
Gravitation of the Moon
Encyclopedia
Gravitation
Gravitation, or gravity, is a natural phenomenon by which physical bodies attract with a force proportional to their mass. Gravitation is most familiar as the agent that gives weight to objects with mass and causes them to fall to the ground when dropped...
of the Moon
Moon
The Moon is Earth's only known natural satellite,There are a number of near-Earth asteroids including 3753 Cruithne that are co-orbital with Earth: their orbits bring them close to Earth for periods of time but then alter in the long term . These are quasi-satellites and not true moons. For more...
has been determined by the tracking of radio signals emitted by orbiting spacecraft. The principle used depends on the Doppler effect
Doppler effect
The Doppler effect , named after Austrian physicist Christian Doppler who proposed it in 1842 in Prague, is the change in frequency of a wave for an observer moving relative to the source of the wave. It is commonly heard when a vehicle sounding a siren or horn approaches, passes, and recedes from...
, whereby the line-of-sight spacecraft acceleration can be measured by small shifts in frequency of the radio signal, and the measurement of the distance from the spacecraft to a station on Earth. Since the gravitational field of the Moon affects the orbit
Orbit
In physics, an orbit is the gravitationally curved path of an object around a point in space, for example the orbit of a planet around the center of a star system, such as the Solar System...
of a spacecraft, it is possible to use these tracking data to invert for gravity anomalies
Gravity anomaly
A gravity anomaly is the difference between the observed acceleration of Earth's gravity and a value predicted from a model.-Geodesy and geophysics:...
. However, because of the Moon's synchronous rotation
Synchronous rotation
In astronomy, synchronous rotation is a planetological term describing a body orbiting another, where the orbiting body takes as long to rotate on its axis as it does to make one orbit; and therefore always keeps the same hemisphere pointed at the body it is orbiting...
it is not possible to track spacecraft much over the limbs of the Moon, and the far-side gravity field is thus only poorly characterized. The gravitational acceleration on the surface of the Moon is 1.63 m/s2, about 16.7% that on Earth's surface. Because weight
Weight
In science and engineering, the weight of an object is the force on the object due to gravity. Its magnitude , often denoted by an italic letter W, is the product of the mass m of the object and the magnitude of the local gravitational acceleration g; thus:...
is directly dependent upon gravitational acceleration, things on the Moon will weigh only 16.7% of what they weigh on the Earth.
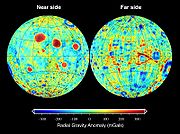
The major characteristic of the Moon's gravitational field is the presence of mascons, which are large positive gravity anomalies associated with some of the giant impact basin
Impact crater
In the broadest sense, the term impact crater can be applied to any depression, natural or manmade, resulting from the high velocity impact of a projectile with a larger body...
s. These anomalies greatly influence the orbit of spacecraft about the Moon, and an accurate gravitational model is necessary in the planning of both manned and unmanned missions. They were initially discovered by the analysis of Lunar Orbiter tracking data, since navigation tests prior to the Apollo program experienced positioning errors much larger than mission specifications.
The origin of mascons are in part due to the presence of dense mare
Lunar mare
The lunar maria are large, dark, basaltic plains on Earth's Moon, formed by ancient volcanic eruptions. They were dubbed maria, Latin for "seas", by early astronomers who mistook them for actual seas. They are less reflective than the "highlands" as a result of their iron-rich compositions, and...
basalt
Basalt
Basalt is a common extrusive volcanic rock. It is usually grey to black and fine-grained due to rapid cooling of lava at the surface of a planet. It may be porphyritic containing larger crystals in a fine matrix, or vesicular, or frothy scoria. Unweathered basalt is black or grey...
ic lava flow
Lava
Lava refers both to molten rock expelled by a volcano during an eruption and the resulting rock after solidification and cooling. This molten rock is formed in the interior of some planets, including Earth, and some of their satellites. When first erupted from a volcanic vent, lava is a liquid at...
s that fill some of the impact basins. However, lava flows by themselves can not explain the entirety of the gravitational variations, and uplift of the crust
Crust (geology)
In geology, the crust is the outermost solid shell of a rocky planet or natural satellite, which is chemically distinct from the underlying mantle...
-mantle
Mantle (geology)
The mantle is a part of a terrestrial planet or other rocky body large enough to have differentiation by density. The interior of the Earth, similar to the other terrestrial planets, is chemically divided into layers. The mantle is a highly viscous layer between the crust and the outer core....
interface is required as well. Based on Lunar Prospector
Lunar Prospector
The Lunar Prospector mission was the third selected by NASA for full development and construction as part of the Discovery Program. At a cost of $62.8 million, the 19-month mission was designed for a low polar orbit investigation of the Moon, including mapping of surface composition and possible...
gravitational models, it has been suggested that some mascons exist that do not show evidence for mare basaltic volcanism
Volcano
2. Bedrock3. Conduit 4. Base5. Sill6. Dike7. Layers of ash emitted by the volcano8. Flank| 9. Layers of lava emitted by the volcano10. Throat11. Parasitic cone12. Lava flow13. Vent14. Crater15...
. The huge expanse of mare basaltic volcanism associated with Oceanus Procellarum
Oceanus Procellarum
Oceanus Procellarum is a vast lunar mare on the western edge of the near side of the Earth's Moon. Its name derives from the old superstition that its appearance during the second quarter heralded bad weather...
does not possess a positive gravity anomaly.

