east. The major rivers are Netravathi, Kumaradhara, Phalguni, Shambhavi, Nandini or Pavanje and Payaswini which all join Arabian sea. Vast areas of evergreen forests which once covered this district, have...
(South Kanara) district was transferred from Madras state, North Kanara, Dharwad
Dharwad
Dharwad, also known as Dharwar, is a city and a DISTRICT PLACE in India's Karnataka state.Dharwad is the administrative seat of the Dharwad District. The municipality of Hubli-Dharwad covers an area of 200.23 km²...
, Belgaum District
Belgaum district
Belgaum district is a district in the state of Karnataka, India. The city of Belgaum is the district headquarters in North Karnataka. By the 2011 Census of India, it had a population of 4778439...
, and Bijapur District from Bombay state, and Bidar District
Bidar District
Bidar is a district of Karnataka state in southern India. The historic city of Bidar is the administrative centre of the district. The district is located in the northeastern corner of the state, near the borders with Andhra Pradesh to the east and Maharashtra to the north and west...
, Gulbarga District
Gulbarga District
Gulbarga district is one of the 30 districts of Karnataka state in southern India. Gulbarga city is the administrative headquarters of the district...
, and Raichur District
Raichur district
Raichur District is an administrative district in the Indian state of Karnataka. It is located in the northeast part of the state and is bounded by Yadgir district in the north, Bijapur and Bagalkot district in the northwest, Koppal district in the west, Bellary district in the south, Anantapur...
from Hyderabad state.
In 1989, Bangalore Rural district was split from Bangalore and, in 1997, Bagalkot district split from Bijapur, Chamrajnagar district split from Mysore, Gadag district split from Dharwad, Haveri district split from Dharwad, Koppal district split from Raichur, Udupi district split from Dakshina Kannada, and Davanagere district was created from parts of Bellary, Chitradurga, Dharwad, and Shimoga.
In 2008, Bangalore Rural district was split into two and a new district of Ramanagaram was constituted. In the same way district of Chickballapur was carved out of the erstwhile Kolar district.
Legislature

The State legislature is bicameral and consists of the Legislative Assembly and the Legislative Council. The Legislative Assembly consists of 224 members with one member nominated by the Governor to represent the Anglo-Indian community. The term of office of the members is five years and the term of a member elected to the council is six years. The Legislative Council is a permanent body with one-third of its members retiring every two years.
Ministry
The government is headed by the Governor who appoints the Chief Minister and his council of ministers. The Governor is appointed for a period of five years and acts as the constitutional head of the State. Even though the governor remains the ceremonial head of the state, the day to day running of the government is taken care of by the Chief Minister and his council of ministers in whom a great deal of legislative powers is vested.The Secretariat headed by the secretary to the governor assists the council of ministers. The council of ministers consists of cabinet Ministers, ministers of state and deputy ministers. The chief minister is also assisted by the Chief Secretary, who is the head of the administrative services.
List of present Karnataka cabinet ministers
As of 2008, the government of Karnataka consists of 34 ministers. The important porfolio of finance has been retained by the Chief Minister.{| class="wikitable sortable"
|-
! style="background:#666; color:white;"|Department(s)
! style="background:#666; color:white;"|Minister
|-
|Chief Minister (Including Finance, Kannada Languages and Cultural, Cabinet Affairs, Personnel and Administrative Reforms, Intelligence Wing, Urban Development, Mines and Geology, Forest)
|DV Sadananda Gowda
|-
|Higher education, Planning, Statistics
|V.S. Acharya
|-
|Law & Parliamentary Affairs, Justice and Municipal Administration
|S.Suresh Kumar
S.Suresh Kumar
S.Suresh Kumar is a cabinet minister in current BJP ministry of Karnataka state of India. He is Minister for Law, Urban Development and Parliamentary Affairs and BWSSB. He is considered as a most honest and an able minister across all parties. He is a much respected man for his honesty, integrity...
|-
|Energy
|Shobha Karandlaje
|-
|Rural Development, Panchayati Raj, Rural Water Supply & Sanitation
|Jagadish Shettar
|-
|Sugar and Horticulture
|S.A. Ravindranath
|-
|Medical Education
|S.A.Ramadas
S. A. Ramadass
S. A. Ramadass is a current Member of the Legislative Assembly of Krishnaraja constituency in Mysore, Karnataka. and he is a member of Bharatiya Janata Party....
