Gurung language
Encyclopedia
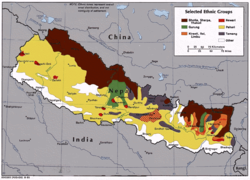
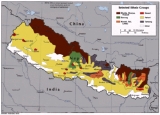
:तमु क्यी) is spoken by the Gurung people in two dialects with limited mutual intelligibility. Total number of all Gurung speakers in Nepal
Nepal
Nepal , officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal, is a landlocked sovereign state located in South Asia. It is located in the Himalayas and bordered to the north by the People's Republic of China, and to the south, east, and west by the Republic of India...
is 227,918 (1991 census). Perhaps, a distinction should be made between Gurung as an ethnic group
Ethnic group
An ethnic group is a group of people whose members identify with each other, through a common heritage, often consisting of a common language, a common culture and/or an ideology that stresses common ancestry or endogamy...
and the number of people who actually speak the language.
Nepali
Nepali language
Nepali or Nepalese is a language in the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European language family.It is the official language and de facto lingua franca of Nepal and is also spoken in Bhutan, parts of India and parts of Myanmar...
, Nepal's official language, is an Indo-European
Indo-European languages
The Indo-European languages are a family of several hundred related languages and dialects, including most major current languages of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and South Asia and also historically predominant in Anatolia...
language, whereas Gurung is a Tibeto-Burman language. Gurung are recognized as an official nationality by the Government of Nepal.
Classification
According to ethnologue, Gurung is two languages, Eastern [ggn] and Western [gvr].Grammar
Some miscellaneous grammatical features of the Gurung languages are;- SOV;
- postpositions;
- genitives;
- adjectiveAdjectiveIn grammar, an adjective is a 'describing' word; the main syntactic role of which is to qualify a noun or noun phrase, giving more information about the object signified....
s relativesRelative clauseA relative clause is a subordinate clause that modifies a noun phrase, most commonly a noun. For example, the phrase "the man who wasn't there" contains the noun man, which is modified by the relative clause who wasn't there...
before noun headsHead (linguistics)In linguistics, the head is the word that determines the syntactic type of the phrase of which it is a member, or analogously the stem that determines the semantic category of a compound of which it is a component. The other elements modify the head....
; - numeralNumber namesIn linguistics, number names are specific words in a natural language that represent numbers.In writing, numerals are symbols also representing numbers...
s after noun heads; - rising intonation in bipolar questionQuestionA question may be either a linguistic expression used to make a request for information, or else the request itself made by such an expression. This information may be provided with an answer....
s; - 1 prefixPrefixA prefix is an affix which is placed before the root of a word. Particularly in the study of languages,a prefix is also called a preformative, because it alters the form of the words to which it is affixed.Examples of prefixes:...
on negative verbNegative verbA negative verb is a type of auxiliary that is used to form the negative of a main verb. The main verb itself has no personal endings, while the negative verb takes the inflection...
s; - maximum number of suffixSuffixIn linguistics, a suffix is an affix which is placed after the stem of a word. Common examples are case endings, which indicate the grammatical case of nouns or adjectives, and verb endings, which form the conjugation of verbs...
es 3; - caseGrammatical caseIn grammar, the case of a noun or pronoun is an inflectional form that indicates its grammatical function in a phrase, clause, or sentence. For example, a pronoun may play the role of subject , of direct object , or of possessor...
of noun phraseNoun phraseIn grammar, a noun phrase, nominal phrase, or nominal group is a phrase based on a noun, pronoun, or other noun-like word optionally accompanied by modifiers such as adjectives....
shown by preposition; - no subjectSubject (grammar)The subject is one of the two main constituents of a clause, according to a tradition that can be tracked back to Aristotle and that is associated with phrase structure grammars; the other constituent is the predicate. According to another tradition, i.e...
or objectObject (grammar)An object in grammar is part of a sentence, and often part of the predicate. It denotes somebody or something involved in the subject's "performance" of the verb. Basically, it is what or whom the verb is acting upon...
referencing in verbs; - split ergativeSplit ergativitySplit ergativity is shown by languages that have a partly ergative behaviour, but employ another syntax or morphology — usually accusative — in some contexts...
system according to tenseGrammatical tenseA tense is a grammatical category that locates a situation in time, to indicate when the situation takes place.Bernard Comrie, Aspect, 1976:6:...
; - causativeCausativeIn linguistics, a causative is a form that indicates that a subject causes someone or something else to do or be something, or causes a change in state of a non-volitional event....
s; - benefactives;
- CV, CCV, CCCV;
Phonetically, Gurung languages are tonal.

