
Grouped data
Encyclopedia
Grouped data is a statistical term used in data analysis
. A raw dataset
can be organized by constructing a table showing the frequency distribution
of the variable (whose values are given in the raw dataset). Such a frequency table is often referred to as a grouped data.
The above data can be organised into a frequency distribution (or a grouped data) in several ways. One method is to use intervals as a basis.
The smallest value in the above data is 8 and the largest is 34. The interval from 8 to 34 is broken up into smaller subintervals (called class intervals). For each class interval, the amount of data items falling in this interval is counted. This number is called the frequency of that class interval. The results are tabulated as a frequency table as follows:
Another method of grouping the data is to use some qualitative characteristics instead of numerical intervals. For example, suppose in the above example, there are three types of students: 1) Smart, if the response time is 5 to 14 seconds, 2) normal if it is between 15 and 24 seconds, and 3) below normal if it is 25 seconds or more, then the grouped data looks like:
 , of the mean
, of the mean
of the population from which the data are drawn can be calculated from the grouped data as:
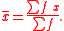
In this formula, x refers to the mid-point of the class intervals, and f is the class frequency. Note that the result of this will be different from the sample mean of the ungrouped data. The mean for the grouped data in the above example, can be calculated as follows:
Thus, the mean of the grouped data is
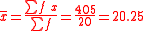
Data analysis
Analysis of data is a process of inspecting, cleaning, transforming, and modeling data with the goal of highlighting useful information, suggesting conclusions, and supporting decision making...
. A raw dataset
Raw data
'\putang inaIn computing, it may have the following attributes: possibly containing errors, not validated; in sfferent formats; uncoded or unformatted; and suspect, requiring confirmation or citation. For example, a data input sheet might contain dates as raw data in many forms: "31st January...
can be organized by constructing a table showing the frequency distribution
Frequency distribution
In statistics, a frequency distribution is an arrangement of the values that one or more variables take in a sample. Each entry in the table contains the frequency or count of the occurrences of values within a particular group or interval, and in this way, the table summarizes the distribution of...
of the variable (whose values are given in the raw dataset). Such a frequency table is often referred to as a grouped data.
Example
The idea of grouped data can be illustrated by considering the following raw dataset:| 20 | 25 | 24 | 33 | 13 |
| 26 | 8 | 19 | 31 | 11 |
| 16 | 21 | 17 | 11 | 34 |
| 14 | 15 | 21 | 18 | 17 |
The above data can be organised into a frequency distribution (or a grouped data) in several ways. One method is to use intervals as a basis.
The smallest value in the above data is 8 and the largest is 34. The interval from 8 to 34 is broken up into smaller subintervals (called class intervals). For each class interval, the amount of data items falling in this interval is counted. This number is called the frequency of that class interval. The results are tabulated as a frequency table as follows:
| Time taken (in seconds) | Frequency |
|---|---|
| 5 and above, below 10 | 1 |
| 10 and above, below 15 | 4 |
| 15 and above, below 20 | 6 |
| 20 and above, below 25 | 4 |
| 25 and above, below 30 | 2 |
| 30 and above, below 35 | 3 |
Another method of grouping the data is to use some qualitative characteristics instead of numerical intervals. For example, suppose in the above example, there are three types of students: 1) Smart, if the response time is 5 to 14 seconds, 2) normal if it is between 15 and 24 seconds, and 3) below normal if it is 25 seconds or more, then the grouped data looks like:
| Frequency | |
|---|---|
| Smart | 5 |
| Normal | 10 |
| Below normal | 5 |
Mean of grouped data
An estimate, , of the mean
, of the meanMean
In statistics, mean has two related meanings:* the arithmetic mean .* the expected value of a random variable, which is also called the population mean....
of the population from which the data are drawn can be calculated from the grouped data as:
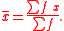
In this formula, x refers to the mid-point of the class intervals, and f is the class frequency. Note that the result of this will be different from the sample mean of the ungrouped data. The mean for the grouped data in the above example, can be calculated as follows:
| Class Intervals | Frequency ( f ) | Midpoint ( x ) | f x |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 and above, below 10 | 1 | 7.5 | 7.5 |
| 10 and above, below 15 | 4 | 12.5 | 50 |
| 15 and above, below 20 | 6 | 17.5 | 105 |
| 20 and above, below 25 | 4 | 22.5 | 90 |
| 25 and above, below 30 | 2 | 27.5 | 55 |
| 30 and above, below 35 | 3 | 32.5 | 97.5 |
| TOTAL | 20 | 405 |
Thus, the mean of the grouped data is
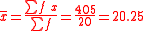
See also
- Data binningData binningData binning is a data pre-processing technique used to reduce the effects of minor observation errors. The original data values which fall in a given small interval, a bin, are replaced by a value representative of that interval, often the central value...
- Level of measurementLevel of measurementThe "levels of measurement", or scales of measure are expressions that typically refer to the theory of scale types developed by the psychologist Stanley Smith Stevens. Stevens proposed his theory in a 1946 Science article titled "On the theory of scales of measurement"...
- Frequency distributionFrequency distributionIn statistics, a frequency distribution is an arrangement of the values that one or more variables take in a sample. Each entry in the table contains the frequency or count of the occurrences of values within a particular group or interval, and in this way, the table summarizes the distribution of...
- Discretization of continuous featuresDiscretization of continuous featuresIn statistics and machine learning, discretization refers to the process of converting or partitioning continuous attributes, features or variables to discretized or nominal attributes/features/variables/intervals. This can be useful when creating probability mass functions – formally, in density...