|-
|Home, Transport
|R. Ashok
R. Ashok
R. Ashok is the former Minister for Home and Transport of Karnataka. He represents the Padmanabha Nagar constituency in Bangalore, and belongs to the Vokkaliga community.BRIEF PROFILE...
|-
|Social Welfare (Excluding Minority Welfare)
|A.Narayanaswamy
|-
|Small Scale Industries and Sericulture
| Raju Gouda
|-
|Revenue
|
|-
|Tourism and Infrastructure Development
|
|-
|Housing, IT, BT, and BWSSB
|
|-
|Health and Family Welfare (Excluding Medical Education)
|
|-
|Labour
|B.N. Bacche Gowda
|-
|Primary and Secondary Education (Excluding Mass Education and Public Libraries)
|Vishweshwar Hegde Kageri
Vishweshwar Hegde Kageri
Vishweshwar Hegde Kageri is a four-time Bharatiya Janata Party MLA and minister for primary and secondary education in the Government of Karnataka. He represented the Ankola Vidhan Sabha constituency for 3 terms: 1994-99, 1999-04 and 2004-2007...
|-
|Animal Husbandry
|Revu Naik Belamgi
|-
|Ports and Inland Water Transport, Ecology and Environment
|J. Krishna Palemar
J. Krishna Palemar
J. Krishna Palemar is a Karnataka politician with the BJP, currently serving as Minister of Environment and Ports in the B. S. Yeddyurappa government....
|-
|Excise
|M.P. Renukacharya
|-
|Public Works Department (Excluding Ports and Inland Water Transport)
|Udasi Channabasappa Mahalingappa
|-
|Agriculture Marketing & Sugar, Minor Irrigation, Kannada & Culture, Information & Tourism, Textiles and Youth Services
|Govind .M. Karjol
|-
|Medium and Major Irrigation
|Basavaraj Bommai
|-
|Medium and Major Industries
|Murugesh Rudrappa Nirani
|-
|Women & Child Development
|C.C.Patil
|-
|Housing Department (Including Slum Clearance Board)
|V. Somanna
|-
|Co-operation (Excluding Agriculture Marketing)
|Laxman Sangappa Savadi
|-
|Municipalities, Local Bodies and Public Enterprises
| Balachandra Jarkihol
|-
|Fisheries, Science and Technology
| Anand Asnotikar
|-
|Mass Education, Public Libraries, Small Savings and Lotteries
|Revu Naik Belamgi
|-
|Haj, Wakf and Minority Welfare
|Ali Khan
Ali Khan
Ali Khan is a citizen of Pakistan, and a permanent resident of the United States.One of his sons, Majid Khan, was held in extrajudicial detention, in secret interrogation centers, run by the CIA, for four years....
|-
|Forest Department from Forest,Ecology & Enviornment Department
|C. P. Yogishwar
|-
}
Bureaucrats
Deputy CommissionersDeputy Commissioner (India)
The deputy commissioner or district magistrate or district collector or district magistrate and collector is the head of the revenue administration of an Indian district. The DC is required to be an Indian Administrative Service officer who is in charge of governmental assets in his district of...
are appointed as the highest officers to look after each district.
Karnataka Panchayat Raj
Panchayat Raj (Rule of Village Committee) system is a three-tier system in the state with elected bodies at the Village, Taluk and District levels. It ensures greater participation of people and more effective implementation of rural development programmes. There will be a Grama Panchayat for a village or group of villages, a Taluk level and the Zilla Panchayat at the district level.All the three institutions will have elected representatives and there is no provision for nomination by the Government to any of these councils. Karnataka is the first in the country to enact new Panchayat Raj Act. Incorporating all provisions of 73rd Amendment to the Constitution.
Executive
A district of an Indian state is an administrat, headed by a Deputy CommissionerDeputy Commissioner (India)
The deputy commissioner or district magistrate or district collector or district magistrate and collector is the head of the revenue administration of an Indian district. The DC is required to be an Indian Administrative Service officer who is in charge of governmental assets in his district of...
or District Magistrate, an officer belonging to the Indian Administrative Service
Indian Administrative Service
The Indian Administrative Service is the administrative civil service of the Government of India. It is one of the three All India Services....
. The district magistrate or the deputy commissioner is assisted by a number of officers belonging to Karnataka Civil Service and other Karnataka state services.
A Deputy Commissioner of Police, an officer belonging to the Indian Police Service
Indian Police Service
The Indian Police Service , simply known as Indian Police or IPS, is one of the three All India Services of the Government of India...
is entrusted with the responsibility of maintaining law and order and related issues of the district. He is assisted by the officers of the Karnataka Police Service and other Karnataka Police officials. A Deputy Conservator of Forests
Deputy Conservator of Forests (India)
A Deputy Conservator of Forests or, equivalently a Divisional Forest Officer is an officer belonging to the elite Indian Forest Service. The Deputy Conservator of Forests is responsible for managing the Forests, Environment and Wild-Life related issues of a Forest Division of a state or a union...
, an officer belonging to the Indian Forest Service
Indian Forest Service
The Indian Forest Service is the Forestry service of India. It is one of the three All India Services of the Indian government, along with the Indian Administrative Service and Indian Police Service; its employees are recruited by the national government but serve under the state governments or...
is responsible for managing the Forests, environment and wild-life related issues of the district. He is assisted by the officers of the Karnataka Forest Service and other Karnataka Forest officials and Karnataka Wild-Life officials. Sectoral development is looked after by the district head of each development department such as PWD, Health, Education, Agriculture, Animal husbandry, etc. These officers belong to the various State Services.
Police Administration
The state is divided into 20 police districts, 77 sub-divisions, 178 circles, State Police consists of 20 police districts, 4 Police Commissioners at Bangalore, Mysore,Mangalore and Hubli-Dharwad cities, 77 sub-divisions, 178 circles, 696 police stations, and 317 police out-posts. There are six ranges viz., Central Range at Bangalore, Eastern Range at Davanagere, Northern Range at Gulbarga, Southern Range at Mysore and Western Range at Mangalore. The Government Railway Police is headed by a D.I.G. of Police.Units that assist the state in law and order include Criminal Investigation Department (Forest Cell, Anti-Dowry Cell, etc.), Dog Squad, Civil Rights Enforcement Wing, Police Wireless and Police Motor Transport Organization and Special units. Also Village Defence Parties protect persons and property in the village and assist the police when necessary. The Police force is at times supplemented by Home Guards.
Politics
Karnataka politics is dominated by the Indian National CongressIndian National Congress
The Indian National Congress is one of the two major political parties in India, the other being the Bharatiya Janata Party. It is the largest and one of the oldest democratic political parties in the world. The party's modern liberal platform is largely considered center-left in the Indian...
(INC), Janata Dal (Secular)
Janata Dal (Secular)
The Janata Dal is a Centre-left ಕನ್ನಡ: ಜನತಾ ದಳIndian political party led by former Prime Minister of India H.D. Deve Gowda.The party recognized as state party in the states of Karnataka and Kerala . It was formed in July 1999 by the split of Janata Dal party. It has political presence mainly in...
(JDS) and the Bharatiya Janata Party
Bharatiya Janata Party
The Bharatiya Janata Party ,; translation: Indian People's Party) is one of the two major political parties in India, the other being the Indian National Congress. Established in 1980, it is India's second largest political party in terms of representation in the parliament...
(BJP).
The previous government was a coalition government
Coalition government
A coalition government is a cabinet of a parliamentary government in which several political parties cooperate. The usual reason given for this arrangement is that no party on its own can achieve a majority in the parliament...
of JDS and BJP. The Chief Minister for an initial term of 20 months was H. D. Kumaraswamy
H. D. Kumaraswamy
Hardanahalli Deve Gowda Kumaraswamy was Chief Minister of the state of Karnataka, India from February 4, 2006 to October 9, 2007. He is one of the sons of former Prime Minister of India H. D. Deve Gowda...
of JDS and the post was supposed to subsequently be transferred to BJP's B. S. Yeddyurappa. A political fall out due to the failure in transfer of power to Yedurappa broke the coalition. The state was then under President's rule until the elections
Karnataka state assembly elections, 2008
The Karnataka Legislative Assembly election of 2008 took place in 3 phases on May 10, May 16 and May 22, 2008 in 224 constituencies in Karnataka, India. The elections were conducted to elect the government in the state of Karnataka for the next five years. The votes were counted on May 25, 2008 and...
in May 2008. As a result of the BJP victory in those elections B. S. Yeddyurappa became chief minister of Karnataka.

